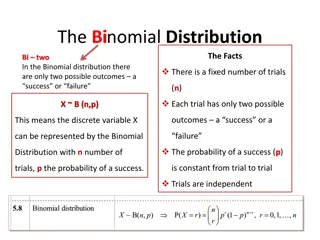
Understanding Binomial and Geometric Distributions for On-Time Performance Analysis
Explore how binomial and geometric distributions are utilized to analyze on-time performance at Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport. Learn about the probability functions, expected values, and applications of these distributions in sampling and data modeling.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Binomial and Geometric Distributions Delta On-Time Performance at Hartsfield- Jackson Atlanta International (June, 2003 - June, 2015) http://www.transtats.bts.gov/OT_Delay/ot_delaycause1.asp?display=data&pn=1
Data / Model Total Operations: 2,278,897 On-Time Operations: 1,824,432 Proportion On-Time: 1824432/2278897 = .8006 (.80) Will consider random samples of various sizes from this population of operations Y # of On-Time operations out of the sample of n Y ~ Binomial(n , pY= 0.80) X # of Flights sampled until the first NOT On-Time Arrival is selected X ~ Geometric(pX= 0.20)
Binomial Distribution Probability Function Binomial Probability Mass Function n y ! n ( ) ( ) ( ) p y ( ) ( ) n y n y = = = = = y y | ~ , 1 1 0,1,..., 0 1 P Y y Y Bin n p p p p p y n p ( ) ! ! y n y ( ) p y = 0 since: 0,1,..., 0 1 y y n p ( ) n a b + Binomial Expansion of : ( ) 2 = a b + = + ab b + 2 2 2: 2 n a ( ) 3 = a b + = + + + + + = + + + 3 2 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 3 3: 2 2 3 3 n a a b ab a b ab b a a b ab b n i n ( ) n n i a b + = i General : n a b = 0 i n y n n ( ) ( ) p y ( ) ( ) n n y = = + = = y n 1 1 1 1 Thus, a probability distribution p p p p = = 0 0 y y
Geometric Distribution Used to model the number of Bernoulli trials needed until the first Success occurs (P(S)=p) First Success on Trial 1 S, y = 1 p(1)=p First Success on Trial 2 FS, y = 2 p(2)=(1-p)p First Success on Trial k F FS, y = k p(k)=(1-p)k-1p = = 1 y ( ) p y (1 ) 1,2,... p p y = = 1 1 y y ( ) p y (1 ) (1 ) p p p p = = = 1 1 1 y y = y = = * * Setting 1 and noting that 1,2,... 0,1,... y y y y 1 p p = = = = * y ( ) p y (1 ) 1 p p p 1 (1 ) p = * 0 = 1 y y
Binomial Distribution Expected Value Binomial Probability Mass Function n y ! n ( ) ( ) ( ) p y ( ) ( ) n y n y = = = = = y y | ~ , 1 1 0,1,..., 0 1 P Y y Y Bin n p p p p p y n p ( ) ! ! y n y Obtaining the Mean of : Y ! n n n E Y ( ) ( ) n y = = = = y 1 Summand = 0 when 0 yp y y p p y ( ) Y ! ! y n y = = 0 0 y y ! ( 1 ! n n ( ) n y = y 1 Pull out , yy n p p n p ( ) Y ! ! y = 1 y ) 1 ! n n n ( ) n y = = = = + 1 y 1 Now, set 1 0,1,..., 1 1 np p p w y w n y w ( ) ( ) Y ! y y = 1 y ( ) ( ) 1 ! w 1 ! 1 n n n 1 1 n n ( ) ( ) ( ) n w 1 1 n w = = = w w 1 1 Now, set 1 np p p np p p m n ( ) ( ) ( ) Y ! 1 ! ! ! w n w w = = 0 0 w w ! m m ( ) ( ) ( ) m m w = = + = w 1 1 np p p np p p np ( ) Y ! ! w m w = 0 w
