Understanding Basalt: Formation, Texture, and Global Abundance
Explore the world of basalt, a volcanic rock rich in clinopyroxene and plagioclase minerals. Learn about its textures, global distribution in various geological settings, classification based on compositional variations, and the concept of the basalt tetrahedron. Basalt plays a crucial role in understanding mantle melting processes and is widely studied for its significance in Earth's geology.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Basalt M.Sc. ( Geology) M.Sc. ( Geology) III III Semester Semester NIRANJAN MOHANTY DEPARTMENT OF GEOLOGY, MLS UNIVERSITY UDAIPUR-313001 (RAJASTHAN) E-mail: niranjan@mlsu.ac.in
What is a Basalt? Definition: A basaltic rock is a volcanic rock characterized by the presence of clinopyroxene and plagioclase as essential minerals. Olivine, orthopyroxene and silica-rich glass may be present as accessory minerals along with iron oxides (magnetite & ilmenite).
Texture of Basalt Three types of textures are common: Ophitic Texture: lath shaped plagioclases included in larger pyroxenes. Sub-ophitic Texture: Here pyroxenes are smaller. Porphyritic texture: phenocrysts (coarser) in a fine groundmass e.g. olivine basalt
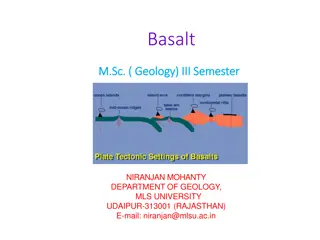
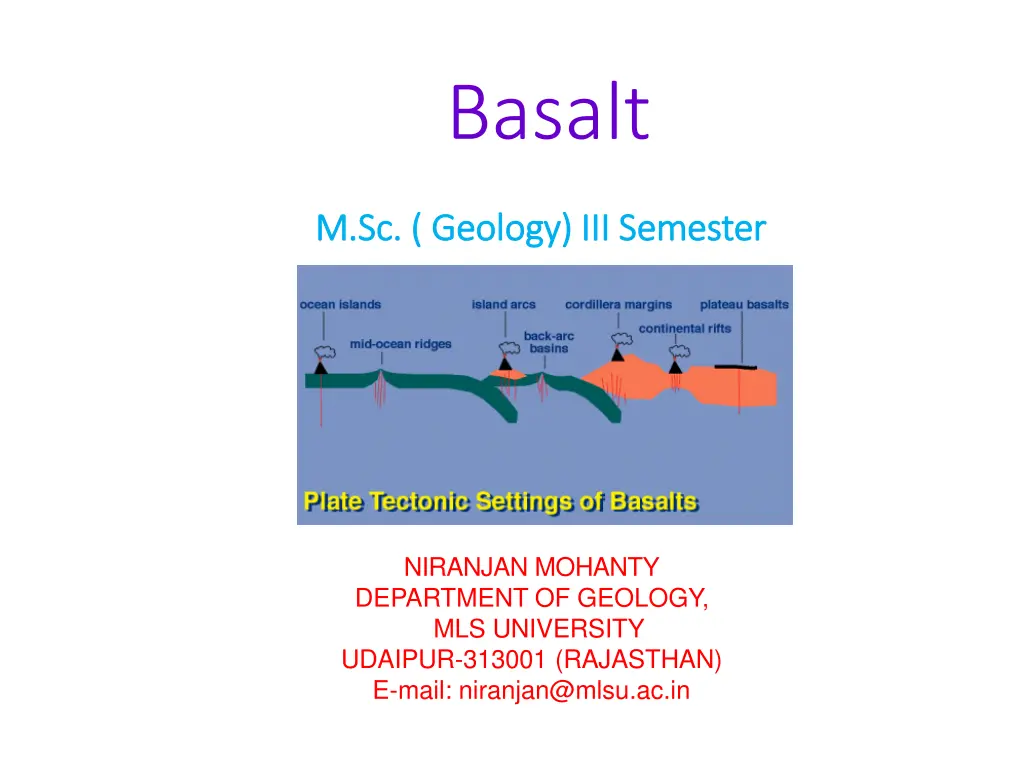
Global abundance of Basalts Basalts are found in 1.Mid Oceanic Ridges (MORB) 2.Ocean Islands (OIB) 3.Orogenic continental margins & island arcs (associated with subduction zones) (Bimodal volcanics along with andesites) 4. Continental plates (not associated with subduction) (Plume or rifting related) Most abundant igneous rock types & hence most well studied experimentally & in field Most of the models of mantle melting is based mostly on the study of basalts.
Classification of Basalts There are a number of compositional variations in basalts resulting in their wide variety. Yoder & Tilley (1962) recognized the importance of representing principal magma types in terms of simple basalt system and introduced concept of basalt tetrahedron. According to them, phases in the quaternary system - diopside (Di)-forsterite (Fo)-nepheline (Ne)- quartz (qz) contains the principal components of all the major and common minerals in basalt group.
Basalt Tetrahedron The dissected by two planes viz., Plane 1: Di-Ab-En plane or CPx- Pl-Opx (Plane of silica saturation) Plane 2: Di-Ab-Fo plane or Cpx-Pl-Ol- plane or (Plane of critical silica undersaturation) tetrahedron is
Five compositional types of Basalts Five compositional types of Basalts The two planes divide basalts into five unique groups on basis of normative components: 1.Quartz Tholeiite (oversaturated): Characterized by normative quartz & hypersthene 2.Hypersthene tholeiite (saturated): characterized by normative hypersthene but no quartz. 3.Olivine-tholeiite (undersaturated): Normative olivine & hypersthene 4.Olivine basalt (undersaturated): Normative olivine but no hypersthene. 5.Alkali olivine basalt or alkaline basalts (strongly undersaturated): Normative olivine & nepheline Most basalts, excepting those contaning normative acmite (peralkaline basalts), are represented in basalt tetrahedron.