Understanding Address Translation in Virtual Memory Systems
Explore the process of address translation in virtual memory systems, covering page hits, page faults, and techniques for speeding up translation such as TLBs. Learn how MMU, CPU, cache, and memory work together to efficiently manage virtual and physical addresses. Discover solutions to optimize memory access and enhance performance.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
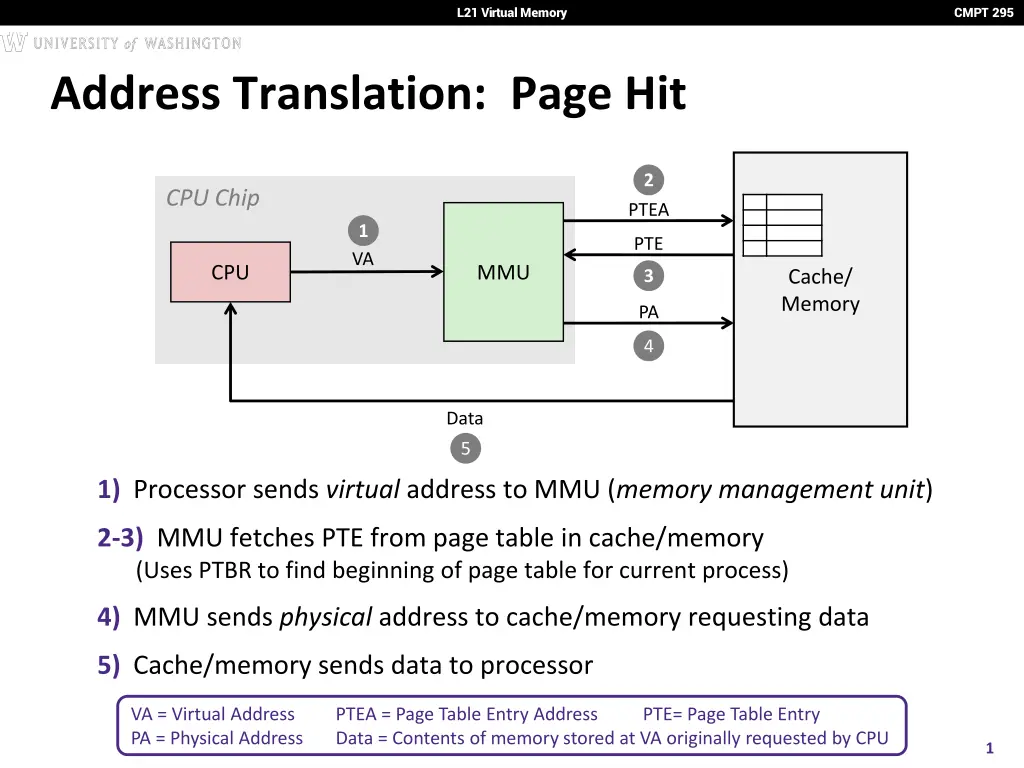
L21 Virtual Memory CMPT 295 Address Translation: Page Hit 2 CPU Chip PTEA 1 PTE VA MMU CPU Cache/ Memory 3 PA 4 Data 5 1) Processor sends virtual address to MMU (memory management unit) 2-3) MMU fetches PTE from page table in cache/memory (Uses PTBR to find beginning of page table for current process) 4) MMU sends physical addressto cache/memory requesting data 5) Cache/memory sends data to processor VA = Virtual Address PA = Physical Address PTEA = Page Table Entry Address Data = Contents of memory stored at VA originally requested by CPU PTE= Page Table Entry 1
L21 Virtual Memory CMPT 295 Address Translation: Page Fault Exception Page fault handler 4 2 CPU Chip Victim page PTEA 1 5 VA PTE Cache/ Memory MMU CPU Disk 3 7 New page 6 1) Processor sends virtual address to MMU 2-3) MMU fetches PTE from page table in cache/memory 4) Valid bit is zero, so MMU triggers page fault exception 5) Handler identifies victim (and, if dirty, pages it out to disk) 6) Handler pages in new page and updates PTE in memory 7) Handler returns to original process, restarting faulting instruction 2
L21 Virtual Memory CMPT 295 Hmm Translation Sounds Slow The MMU accesses memory twice: once to get the PTE for translation, and then again for the actual memory request The PTEs may be cached in L1 like any other memory word But they may be evicted by other data references And a hit in the L1 cache still requires 1-3 cycles What can we do to make this faster? Solution: add another cache! 3
L21 Virtual Memory CMPT 295 Speeding up Translation with a TLB Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB): Small hardware cache in MMU Split VPN into TLB Tag and TLB Index based on # of sets in TLB Maps virtual page numbers to physical page numbers Stores page table entries for a small number of pages Modern Intel processors have 128 or 256 entries in TLB Much faster than a page table lookup in cache/memory TLB Set Virtual Page Number Page offset V TLBT PTE 0 V TLBT PTE V TLBT PTE TLBT TLBI 1 V TLBT PTE 4
L21 Virtual Memory CMPT 295 TLB Hit TLB PTE VPN PTE VPN PTE VPN CPU Chip TLB PTE 2 3 VPN 1 PA VA MMU CPU Cache/ Memory 4 Data 5 A TLB hit eliminates a memory access! 5
L21 Virtual Memory CMPT 295 TLB Miss TLB PTE VPN PTE VPN PTE VPN CPU Chip TLB 4 2 PTE VPN 1 3 VA PTEA MMU CPU Cache/ Memory PA 5 Data 6 A TLB miss incurs an additional memory access (the PTE) Fortunately, TLB misses are rare 6
L21 Virtual Memory CMPT 295 Fetching Data on a Memory Read 1) Check TLB Input: VPN, Output: PPN TLB Hit: Fetch translation, return PPN TLB Miss: Check page table (in memory) Page Table Hit: Load page table entry into TLB Page Fault: Fetch page from disk to memory, update corresponding page table entry, then load entry into TLB 2) Check cache Input: physical address, Output: data Cache Hit: Return data value to processor Cache Miss: Fetch data value from memory, store it in cache, return it to processor 7