Geometric Distribution Expected Value ( ) ( ) y q = = 1 y E Y yp y p = = 1 1 dq dq y y y = = 1 y Note: 1 and q p yq y dq dq d dq ( ) = = y E Y p p q = = 1 1 y y This interchange is justified due to nature of the convergent series. = 1 since 0 1 y z q = = = = d dq ( ) 1 y E Y p q q = 1 y = = 1 y z 1 q q q 1 0 ( ) + ( 1) (1 (1 ) ) p q q q (1 )(1) (1 1 p d dq q q q p p ( ) = = = E Y p p 2 2 2 1 ) q q
Binomial Distribution Variance and SD Obtaining the Variance of : First obtain Y E Y Y E Y ( ) E Y = 2 1 ! n n n ( ) ( ) ( ) 1 p y ( ) ( ) n y = = = y 1 1 1 Summand = 0 when 0,1 E Y Y y y y y p p y ( ) ! ! y n y = = 0 0 y y ! n n ( ) ( ) ( ) n n ( ) n y = 2 y 1 1 1 Pull out 1 , E Y Y y y p p p ( ) ! ! y n y = 2 y ( ) 2 ! n w = n n ( ) ( ) ( ) n y = 2 2 y 1 1 1 E Y Y n n p p p ( ) ( y ) 2 2 ! ! y y = 2 n y = = + Now, set 2 0,1,..., 2 w y w ( ) 2 ! w n 2 n ( ) ( ) ( ) n w 2 = = 2 w 1 1 1 E Y Y n n p p p ( ) ! 2 ! w n = 0 w ( ) 2 ! 2 n n 2 n ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 n w = = 2 w 1 1 Now, set 2 n n p p p m n ( ) ( ) ! ! w w = 0 w ! m m ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) m m w = = + = 2 2 2 w 1 1 1 1 1 1 E Y Y n n p p p n n p p p n n p w m ( = ) ! ! w = 0 w E Y ( ) E Y ( ) = + + = + 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 E Y Y E Y n p np np n p np p E Y ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 2 = = = + = = 2 Y 2 2 2 1 1 1 V Y n p np p np np p np p Y
Geometric Distribution Variance and SD 2 y d q dq ( ) = = = 1 y ( 1) ( 1) E Y Y y y q p pq 2 = = 1 1 y y 2 2 d dq d dq = = = 1 y y pq q pq q q 2 2 = = 1 1 y y 2 1 2 2 2 p d dq q d dq pq q p pq p q ( ) = = = = = = 3 2(1 ) ( 1) pq pq pq q ( 2 ) 3 2 2 3 2 1 (1 ) q q 1 + 2 p 1 p 2(1 ) q p p ( ) ( ) = + = + = = 2 ( 1) ( ) E Y E Y Y E Y 2 2 2 p p 2 2 1 p 2 1 1 p p p q p E Y ( ) 2 = = = = = 2 ( ) ( ) V Y E Y 2 2 2 2 p p p q p = 2
Binomial Distribution for On-Time Flights = 1 (Bernoulli Distribution): 1 0.8 1 0.8 y = = n ( ) p y ( ) ( ) 0 ( ) ( ) ( ) 1 ( ) ( ) 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 y = = = = = = y 0,1 1 0.8 0.2 0.2 1 0.8 0.2 0.8 y p p E Y ( ) ( )( ) = = = 1 0.8 0.8 1 0.8 0.2 0.16 0.40 V Y Y = 2 n 2 y ( ) p y ( ) 2 y = = y 0.8 1 0.8 0,1,2 y ( ) 0 E Y ( ) ( ) ) ( ) 1 ( ) ( 0.32 ) ( ) 2 ( ) ( ) 2 0 2 1 2 2 0 1 2 = = = = = = = 1 0.8 ( 2 0.8 = 0.2 = 0.04 V Y 2 0.8 ) 0.2 0.32 1 0.8 0.2 0.64 p p ( p )( = = 1.6 2 0.8 0.2 0.566 Y ( ) ( ) p n = In general, what needs to happen for 1 ? p n = For what value of does that occur for n .8? p
