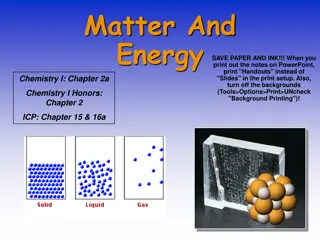
Tools for Measuring Physical Properties of Matter
This guide highlights essential tools used to measure physical properties of matter, including mass, volume, density, length, temperature, and weight. Each property is defined, along with its respective units of measurement and the tools required for accurate determination. Understanding how these tools function is crucial for conducting precise scientific measurements in various experiments and analyses.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Tools for Measuring some Physical Properties of Matter Fill in your vocabulary map with the following information!
1. mass: measure of the amount of matter in an object unit: gram tool: triple beam balance (TBB) http://ts1.mm.bing.net/images/thumbnail.aspx?q=232418975892id=0b9f8b3b1e1b7fab047a973cb36dfbd1url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.laddresearch.com%2fNew_Products%2fOhaus_Balances___Scales%2fTriple_Beam_Balances_-_Standar%2fTrip
2. volume: measure of amount of space occupied by an object unit: milliliters (mL) or cubic centimeters (cm3) tool: graduated cylinder mL 1 mL = 1 cm3 cm cm cm cm x cm x cm = cm3
3. density: measure of amount of matter in a given space g/mL OR g/cm3 unit: TBB AND graduated cylinder tool: http://ts1.mm.bing.net/images/thumbnail.aspx?q=232418975892id=0b9f8b3b1e1b7fab047a973cb36dfbd1url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.laddresearch.com%2fNew_Products%2fOhaus_Balances___Scales%2fTriple_Beam_Balances_-_Standar%2fTrip density = mass g volume mL matter space
4. length: measure of distance from one point to another unit: centimeters (cm) or millimeters (mm) tool: ruler ruler%2520cm%2520with%2520zero%2520mark%2520not%2520at%2520edge
5. temperature: measure of how fast the particles in an object are moving http://ts4.mm.bing.net/images/thumbnail.aspx?q=234606760067id=605244f4e8fe685745399fdb0437f617url=http%3a%2f%2fwww.rockingham.k12.va.us%2fsound_sorting%2finitial_diagraphs%2fth%2fimages%2fthermometer.jpg unit: degrees Celsius (0C) or Fahrenheit (0F) tool: thermometer For Water: B pt.= 100 0C F pt.= 0 0C For Water: B pt.= 212 0F F pt.= 320F
6. weight: measure of the amount of gravitational pull on an object unit: newton (N) http://ts2.mm.bing.net/images/thumbnail.aspx?q=211677556941id=69a09ba954e8aa6c1e771f9d4cf608aburl=http%3a%2f%2fwww.amep.com%2fprodPix%2fscience%2fDD7-G63.jpg tool: spring scale