Understanding Aquifer Anisotropy in Groundwater Hydrology
Explore the concept of aquifer anisotropy and its impact on groundwater flow in layered systems. Learn how to calculate equivalent hydraulic conductivities and understand the general groundwater flow equations based on Darcy's Law and storage properties.
Uploaded on | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
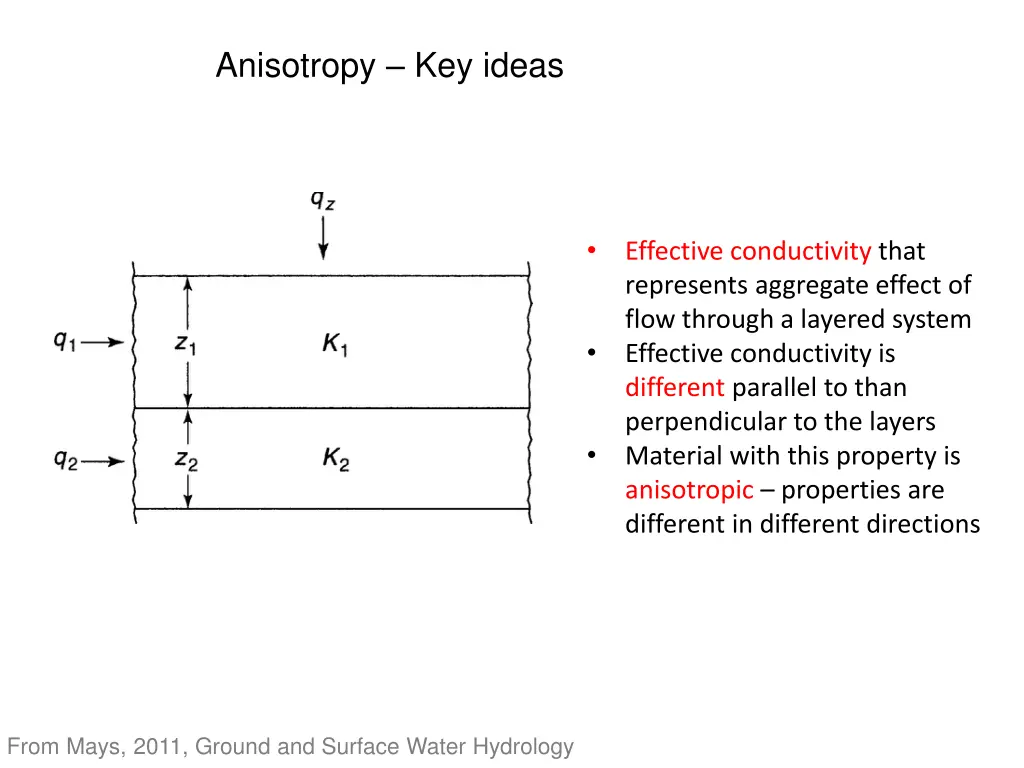
Anisotropy Key ideas Effective conductivity that represents aggregate effect of flow through a layered system Effective conductivity is different parallel to than perpendicular to the layers Material with this property is anisotropic properties are different in different directions From Mays, 2011, Ground and Surface Water Hydrology
Example An aquifer has 3 layers with K values indicated. Compute the equivalent horizontal and vertical hydraulic conductivities 10 m K=11.6 m/day 4.4 m K=4.5 m/day 6.2 m K=2.2 m/day
Aquifer Anisotropy and general flow equations Objective To be able to quantify the anisotropy of an aquifer due to layering To be able to describe the equations used in general groundwater flow calculations
General Groundwater Flow Equations Based on Darcy s Law Storage properties Used in groundwater models to examine more complex groundwater flow problems From Mays, 2011, Ground and Surface Water Hydrology