Binomial Distributions for n=1,2,3,4,10,25 In EXCEL: Create a column of values 0,1,2, ,n (Say 0 is in cell A2) In Cell B2, Type: =BINOM.DIST(A2,n,p,0) Copy and paste that cell alongside 1 (A3), ,n Note that the 0 at the end gives P(Y = y) = p(y) If you use 1 instead, you get P(Y y) = F(y)
Several Binomial Distributions with p=0.8 n n n n n n 1 2 3 4 10 25 p p p p p p 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.8 y p(y) y p(y) y p(y) y p(y) y p(y) 0 1.02E-07 1 4.1E-06 2 7.37E-05 3 0.000786 4 0.005505 5 0.026424 6 0.08808 7 0.201327 8 0.30199 9 0.268435 10 0.107374 y p(y) 0 3.36E-18 1 3.36E-16 2 1.61E-14 3 4.94E-13 4 1.09E-11 5 1.83E-10 6 2.43E-09 7 2.64E-08 8 2.38E-07 9 1.8E-06 10 1.15E-05 11 6.27E-05 12 0.000293 13 0.001171 14 0.004015 15 0.011777 16 0.029442 17 0.062349 18 0.110842 19 0.163346 20 0.196015 21 0.186681 22 0.135768 23 0.070835 24 0.023612 25 0.003778 20 0 1 0.2 0.8 0 1 2 0.04 0.32 0.64 0 1 2 3 0.008 0.096 0.384 0.512 0 1 2 3 4 0.0016 0.0256 0.1536 0.4096 0.4096 1 0.8 0.4 1.6 0.565685 2.4 0.69282 3.2 0.8 8 1.264911 2
Probability Distribution of On-Time Flights Y ~ Bin(n=1,p=0.80) 1 0.95 0.9 0.85 0.8 0.75 0.7 0.65 0.6 0.55 0.5 p(y) 0.45 0.4 0.35 0.3 0.25 0.2 0.15 0.1 0.05 0 0 1
Probability Distribution of On-Time Flights Y ~ Bin(n=3,p=0.80) 0.7 0.65 0.6 0.55 0.5 0.45 0.4 0.35 p(y) 0.3 0.25 0.2 0.15 0.1 0.05 0 0 1 2 3
Probability Distribution of On-Time Flights Y ~ Bin(n=4,p=0.80) 0.45 0.4 0.35 0.3 0.25 p(y) 0.2 0.15 0.1 0.05 0 0 1 2 3 4
Probability Distribution of On-Time Flights Y ~ Bin(n=10,p=0.80) 0.4 0.36 0.32 0.28 0.24 0.2 p(y) 0.16 0.12 0.08 0.04 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Probability Distribution of On-Time Flights Y ~ Bin(n=25,p=0.80) 0.25 0.225 0.2 0.175 0.15 0.125 p(y) 0.1 0.075 0.05 0.025 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
Probability Distribution of On-Time Flights Y ~ Bin(n=100,p=0.80) 0.12 0.1 0.08 0.06 p(y) 0.04 0.02 0 0 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 30 33 36 39 42 45 48 51 54 57 60 63 66 69 72 75 78 81 84 87 90 93 96 99
Geometric Distribution Probabilities ( ( ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) p x = = = = = 1 1 X 1 1 0.20 P X p p q p X p q X p q ) ) ( ) = = = = = = 2 1 X 2 2 0.20 0.80 0.16 P X p X X X ( ) 1 x = = = = 1 x X 0.20 0.80 P X x p q X 1 1 p 1 1 0.20 .20 .80 .04 p E X V X = = = = = = = 5.00 20.00 X 2 X 2 0.20 p X = = 20 4.47 X x X 1 1 x x x q q ( ) ( ) ( ) p x ( ) x = = = = = = = 1 1 i X i X x X 1 1 .80 F x P X x p q p q p q X X X = = = 1 1 1 i i i X ( ) In general, what is the smallest such that for fixed 0 1 x P X x c c ( ) For the Airline data, what is the smallest x such that 0.95 P X x
