Time Planning Techniques for Efficient Project Management
Explore the significance of time planning in project management, understand the dimensions of planning, and learn why it is necessary. Discover who needs time planning and the essential processes involved in effective time planning. Dive into Gantt (Bar) chart techniques for project time planning.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
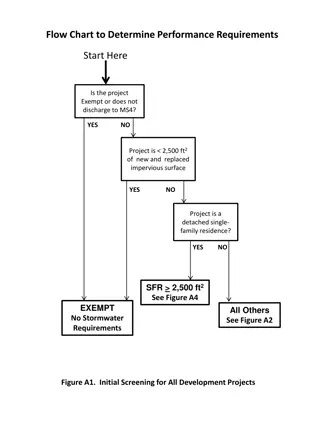
Lecture 3: Project Time Planning Gantt (Bar) Chart Technique Lecture 3: Project Time Planning Gantt (Bar) Chart Technique 1
Definition of Planning Definition of Planning Planning is the process of thinking systematically about the future in order to decide what our goals goals are, and how how we are going to achieve them. Planning means looking ahead, making preparations, and deciding the best course of action.
Dimensions of Planning Dimensions of Planning Planning can be viewed from following points: Subject Subject:- Financial Financial Planning, Time Time Planning, Quality Quality P lanning, Organizational Organizational Planning, . Organization Organization:- Corporate Corporate Planning, Project Project Planning,.. Time Time:- Long Long- -Range Range.Planning, Short Short- -Range Range Planning, Weekly Weekly Planning, .
Why is Time Why is Time Planning Planning necessary? necessary? The increasing importance of timely timely completion completion. The continuous complexity and growth in the size of the project generates the necessity for specialization. Specialization may lead to a breakdown of communications. Time planning must be found to to facilitate facilitate communications communications. Planning is essential for resource and maximum utilization utilization of resource management management and the efficient of resources resources. Planning is basis for evaluating progress, controlling controlling the work and making decisions.
Why is Time Why is Time Planning Planning necessary? necessary? For achieving an increase increase in in production production. Financiers Financiers require a workable plan. Essential in projects when their is transfer transfer of of personnel personnel. Minimum Minimum risk risk of the problems occurring.
Who Who Needs Needs Time Time Planning? Planning? Customer/ Client/ Owner Designer/ Consultant Project management team (Manager, Engineers) Cost estimating department Planning and controlling department Supervisors, foremen, labors Supplier Financiers
Processes of Time Planning Processes of Time Planning 1.Visualize and define the activities activities. 2.Sequence the activities (Job Logic Logic). 3.Estimate the activity activity duration duration. 4. 4.Schedule Schedule the project or phase. 5.Allocate and balance resources resources. 6. Compare target, planned and actual dates and update update as necessary. 7. 7. Control Control the time schedule with respect to changes changes.
Visualize and define the activities Visualize and define the activities 1. An activity is a single work beginning and end and requires time for its accomplishment. Activity definition involves identifying identifying and specific activities that must be performed to produce the deliverables and sub-deliverables. work step step (element) (element) that has a recognizable and documenting documenting the 2. The technique of decomposition in defining activities. Decomposition involves subdividing project work packages into smaller, more manageable components to provide better management control. decomposition (Work (Work Breakdown) Breakdown) may be used 3. The output from activity definition is the activity activity list list. . 4. The Level Level of of detail detail of the plan should be considered in this phase
Visualize and define the activities Visualize and define the activities Case Case Study Study: : Install Install a a new new machine machine Activity Activity Code Code Activity Description Activity Description Depends Depends on on Level Level Duration Duration (day) (day) Inspect the machine after installation Hire the operator Install the new machine Inspect and store the machine after delivery Hire labor to install the new machine Train the operator Order and deliver the new machine
Sequence the activities Sequence the activities 1. Sequence the activities or job logic refers to identifying documenting documenting interactivity interactivity logical logical relationships in which the activities are to be accomplished in the project. identifying and and order relationships, i.e. determined order 2. Job plan must reflect the practical restraints or limitations that apply to most job activities. The types of restraints are: Mandatory dependencies or hard logic (natural dependency), Preferred logic (Discretionary dependencies), External dependencies, Resource restraints and Safety restraints. 3. 3. Predecessor Predecessor activities mean coming after. activities mean coming before, while successor successor activities activities 4. 4. Overlap Overlap the activities to reduce the project time.
