Timing Problem in Sequential Coordinated Monostatic DMG Sensing Instance
Explore the timing problem in a sequential coordinated Monostatic DMG sensing instance and discover proposed solutions to optimize performance and reduce interference between stations. Should scheduling be set for each station? Find out the complexities involved and efficient approaches to address the issue.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
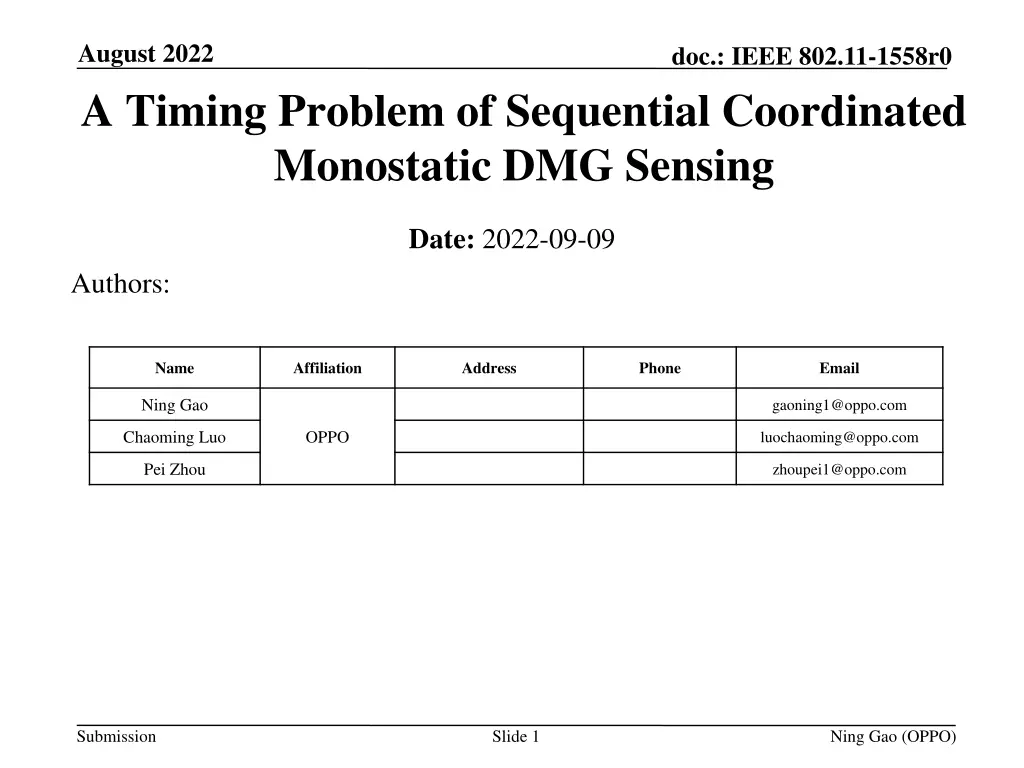
August 2022 A Timing Problem of Sequential Coordinated Monostatic DMG Sensing doc.: IEEE 802.11-1558r0 Date: 2022-09-09 Authors: Name Affiliation Address Phone Email Ning Gao gaoning1@oppo.com Chaoming Luo OPPO luochaoming@oppo.com Pei Zhou zhoupei1@oppo.com Submission Slide 1 Ning Gao (OPPO)
August 2022 doc.: IEEE 802.11-1558r0 Abstract The Coordinated Monostatic DMG Sensing instance has two types: sequential and parallel. In this contribution, a timing problem of sequential Coordinated Monostatic DMG Sensing instance is shown and three possible solutions for this timing problem are proposed and compared. Submission Slide 2 Ning Gao (OPPO)
August 2022 doc.: IEEE 802.11-1558r0 Timing Problem in Sequential Coordinated DMG Monostatic Sensing Instance The STA B may not get the accurate timing when to send the Monostatic PPDU. The Ack frame is directionally sent from the initiator to the STAA so the STA B may not receive it. The length/durationof the Monostatic PPDU and the DMG Sensing Measurement Report frame of STA A are unknown to STA B. As a result, the STA B may fail to send the Monostatic PPDU and the DMG Sensing Measurement Report frame or cause interference between STAs in this instance. Submission Slide 3 Ning Gao (OPPO)
August 2022 doc.: IEEE 802.11-1558r0 Should we set scheduling for each STA? It is not a good approach. It is complicated for the initiator to set scheduling information for multiple responder STAs in each DMG Sensing Request frame. The length/duration of the Monostatic PPDU(Not defined)and the DMG Sensing Measurement Report frame(Different MCSs) of different STAs can be different. So, each responder STA needs to inform the initiator of the above information in the Measurement Setup phase. Then, in every instance, the initiator shall schedule each STA except the first to send a Monostatic PPDU no later than SIFS time after the Ack frame of the previous STA. Note that the number and the order of responder STAs in each instance may be different. Use a poll frame to poll each STA is a better way. Submission Slide 4 Ning Gao (OPPO)
