Triangle Angles and Sides Relationship Examples
Explore various examples illustrating the relationship between angles and sides in triangles. Learn about how the largest angle corresponds to the longest side, the smallest angle to the shortest side, and more intriguing geometric properties. Dive into the world of triangles through visual representations and clear explanations.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
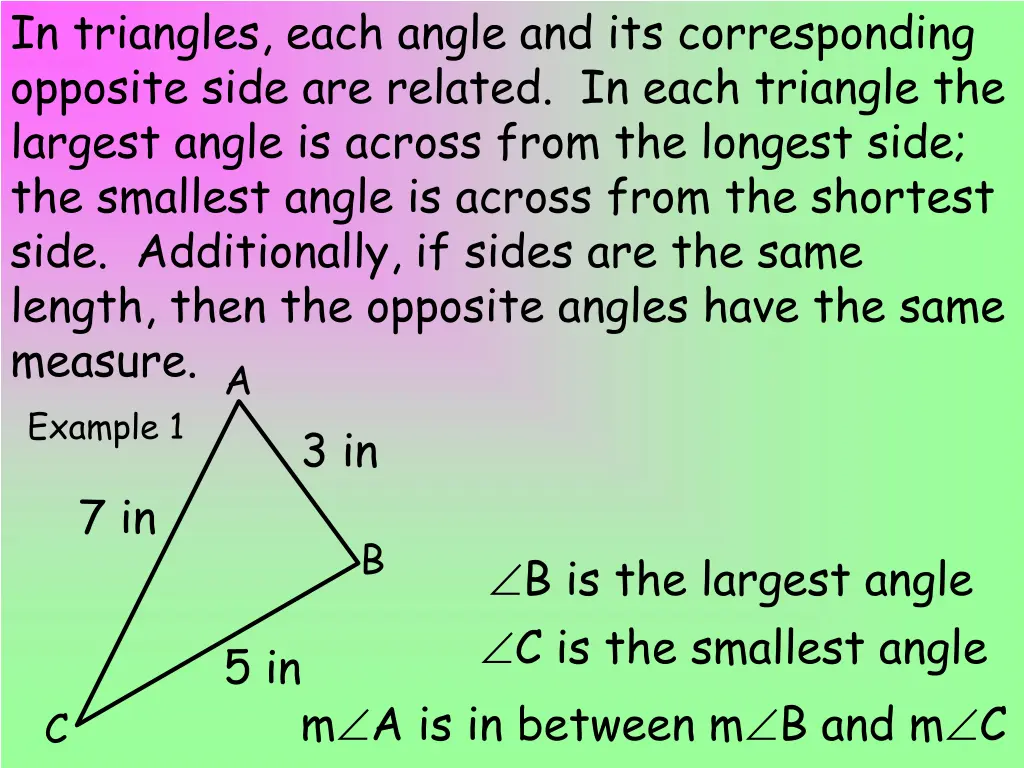
In triangles, each angle and its corresponding opposite side are related. In each triangle the largest angle is across from the longest side; the smallest angle is across from the shortest side. Additionally, if sides are the same length, then the opposite angles have the same measure. A Example 1 3 in 7 in B B is the largest angle C is the smallest angle m A is in between m B and m C 5 in C
Example 2 A GSP GSP 60 100 20 C B AC is the longest side. AB is the shortest side. The length of BC is between the lengths of AB and AC.
Y Example 3 Y is the largest angle 5 in 5 in X and Z are the same measure. They are both less than m Y. X 7 in Z J Example 4 7 in 7 in This triangle is Equilateral and Equiangular. 7 in L J, K, and L are all the same measure. K
DE is the longest side DF is the shortest side D The length of FE is in between the lengths of the other two sides. 70 Example 5 90 20 E F G JH is the longest side 80 GJ and GH have the same length. The length is less than the length of JH. Example 6 50 50 H J