L21 Virtual Memory CMPT 295 Address Translation Virtual Address TLB Lookup TLB Miss TLB Hit Check the Page Table Protection Check Page not in Mem Page in Mem Access Denied Protection Fault Access Permitted Physical Address Update TLB Page Fault (OS loads page) SIGSEGV Find in Disk Find in Mem Check cache Miss Hit 8
L21 Virtual Memory CMPT 295 Address Manipulation ?-bit virtual address request from CPU: split to access TLB: TLB Tag TLB Index Page Offset (on TLB miss) access PT: Virtual Page Number Page offset TRANSLATION ?-bit physical address: Physical Page Number Page offset split to access cache: Cache Tag Cache Index Offset 9
L21 Virtual Memory CMPT 295 Summary of Address Translation Symbols Basic Parameters N = 2? Number of addresses in virtual address space M = 2? Number of addresses in physical address space P = 2? Page size (bytes) Components of the virtual address (VA) VPO Virtual page offset VPN Virtual page number TLBI TLB index TLBT TLB tag Components of the physical address (PA) PPO Physical page offset (same as VPO) PPN Physical page number 10
L21 Virtual Memory CMPT 295 Page Table Address Translation CPU Virtual address (VA) Page table base register (PTBR) Virtual page number (VPN) Virtual page offset (VPO) Page table Page table address for process Valid PPN Valid bit = 0: page not in memory (page fault) Physical page number (PPN) Physical page offset (PPO) In most cases, the MMU can perform this translation without software assistance Physical address (PA) 11
L21 Virtual Memory CMPT 295 Peer Question How many bits wide are the following fields? 16 KiB pages 48-bit virtual addresses 16 GiB physical memory VPN PPN 34 32 30 34 24 18 20 20 (A) (B) (C) (D) 12
L21 Virtual Memory CMPT 295 Page Hit Page hit: VM reference is in physical memory Page Table (DRAM) Physical memory (DRAM) VP 1 VP 2 VP 7 VP 4 Virtual address Valid PPN/Disk Addr null PP 0 0 1 1 0 1 PTE 0 PP 3 null 0 Virtual memory (DRAM/disk) 0 1 ... PTE 7 ... VP 3 Example: Page size = 4 KiB 0x00740b VP 6 Virtual Addr: Physical Addr: VPN: PPN: 13
L21 Virtual Memory CMPT 295 Page Fault Page fault:VM reference is NOT in physical memory Page Table (DRAM) Physical memory (DRAM) VP 1 VP 2 VP 7 VP 4 Virtual address Valid PPN/Disk Addr null PP 0 0 1 1 0 1 PTE 0 PP 3 null 0 Virtual memory (DRAM/disk) 0 1 ... PTE 7 ... VP 3 Example: Page size = 4 KiB Provide a virtual address request (in hex) that results in this particular page fault: VP 6 Virtual Addr: 14
L21 Virtual Memory CMPT 295 Simple Memory System Example (small) Addressing 14-bit virtual addresses 12-bit physical address Page size = 64 bytes 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 VPN VPO Virtual Page Number Virtual Page Offset 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 PPN PPO Physical Page Number Physical Page Offset 15
L21 Virtual Memory CMPT 295 Simple Memory System: Page Table Only showing first 16 entries (out of _____) Note: showing 2 hex digits for PPN even though only 6 bits Note: other management bits not shown, but part of PTE VPN 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 PPN 28 33 02 16 Valid 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 VPN 8 9 A B C D E F PPN 13 17 09 2D 0D Valid 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 16
