TIME SERIES ANALYSIS
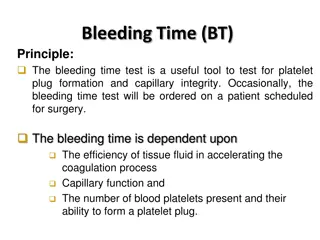
Time series analysis involves recording data points at consistent intervals over a set period of time to identify trends, seasonal patterns, cyclical movements, and irregular fluctuations. By analyzing a large data set, analysts can predict future trends based on historical data, distinguishing between noise and significant patterns. The four major components of time series analysis — trend, seasonal, cyclical, and irregular — provide valuable insights for forecasting and decision-making in various fields.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Time series analysis is a specific way of analyzing a sequence of data points collected over an interval of time. In time series analysis, analysts record data points at consistent intervals over a set period of time rather than just recording the data points intermittently or randomly. Time series analysis typically requires a large number of data points to ensure consistency and reliability. An extensive data set ensures you have a representative sample size and that analysis can cut through noisy data. It also ensures that any trends or patterns discovered are not outliers and can account for seasonal variance. Additionally, time series data can be used for forecasting predicting future data based on historical data. TIME SERIES ANALYSIS
Trend component Seasonal component Cyclical component Irregular component MAJOR COMPONENTS:
This is useful in predicting future movements. Over a long period of time, the trend shows whether the data tends to increase or decrease. The term trend refers to an average, long-term, smooth tendency. Not all increases simultaneously. Different sections of time show varying tendencies in terms of trends that are increasing, decreasing, or stable. must, however, be an overall upward, downward, or stable trend. or decreases have to occur There 1. TREND COMPONENT:
The seasonal component of a time series is the variation in some variable due to some predetermined patterns in its behavior. This definition can be used for any type of time series including individual commodity price quotes, interest rates, exchange rates, stock prices, and so on. In many applications, seasonal components can be represented by simple regression equations. This approach is sometimes referred to as a seasonalized regression or a bimodal regression 2. SEASONAL COMPONENT:
The cyclical component in a time series is the part of the movement in the variable which can be explained by other cyclical movements in the economy. In other words, this term gives information about seasonal patterns. It is also called the long-period (LP) effect or boom-bust process. For example, during recessions, characterized by slower growth rates than before the recession started. business cycles are usually 3. CYCLICAL COMPONENT:
The irregular component is the part of the movement in the variable which cannot be explained by cyclical movements in the economy. In other words, this term gives information about non-seasonal patterns. This term refers to changes that are not cyclical. These include boom-bust processes, permanent changes in the long-term trend of a variable, or not seasonally adjusted information which is not normally found in national income and product accounts (such as depreciation, research and development agricultural subsidies). expenditures, and 4. IRREGULAR COMPONENT: