Understanding Allergic Rhinitis: Symptoms, Prevalence & Management
Explore the prevalence and symptoms of Allergic Rhinitis (AR), a common childhood chronic disease. Discover the impact of age, gender, and environmental factors on AR. Learn about the classic symptoms, signs, and comorbid conditions associated with AR. Gain insights into the allergic response mechanisms and management strategies for AR.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Prevalence is 15%-25%. Uncommon in less than two years of age Boys outnumber girls, but then there is no gender disparity by adulthood. Mean age of onset is 10 years. 80% of cases develop before 20 years of age. 20% of AR is seasonal, 40% is perennial, and 40% is mixed Increasing in prevalence as parallel with other atopic disease.
industrialized countries younger age groups Maternal smooking
Nasal congestion, headache, and post-nasal drip were rated the most bothersome symptoms AR is the most common, chronic disease of childhood
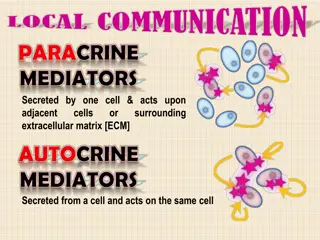
1 1.Immediate A.Histamin o Itch o Sneeze o Rhinorrhea o Nasal congestion B.PGD C.Leukotrienes D.Kinins .Immediate Allergic A.Histamin Allergic Response(Mast Cell): Response(Mast Cell): B.PGD2 2 C.Leukotrienes D.Kinins: nasal congestion and/or blockage.
2.Late Allergic Late Allergic Response Response A.Eosinophil B.Basophil C.Lymphocyte D.Nutrophil E.IL A.Eosinophil B.Basophil C.Lymphocyte Th D.Nutrophil E.IL4 4,IL Th2 2 ,IL13 13 Predominant symptoms include nasal congestion and mucus production 80% of Asthma have AR and 40% of AR have asthma FeNo increase in AR and allergic asthma and decrease in sinusitis
Classically, symptoms of AR include: a.Rhinorrhea b.Nasal pruritus c.Nasal congestion d.Sneezing.
Signs of AR include: a.Allergic shiners b.Allergic crease c.Dennie-Morgan lines (ie, linear creases or furrows underneath the lower eyelids) d.Pale nasal mucosa e.Turbinate hypertrophy f.Mouth breathing g.Cobblestoning of the oropharynx. Allergic conjunctivitis, sinusitis, and asthma (present in up to 40% of patients with AR) are common comorbid conditions.
Hx. skin testing (prick or intradermal) serum-specific IgE (RAST)
Nasal antihistamines (nonsedating) Antileukotriene therapy Intranasal decongestants (short-term use only) Oral decongestants or chromones Immunotherapy Intranasal steroids medication for AR and, therefore, are the medication treatment of Intranasal steroids are the most effective medication for AR and, therefore, are the medication treatment of choice are the most effective choice
NARES Eosinophilia on nasal smear(Rare in child) Vasomotor: Irritant, gustatory, cold (Skier Nose),Light(Reflex rhinitis),Rx:Ipratropum Medications : ASA, NSAID s, topical decongestants, blockers, other anti-hypertensives Hormonal : OCPs, pregnancy, menstrual associations, hypothyroidism Atrophic: Elderly or surgery Infectious: Common cold viruses Occupational : Flour (Baker), latex (health care workers), pet dander (animal handlers) Miscellaneous : Anatomical, tumor, systemic disease, CSF rhinorrhea
No ninflammatory cause of the disease that is associated with the loss of the normal secretory function of the nose Nasal congestion Nasal pain upon inspiration from excess mucosal dryness Nasal crusting A foul smell in the nasal vault (ozena: Klebsiella Ozaenae) ) Treatment may include nasal saline irrigation and topical antibiotics
Rare in child ASA and NSAIDs (as a feature of AERD) blockers, Prolonged use of intranasal decongestants (rebound rhinitis) ACE inhibitors Oral contraceptive pills (OCPs) Sildenafil Cocaine Treatment:DC of drugs Sildenafil
Approximately 60% of children with allergic rhinitis have symptoms of reactive airways disease/asthma otitis media, sinusitis, tonsillar and adenoid hypertrophy sleep disturbances, limitations of activity and school performance, irritability, and mood and cognitive disorders
Seasonal allergic rhinitis:Outdoor Allergen(Trees,weeds,grasses,fungi) Perennial allergic rhinitis:Indoor Allergen(Pets,dander:HEPA,mites,mold , coackroach)