L21 Virtual Memory CMPT 295 Simple Memory System: TLB 16 entries total Why does the TLB ignore the page offset? 4-way set associative TLB tag TLB index 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 virtual page number virtual page offset Set Tag PPN Valid Tag PPN Valid Tag PPN Valid Tag PPN Valid 0 03 0 09 0D 1 00 0 07 02 1 1 03 2D 1 02 0 04 0 0A 0 2 02 0 08 0 06 0 03 0 3 07 0 03 0D 1 0A 34 1 02 0 17
L21 Virtual Memory CMPT 295 Note: It is just coincidence that the PPN is the same width as the cache Tag Simple Memory System: Cache Direct-mapped with K = 4 B, C/K = 16 Physically addressed cache tag cache index cache offset 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 physical page number physical page offset Index 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Tag 19 15 1B 36 32 0D 31 16 Valid 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 B0 99 00 43 36 11 B1 11 02 6D 72 C2 B2 23 04 8F F0 DF B3 11 08 09 1D 03 Index 8 9 A B C D E F Tag 24 2D 2D 0B 12 16 13 14 Valid 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 B0 3A 93 04 83 B1 00 15 96 77 B2 51 DA 34 1B B3 89 3B 15 D3 18
L21 Virtual Memory CMPT 295 Current State of Memory System Page table (partial): VPN PPN V 0 28 1 1 0 2 33 1 3 02 1 4 0 5 16 1 6 0 7 0 TLB: VPN PPN 8 9 A B C D E F V 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 Set Tag PPN 0 03 1 03 2 02 3 07 V 0 1 0 0 Tag PPN 09 02 08 03 V 1 0 0 1 Tag PPN 00 04 06 0A V 0 0 0 1 Tag PPN 07 0A 03 02 V 1 0 0 0 13 17 09 2D 0D 0D 0D 02 2D 34 Cache: Index 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Tag 19 15 1B 36 32 0D 31 16 V 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 B0 99 00 43 36 11 B1 11 02 6D 72 C2 B2 23 04 8F F0 DF B3 11 08 09 1D 03 Index 8 9 A B C D E F Tag 24 2D 2D 0B 12 16 13 14 V 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 B0 3A 93 04 83 B1 00 15 96 77 B2 51 DA 34 1B B3 89 3B 15 D3
L21 Virtual Memory CMPT 295 Note: It is just coincidence that the PPN is the same width as the cache Tag Memory Request Example #1 Virtual Address: 0x03D4 TLBT 13 12 11 TLBI 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 VPN VPO VPN ______ TLBT _____ TLBI _____ TLB Hit? ___ Page Fault? ___ PPN _____ Physical Address: CO CI CT 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 PPN PPO CT ______ CI _____ CO _____ Cache Hit? ___ Data (byte) _______ 20
L21 Virtual Memory CMPT 295 Memory Overview LD t1, 0 (sp) Disk Page requested 32-bits Main memory (DRAM) CPU Cache Page Line Block MMU TLB 21
L21 Virtual Memory CMPT 295 Practice VM Question Our system has the following properties 1 MiB of physical address space 4 GiB of virtual address space 32 KiB page size 4-entry fully associative TLB with LRU replacement a) Fill in the following blanks: ________ Entries in a page table ________ Minimum bit-width of PTBR ________ TLBT bits ________ Max # of valid entries in a page table 22
L21 Virtual Memory CMPT 295 Practice VM Question One process uses a page-aligned square matrix mat[] of 32- bit integers in the code shown below: #define MAT_SIZE = 2048 for(int i = 0; i < MAT_SIZE; i++) mat[i*(MAT_SIZE+1)] = i; b) What is the largest stride (in bytes) between successive memory accesses (in the VA space)? 23
L21 Virtual Memory CMPT 295 Practice VM Question One process uses a page-aligned square matrix mat[] of 32- bit integers in the code shown below: #define MAT_SIZE = 2048 for(int i = 0; i < MAT_SIZE; i++) mat[i*(MAT_SIZE+1)] = i; Assuming all of mat[] starts on disk, what are the following hit rates for the execution of the for-loop? c) ________ TLB Hit Rate ________ Page Table Hit Rate 24






