Geometric Distribution In EXCEL: Create a column of values 1,2, ,Y* for some large value of Y* (Say 1 is in cell A2) In Cell B2, Type: =NEGBINOM.DIST(A2-1,1,p,0) Copy and paste that cell alongside 1 (A3), ,Y* Note that the 0 at the end gives P(Y = y) = p(y) If you use 1 instead, you get P(Y y) = F(y)
Geometric Distribution Probabilities and CDF Geometric Distribution for Probability of y Trials until 1st NON On-Time Flight Geometric (p=.20) y 1 2 3 4 5 6 0.065536 0.737856 7 0.052429 0.790285 8 0.041943 0.832228 9 0.033554 0.865782 10 0.026844 0.892626 11 0.021475 0.914101 12 0.01718 0.931281 13 0.013744 0.945024 14 0.010995 15 0.008796 0.964816 16 0.007037 0.971853 17 0.005629 0.977482 18 0.004504 0.981986 19 0.003603 0.985588 20 0.002882 0.988471 21 0.002306 0.990777 22 0.001845 0.992621 23 0.001476 0.994097 24 0.001181 0.995278 25 0.000944 0.996222 p(y) F(y) 0.2 0.16 0.128 0.1024 0.08192 0.2 0.36 0.488 0.5904 0.67232 0.25 0.2 0.15 p(y) 0.95602 0.1 0.05 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
Moment-Generating Function E Y ' k = k Define: ( ) 2! ' k ( ) 3! ( ) 4! 2 3 4 ty ty ty = + + + + + ty 1 ... e ty = Assuming for 1,2,3,....: k ( ) 2! ( ) 3! ( ) 4! 2 3 4 ty ty ty E e ( ) ( ) ( ) p y = = = + + + + + tY ty 1 ... m t e p y ty y y 2 3 4 t t t ( ) p y ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) y = + + + + + 2 3 4 1 ... t yp y y p y y p y y p 2! 3! 4! y y y y y 2 3 4 t t t ' ' ' ' = + + + + + 1 ... t 1 2 3 4 2! 3! 4! ( ) k k d m t dt E Y ' k ( ) ( )( ) k = = = k If exists: 0 m t m = 0 t 2 3 2 2! 3 3! ' 4 4! t t t ' ' ' ' ' ( ) ( ) ' 0 = + + + + + = Note: ' 0 ... m t m 1 2 3 4 1 2 6 3! 12 t t ' ' ' ( ) ( ) '' 0 = + + + + = '' 0 ... m t m 2 3 4 2 4!
Moment-Generating Function Binomial Distribution Binomial Distribution: n y n y n n n E e ( ) e y ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) n y n y = = = = = tY ty ty y t y 1 1 m t e p y e p p p p = = = 0 0 0 y y y n y n ( ) ( ( ) y n ) ( ) n y = + t t 1 1 pe p p pe = 0 y ( ) ( ) ( ) 1 n ( ) ( ) ( ) ' 0 ( ) ( ) p 1 n = + = + = t t ' 1 1 m t n p pe pe m n p p np ) ( ( 1 ) 1 ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 2 1 n n ( ) ( ) '' 0 ( ) ( ) = + + + t t t t '' 1 1 m t n n p pe pe n ) p pe pe ( ( = + = + 2 2 2 1 m n n p np n p np p ( ) 2 E Y ' ' ' ' E Y ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 = = = = + = = + = 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 np n p np p V Y n p np p np np p 1 2 2 1 Airline Values: ( ) ( ) n n ( ) ( ) = 1 0.80 + = 0.20 0.80 + t t 0.80 m t e e