Sequence the activities Case Case Study Study: : Install Install a a new new machine machine Activity Activity Code Code Activity Description Activity Description Depends Depends on on Level Level Duration Duration (day) (day) 100 Inspect the machine after installation 300 4 200 Hire the operator None 1 300 Install the new machine 500, 400 3 400 Inspect and store the machine after delivery 700 2 500 Hire labor to install the new machine None 1 600 Train the operator 200, 300 4 700 Order and deliver the new machine None 1
Estimate the activity duration Estimate the activity duration 1. Select the time unit time unit (week, day,..) to be used. 2. Use one of the following tools and techniques for estimating the activity duration: Expert judgment Expert judgment Quantitatively b Quantitatively based durations Duration of activity (D) Duration of activity (D) = Quantity of work / [Production rate of a crew or equipment * No. of crews]. = Quantity of work / [Production rate of a crew or equipment * No. of crews]. Where production rate = Quantity produced in unit of time Duration of activity (D) Duration of activity (D) = Quantity of work * Unit rate productivity of a crew or = Quantity of work * Unit rate productivity of a crew or equipment equipment Where unit rate productivity = Time needs to produce one unit of output
Estimate the activity duration Estimate the activity duration Case Case Study Study: : Install Install a a new new machine machine Activity Activity Code Code Activity Description Activity Description Depends Depends on on Level Level Duration Duration (day) (day) 100 Inspect the machine after installation 300 4 1 200 Hire the operator None 1 25 300 Install the new machine 500, 400 3 2 400 Inspect and store the machine after delivery 700 2 1 500 Hire labor to install the new machine None 1 20 600 Train the operator 200, 300 4 3 700 Order and deliver the new machine None 1 30
Removal of Redundant Dependencies Removal of Redundant Dependencies 14
Removal of Redundant Dependencies (Cont.) Removal of Redundant Dependencies (Cont.) 15
Schedule the Project or Phase Schedule the Project or Phase Scheduling Scheduling is the determination of the project time a nd the timing of the activities comprising the project In scheduling we consider the questions of: how long the project is expected to take, and when each activity may be scheduled (starts and ends) To schedule the project, the planner needs a Time Planning Planning Technique. Technique. Time
Time Planning Techniques Time Planning Techniques Practically every project is sufficiently complex that it s breakdown and its inner relationships must be recorded on paper or any other media, and not only in the head of the planner. Therefore as a plan is formulated, some type of "paper paper model model" of the project would be developed to communicate results of the plan to others and to serve as a base for evaluating progress and controlling the work.
Time Planning Techniques Time Planning Techniques Bar Bar Charts Charts and and Linked Linked Bar Bar Charts Charts; ; Network Network Model Model (Analysis), (Analysis), either either Activity Activity on on arrow, arrow, Activity Activity on on node, node, Precedence Precedence Diagram Diagram PERT PERT (Program (Program Evaluation Evaluation and and Review Review Technique) Technique)
BAR CHART BAR CHART During World War 1, Henry Gantt Gantt developed the Bar chart planning technique. A bar chart graphically describes a project consisting of well-defined activities, the completion of which marks its end. An activity is a task whose performance contributes to completion of the overall project.
BAR CHART BAR CHART All activities are listed in a column at the left side of the diagram. A horizontal time scale extends to the right of the list. A bar presenting each activity is drawn between its corresponding scheduled start and finish times.
Uses of Bar Chart Planning Technique Uses of Bar Chart Planning Technique Showing the order of the different activities Showing when operations should start and finish Checking what labor or equipment are needed and when Checking out delivery dates for materials Explaining to everyone concerned what is due to happen and when Forecasting cash flow During execution, the chart used to control the work
Case study Case study
Case study Case study
Preparing a Bar Chart Preparing a Bar Chart
Gant Chart (Example) Gant Chart (Example) W1 W2 W3 W4 W5 W6 W7 W8 W9 ID 1 Task Name Demolition Duration 8 days Foundation 14 days 2 UndergroundServices 6 days 3 RoughMech & Electrical 12 days 4 Structural Steel 5 days 5 Exterior Walls 12 days 6 Roof 6 days 7 First Floor Slab 4 days 8 Second Floor Slab 6 days 9 Finish Mech. & Electrical 12 days 10 Interior Partitions 10 days 11 Paint 8 days 12
Advantages of Bar Chart Advantages of Bar Chart Simple graphical form. Easy understood for all levels of management. Good form of communication.
Limitations of Bar Chart Very cumbersome as the number of activities, increases Logic is not expressed in the diagram Difficult to use for forecasting the effects of changes, It is therefore limited as a control tool No indication where management attention should be focused. Ineffective for project shortening.
Logic is not represented in the Bar Chart Logic is not represented in the Bar Chart A B C Activities D E F G H Time days 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14