Types of Reproduction in Organisms
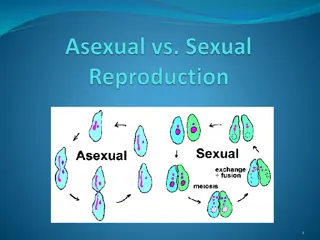
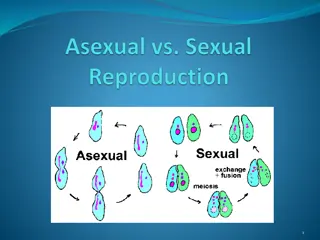
Reproduction in organisms can be classified into asexual and sexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction is uniparental, producing genetically identical offspring through processes like fission, budding, and fragmentation. On the other hand, sexual reproduction involves the formation and fusion of gametes from two parents, leading to genetically diverse offspring. Various modes of asexual reproduction include fission, fragmentation, budding, and regeneration. Additionally, vegetative propagation occurs through different structures such as roots, underground stems, and suckers, aiding in plant propagation and survival.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
REPODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
TYPES OF REPRODUCTION Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Always uniparental. It does not involve formation or fusion of gametes. Offsprings are genetically identical to parents. It is simple and fast process. It helps in maintaining same characters for generations. It is common among single celled organisms, plants and animals with simple organisation. It involves mitosis. Usually biparental. Involves formation and fusion of gametes. Offsprings are not identical to the parents. It is elaborate, complex and slow process. It plays a vital role in evolution process. It is common in higher organisms with complex organisation. It involves meiosis
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION FISSION-The splitting up of parental cell into two or more daughter cells. a) Binary fission-splitting of parental cell into two equal daughter cells. Division in any plane(amoeba), longitudinal(euglena), transverse(paramecium) and oblique(dinoflagellates). b) Multiple fission-splitting of a parent cell to numerous daughter cells e.g. Plasmodium. Sporulation in amoeba.
Contd. Fragmentation- in algae (Spirogyra), fungi (Rhizopus) Budding- External budding in yeast, hydra. Unequal division during budding. Internal budding (Gemmule formation) in fresh water sponges(Spongilla) Regeneration- regrowth in the injured region e.g. Planaria, Hydra.
VEGETATIVE PROPAGATION Roots- Both tap roots(e.g. Guava) and adventitious roots(sweet potato) take part in vegetative propagation. Underground Stems- (i) Tubers- Have axillary buds on the nodes e.g. Potato. (ii) Bulbs-Underground condensed shoots e.g. garlic, onion. (iii) Corms-Unbranched swollen underground stems e.g. Colocasia (iv) Rhizomes- store food for perennation during unfavourable conditions,e.g. banana, ginger, turmeric (v) Suckers-These are selender underground branches that develops from base of aerial shoot. Breaking of suckers form new plants e.g. mint, chrysanthemum.
Contd. Subaerial or creeping stems (i) Runners-narrow green horizontal branches which develop at base of crown and root at intervals where new crowns are formed,e.g. lawn grass(doob grass) Stolons-They are arched horizontal branches that develop at base of crown,e.g. Strawberry (i) Offsets-These are one internode long runners occur in aquatic plants,e.g. Eichhornia(water hyacinth) and Pistia (Water lettuce) Aerial Stems-Fleshy Phylloclades accur in Opuntia. Leaves- of many plants have adventitious buds, e.g. Bryophyllum. Bulbils-these are multicellular fleshy buds, e.g. Agave
Artifical Method of Vegetative Propagation Cuttings-roots, stems and leaves Layering Grafting Micropropagation
Multiple Choice Questions (i) External fertilisation occurs in majority of (a) algae (b) fungi (c) liverworts (d) mosses Vegetative reproduction in Pistia occurs by (a) stolon (b)offset (c) runner (d) sucker (iii) The type of asexual reproduction found in Hydra is (a) multiple fission (b) budding (c) binary fission (d) gemmule (iv) Which of the following pairs is not correctly matched (a) Conidia-Penicillium (b) Offset- Water hyacinth (c)Rhizome-Banana (d) Binary fission- Sargassum (ii) formation
Contd. (v) The part of the fruit formed from the wall of ripened ovary (a) pericarp (b) nucellus (c) gemmule (d) endosperm (vi) The eyes of potato tubers are (a) flower buds (b) shoot bud (c) axillary buds (d) root buds (vii) In Bryophyllum adventitious buds arise from (a) leaves (b) root (c) stems (d) flowers (viii) Which of the following is post- fertilisation event in flowering plants? (a) transfer of pollen grains (b) embryo development (c) formation of flower (d) formation of pollen grains
QUESTIONS: CHAPTER 1 REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS Q1. How are Cucurbita plants different from papaya plants with reference to the flowers they bear? When are the non-flowering plants said to be homothallic and monoecious; and heterothallic and dioecious? Give an example of each. Name and explain the technique that can be used in developing improved crop varieties in plants bearing female flowers only. Meiosis is an essential event in the sexual cycle of any organism. Give two reasons. Name the group of organisms that produces non motile male gametes. How do they reach the female gamete for fertilisation? Q2. Q3. Q4. Q5.
Contd. Q6. Unicellular organisms are immortal, whereas multicellular organisms are not. Justify. Why is it difficult to get rid of water hyacinth from a water body? Name one abiotic component and one biotic component of the ecosystem that gets affected by its spread in the water body. Plants like potato and sugarcane do not require seeds for producing new plants. How do they produce new plants? Give two other examples, where new plants are produced in the same way. The cell division involved in gamete formation is not of the same type in different organisms. Justify. Why do moss plants produce very large number of male gametes? Provide one reason. What are these gametes called? Describe the process of sporulation seen in Amoeba. What are its advantages? Differentiate between oviparous and viviparous animals with an example of each. Q7. Q8. Q9. Q10. Q11. Q12.