August 2022 doc.: IEEE 802.11-1558r0 Option 1-A In every instance, the initiator poll each responder sequentially with a new poll frame (format is TBD)before each responder STA sending a Monostatic PPDU. DMG Sensing Request (STA ID=0) DMG Sensing Request (STA ID=1) DMG Sensing Measurement Poll frame DMG Sensing Measurement Poll frame SIFS SIFS SIFS SIFS SIFS SIFS SIFS SIFS ACK SIFS SIFS SIFS ACK Initiator STA DMG Sensing Measurement Report RSP Responder STA A Monostatic PPDU DMG Sensing Measurement Report RSP Monostatic PPDU Responder STA B Initiator & STA A Initiator & STA B Submission Slide 5 Ning Gao (OPPO)
August 2022 doc.: IEEE 802.11-1558r0 Option 1-B In every instance, the initiator poll each responder except the first responder sequentially with a new poll frame(format is TBD) before each responder STA sending a Monostatic PPDU. DMG Sensing Request (STA ID=0) DMG Sensing Request (STA ID=1) DMG Sensing Measurement Poll frame SIFS SIFS SIFS SIFS SIFS SIFS SIFS ACK SIFS SIFS SIFS ACK Initiator STA DMG Sensing Measurement Report RSP Responder STA A Monostatic PPDU DMG Sensing Measurement Report RSP Responder STA B Monostatic PPDU Initiator & STA A Initiator & STA B No new poll frame Submission Slide 6 Ning Gao (OPPO)
August 2022 doc.: IEEE 802.11-1558r0 Option 2 Each responder STA sends the Monostatic PPDU no later than SIFS time after the DMG Sensing Response frame. The initiation, sounding and reporting phases are repeated per responder STA in each instance. DMG Sensing Request (STA ID=0) DMG Sensing Request (STA ID =1) SIFS SIFS SIFS SIFS ACK SIFS SIFS SIFS SIFS ACK SIFS Initiator STA DMG Sensing Measurement Report RSP Responder STA A Monostatic PPDU DMG Sensing Measurement Report RSP Responder STA B Monostatic PPDU Initiator & STA A Initiator & STA B Submission Slide 7 Ning Gao (OPPO)
August 2022 doc.: IEEE 802.11-1558r0 Comparison Option Pros. Cons. Need to define a new frame More overhead (poll frame for each STA) Opt.1-A Same procedure for all STAs Need to define a new frame Different procedure for the first STA Little overhead (no poll frame for the first STA) Opt.1-B No need to define a new frame Same procedure for all STAs Much more changes to the current procedure Opt.2 Submission Slide 8 Ning Gao (OPPO)
August 2022 doc.: IEEE 802.11-1558r0 SP 1 Which option do you support to solve the timing problem of the sequential Coordinated Monostatic DMG Sensing instance as shown in slide 3? Option 1-A: use a new poll frame to poll each responder STA, as shown in slide 5 Option 1-B: use a new poll frame to poll each responder STA except the first, as shown in slide 6 Option 2: use the DMG Sensing Request frame to poll each responder STA, as shown in slide 7 Neither Abstain - - - - - Submission Slide 9 Ning Gao (OPPO)