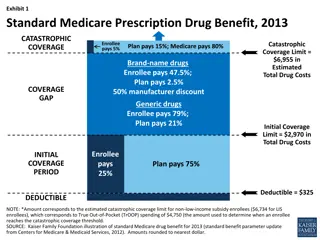
Understanding 8255 Programming Modes and Interfacing Example
Learn about the different programming modes of the 8255 chip by Dr. RN Rajotiya including BSR mode, I/O mode, and basic functional definitions in modes 0, 1, and 2. Explore an interfacing example with instructions for configuring port addresses and writing control words in mode 0. Discover how to interface an 8255 chip with an 8086 to function as an I/O port and sense switch positions connected to port B.
Uploaded on | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
8255 Programming Mode By Dr. RN Rajotiya
8255 8255 can operate in different modes i.e. BSR mode is used for controlling individual bits of port C in read/write operation, Mode-0 is used when simple I/O activity is required on all three ports Mode-1 is used for handshake mode for Gp-A and G-B ports with handshake signals performed by Port-CLower and Port-Cupper Mode-2 is for bidirectional communication on Port-A with port-B in mode-0 or mode-1.
BSR Mode Bit Set/Reset (BSR) Mode of Operation : BSR mode is used for Port-C to control read/write operation on individual pins of port C. The control word of the BSR mode is shown in figure Example of BSR Mode
IO Mode of Operation The IO mode is used for reading and writing from or to IO device. The read write operations to/from IO devices can be performed in different modes. The control word setting for the IO mode is shown
Mode 0 Basic Functional Definitions: (i) Two 8-bit ports and two 4-bit ports, Any Port can be input or output (ii)Outputs are latched (iii) Input are not latched Mode1BasicFunctionDefinitions: (i) Group A and Group B i/o with and Port C 4-bit control/data port for PA and PB (ii) Both inputs and outputs are latched. (iii) The 4-bit ports of PC is used for control and status of the 8-bit port. Mode 2 Basic Functional Definitions : (i) Gp-A used as 8-bit, bi-directional bus with port-C as 5- bit control hed (ii)The 5-bit control port (Port C) is for the 8-bit, bi- directional bus port (Por t A) (iii) Both inputs and outputs are latched
Interfacing Example The control word setting for mode-0 is shown in following figure. Example: a) Identify port addresses in figure below. b) Write the control word to configure port A and port Cu as output port and port B and port CL as input port c) Write a program to read the DIP switches and display the reading from port B at port A and from port Cl at port Cu.
Example 1:-Interface an 8255 chip with 8086 to work as an I/O port. Initialize port A as output port, Port B as I/P port and Port C as O/P port. Port A address should be 0740H. Writean ALP to sense switch positions SW0 SW7 connected at port B. The sensed pattern is to be displayed on port A, to which 8 LED's are connected, while port C lower displays number of on switches out of the total eight switches ? D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 hEX 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 =82H i/o Mode PA Mode-0 PA o/p PCU o/p PB- Mode- 0 PB-i/p PCL- O/P Port Addresses PORT A 0740 PORT B 0742 PORT C 0744 CW 0746
MOV MOV OUT MOV IN MOV MOV MOV AL JNC INC DX, AL, DX, DX, DX, BL, CH, 0746H 82h AL 0742H AL, 0740H 00H; Switch Count 08H; Total Switchs X1: ROL X2: DEC CH HLT DX X2 BL JNZ MOV ADD OUT X1 AL, DX, DX, BL 0H AL
Example 2:-. Interface a 4 4 keyboard with 8086 using 8255, and write an ALP for detecting a key closure and return the key code in AL. The debouncing period for a key in 20 ms ? Answer: Here we use port-A as output port for selecting a row of keys, a low ( 0 ) is outputted on PA3-0 one at a time while port-B is used as an input port for sensing a closed key ( A low on any of PB3-0. Hence the key board lines are selected one by one through Port-A and the Port-B lines are polled continuously till a key closure is sensed. Figure shows the interfacing of the 4x4 keyboard using a 8255 PPI To get the data from a keyboard requires three steps : (1) Detect a key press (2) Debounce the key press (3) Encode the key press The rows of the matrix are connected to four output port (PA3-0)lines. The column line of the matrix are connected to four input port (PB3-0) lines
Example3:-Interface an 8255 with 8086 at 80H as an I/O address of PortA. Interface five 7 segment displays with the 8255. Write an ALP to display 1,2,3,4and5 over the 5 displays continuously as per their positions starting with 1 at the least significant position? Assuming a segment to light when a low signal is applied. The decimal to seven-segment code are No to be displayed PA7 PA6 PA5 PA4 PA3 PA2 PA1 PA0 CODE DP a b C d e f G 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 CF 2 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 92 3 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 86 4 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 CC 5 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 A4 6 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 B0 7 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 8F 8 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 80 9 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 84 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 81
Challenging Problem: Interface a 4x4 keypad and five 7-segment displays using 8255 and WAP in assembly language to display a five digit number on the 7-segments

![❤[READ]❤ Robotic Exploration of the Solar System: Part I: The Golden Age 1957-19](/thumb/21623/read-robotic-exploration-of-the-solar-system-part-i-the-golden-age-1957-19.jpg)