Geometric Distribution MGF ( ) = = = 1 tY ty y ( ) m t E e e q p = 1 y t t t p q p q pqe q pe pe ( ) ( ) 1 y y = = = = = ty y t t e q qe qe 1 (1 t t 1 ) qe p e = = = 1 1 1 y y y ( ) ( ) ) 1 (1 t t t t ) (1 ) p e pe pe p e + 2 2 t t t (1 ) (1 ) pe p p e p p e ( ) = = = ' m t ( ( 1 p ) 2 2 1 (1 t t 1 (1 ) ) p e p e t pe p p p ( ) ' 0 E Y = = = = = m ( ) ( ) 2 2 2 1 (1 ) p 1 (1 t ) p e ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 1 (1 t t t t t ) 2 1 (1 ) (1 ) p e pe pe p e p e ( ) t = = '' m ( ) 4 1 (1 t ) p e ( ) 1 2(1 + + 2 2 2 2 t t t t t 1 (1 ) (1 ) 2(1 ) 2(1 ) pe p e p e p e p e 2 2 t t ) pe p e = = ( ) ( ) 4 4 1 (1 t t ) 1 (1 ) p e p e ( ) ( )( p ) ( ) ( ) 2 2 1 p q + + + 1 1 1 1 q q q q 1 p q p ( ) '' 0 = = = = = m V Y 4 3 2 2 2 p p p
Probability-Generating Functions 1 ... 1 where is a positive integer is a Random Variable that takes on integer values: ( ) ( ) = + Define: E Y Y Y k k k = 0,1,2,... Y y E t ( ) ( ) ( ) 0 ( ) 1 ( ) 2 ( ) 3 = = = + + + + 0 1 2 3 Y y ... P t t p y t p t p t p t p = 0 y ( ) ( ) ' ( ) ' 1 ( ) 2 p ( ) 3 tp = + + + + 2 3 1 1 ... tp t p t p ( ) 1 ( ) 1 ( ) 2 ( ) 2 ( ) 3 3 = + = + + + + + + 2 0 2 3 ... P t t p ( ) + 0 2 3 ... P p p p ( ) E Y = = yp y = 0 y ( ) ( ) '' 1 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) E Y Y = ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 1 0 0 2 1 = + + = + + + + + + '' 2 3 2 3 ... P t p tp 0 0 2 1 2 3 2 3 ... P p p ( ) ( ) 1 p y ( ) = y y = 0 y ( ) k k d P t dt ( )( ) ( )( ) ( ) ( 1 ... ) k k = = = + 1 P t P t E Y Y Y k k = 1 t
Probability-Generating Functions - Binomial Binomial Distribution: Note: 1 2 ... p n p n p + = + = = = ( ) ( ) ( ) n y 0 n E t ( ) ( ) ( ) n y = = = Y y y y 1 P t t p y t p p = = 0 0 y y n y n ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) n n y y = = + 1 1 pt p p pt = 0 y ( ( ( ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) '' 1 ( ( ) ) ( ( 1 n = + ' 1 P t n p pt p ) E Y 1 n = + = = ' 1 1 P n p p p np ) ) ( ) ( 1 ) ) 2 n = + 2 '' 1 1 P t n n p pt p ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 2 n n = + = + = 2 2 1 1 1 1 P n n p p p n n p p p E Y Y ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) n n = 1 0.80 + = 0.20 0.80 + For Airline Data: 0.80 P t t t
Geometric Distribution PGF p q p q ( ) E t ( ) tq y = = = = = 1 Y y y y y ( ) P t t q p t q = = = 1 1 1 y y y ptq q pt pt ( ) tq 1 y = = = 1 (1 1 ) tq p t = 1 y ( ) ( ) ) 1 (1 + 1 (1 ) (1 ) ) (1 ) p p t p t p t p pt p p ( ) = = = ' P t ( ( ) ( ) 2 2 2 1 (1 1 (1 1 (1 p ) ) ) p t p t p t 1 p p p ( ) ' 1 E Y = = = = P ( ) 2 2 1 (1 ) p 2 (1 p 1 (1 ) p ( ) t ( ) ( ) 3 = 1 (1 = '' 2 ) (1 ) P p p t p ( ) 3 ) p t ( ) 2 1 p 2 (1 p ) p ( ) '' 1 ( ) = = = 1 P E Y Y 3 2 p p ( ) 2 2 2 + 2 1 p 1 p 1 p 1 1 p p p p = + = = V Y 2 2 2 p p