Understanding Atoms and Molecules in Matter Exploration
Explore the foundational concepts of atoms and molecules in the study of matter, including the structure of an atom, the roles of protons, neutrons, and electrons, and the significance of the periodic table. Delve into the atomic mass/weight and the intricate nature of elements. Unravel the scientific perspective on the essential building blocks of our universe.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Vocabulary 1.6 Atoms/Molecules ON-LEVEL 10 INDEX CARDS
CCGPS S8P1. Students will examine the scientific view of the nature of matter. a. Distinguish between atoms and molecules.
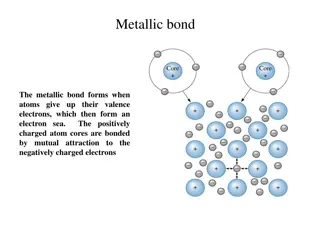
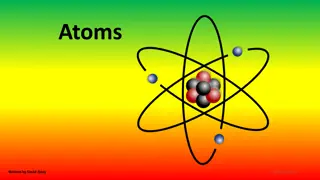
Atom An atom is a particle of matter that uniquely defines a chemical element. The atom is the basic building block for all matter in the universe. Atoms are extremely small and are made up of a few even smaller particles.
Nucleus The positively charged dense center of an atom.
Electron The electron is a negatively charged particle that spins around the outside of the nucleus. Electrons spin so fast around the nucleus, scientists can never be 100% sure where they are located, so they estimate their location.
Proton The proton is a positively charged particle that is located at the center of the atom in the nucleus.
Neutron Located in the center of the nucleus with the Proton. The neutron doesn't have any charge. The number of neutrons affects the mass and the radioactivity of the atom.
Just How Small is an Atom? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yQP4UJhNn0I
Periodic Table of Elements The periodic table is an arrangement of the chemical elements. Ordered by their atomic number (number of protons), electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties.
Introduction to the Periodic Table https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8migjQOY3hM
Atomic Mass/Weight The sum of the masses of the protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom, or the average mass, in a group of atoms. This can be found by looking at the bottom number on the Periodic Table.
Atomic Number The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. This can be found by looking at the top number on the periodic table.
Chemical/Elemental Symbol A one or two-letter representation of an element. Chemical Symbol
Valance Electrons The electrons that are in the highest energy level of an atom.
Draw My Science https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G8QbUdC3Rps Start Video at 1:05 minutes