Understanding Cell Biology: Structures and Functions | National 5 Biology Lesson
Explore the fascinating world of cell biology with a focus on cell ultrastructure and functions. Learn about the roles of organelles such as the cell wall, mitochondrion, chloroplast, and more in plant, animal, fungal, and bacterial cells. Discover how to view and identify organelles in animal and plant cells under a microscope using stains. Cells are the essential building blocks of life, and this lesson provides a comprehensive introduction to their structure and function.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Unit 1: Cell Biology Key Area 1.1a: Cell ultrastructure and functions National 5 Biology 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 1
National 5 Biology Learning Intentions: KA1.1a By the end of this key area, you should be able to describe cell structure ultrastructure and the functions of each or the organelles, specifically be able to discuss The roles of the cell wall, mitochondrion, chloroplast, cell membrane, cytoplasm, vacuole, nucleus, ribosome and plasmid. Ultrastructure by using examples from typical plant, animal, fungi and bacterial cells. - Explain fungal structure in terms of similarity to plant and animal cells but with a different cell wall structure. (Cell wall structure in fungal and bacterial cells is different from plant cells, ie chitin not cellulose) - Bacterial structure description should include the absence of organelles (no nucleus, mitochondria vacuole or chloroplasts) and a different cell wall structure to plant and fungal cells. It should also include a description of their chromosomes and plasmid. In addition you will investigate how view animal and plant cells under the microscope. By using stains to highlight organelles you will be able to identify the cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, vacuole & chloroplasts 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 2
Unit 1: Cell Biology Ka1.1a Cell ultrastructure and functions. Lesson 1: Microscopy and BGE revision 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 3
What is a cell? In what way is a single cell like a LEGO brick? 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 4
What is a cell? All organisms are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of life 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 5
CELLS ARE THE STARTING POINT! All living organisms on Earth are divided into cells. The main concept of cell theory is that cells are the basic structural unit for all organisms. Nothing smaller than a cell can lead to independent life. Cells are small compartments that hold the biological equipment necessary to keep an organism alive and successful. Living things may be single-celled or they may be very complex such as a human being. 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 6
Plant Cells Can be viewed under the microscope Below are examples of plant cells viewed under the microscope Some of a plant cells parts can be seen clearly when mounted in water (see below) Other cell structures that are not so obvious can often be shown up more clearly by the addition of a STAIN (dye). Iodine solution can be used on onion cells to stain the nuclei. Elodea leaf cells in water Onion leaf cells in iodine solution 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 7
Using stains with the microscope. Stains can be used to make cells more visible under the microscope, e.g. Iodine solution. Onion skin: 2 pieces were taken from the bottom layer of an onion and placed on 2 different slides. With one, some iodine was placed n the slide to see the different layers, The other slide was left unstained. 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 8
Onion Cell Lab Instructions. Add 2 drops of iodine to the centre of a glass slide. Be careful! Iodine can stain your clothes. Take a small piece of onion. Use tweezers to peel off the skin from the underside (the rough, white side) of the onion. Throw the rest of the onion piece away. Carefully lay the onion skin flat in the centre of the slide on top of the iodine. Add 2 drops of iodine to the top of the onion skin. Stand a thin glass cover slip on its edge near the onion skin, next to the drop of iodine. Slowly lower the other side of the cover slip until it covers the onion skin completely. If there are air bubbles, gently tap on the glass to chase them out. 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 9
Draw what you see (is this a good diagram??) Why are there no chloroplasts in onion cells? Iodine Solution with air bubbles Chloroplasts are absent from onion skin cells because it grows underground in the darkness (so what would be the point?) 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 10
This is what our Onion cell looked like! 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 11
Plant Cell (Pond weed). Lab Instructions Tear off one small leaf/stem from the plants in the fish tank. Add one drop of tap water to the slide. Stand a thin glass cover slip on its edge near the leaf, next to the drop of water. Slowly lower the other side of the cover slip until it covers the leaf completely. Make sure there are no air bubbles. 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 12
Draw what you see. 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 13
So far we have learned that while some cells do look different, MOST cells have these three basic features. nucleus cytoplasm cell membrane 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 14
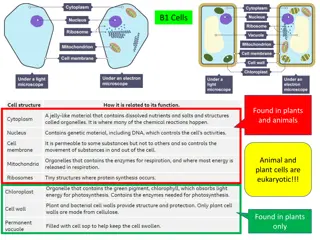
Cell Nucleus Cytoplasm Membrane The cell membrane is selectively permeable and controls what substances may enter and leave the cell. It is a jelly like material. All the chemical reactions taking place in the cell occur here Contains genetic material and Controls the cell s activities/ chemical reactions inside the cell 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 15
And that plant cells also have .. Cell wall Strengthens the cell Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, traps light energy for photosynthesis help the plant make their own food Vacuole Contains cell sap to help keep the cell turgid We call all these cell parts ORGANELLES 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 16
Task tick off the technique and apparatus used in your skills folder You should have completed the following skills techniques: Using a compound microscope with a low power objective lens. Preparing a microscope slide as a wet mount. During this you have gained knowledge using the following pieces of apparatus Microscope Dropper (when using Iodine Solution) Glass Sided and Cover Slips 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 17
Unit 1: Cell Biology Ka1.1a Cell ultrastructure and functions. Lesson 2: Organelles/ultrastructure and the Cell race task (co-op activity comparing organelles in 4 different types) 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 18
ORGANELLES ORGANELLES are tiny structures (such as chloroplasts) that are: Present in a cells cytoplasm as discrete units normally surrounded by a membrane. Responsible for a specialised function (such as photosynthesis Cell structure is actually way more complicated than we have been teaching you, there are even more organelles, than the 6 that you know. A cell holds lots of other smaller structures (even more organelles), which are all essential to the cell function. Understanding about these tiny structures is called the CELL ULTRASTRUCTURE 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 19
Ultrastructure These minute structures cannot be seen with a normal light microscope. The ultrastructure can only be examined by using a more sophisticated piece of equipment called the electron microscope. 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 20
20 Cooperative activity Cell race minutes max! Your group will be issued with four different cell diagrams and four different descriptions as well as your own summary sheet. 1. Read each description carefully. 2. Match up each description with the correct cell. 3. Copy each cell picture into your jotter 4. Using all of the descriptions complete your table with a general function for each of the cell parts you have identified. 5. Complete the table by stating which of the cell parts are present in each cell type. You have finished the cell race only when every member of the group has completed their own diagram and table and this has been checked by your teacher so assign group tasks wisely and remember to include everybody. 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 21
Animal Cell Animal cells are bounded by a cell membrane that controls entry and exit of substances. The cytoplasm is the factory part of the animal cell in which chemical reactions take place to manufacture various substances. The nucleus holds the DNA molecules (chromosomes) that are composed of sections called genes. Gene code for the making of proteins that control the activity of the cell. Embedded in the cytoplasm are mitochondria- sausage shaped structures with a smooth outer membrane and a folded inner membrane. It is in the mitochondria that aerobic respiration (respiration that uses oxygen) takes place. Also in the cytoplasm of animal cells free or attached to membranes are ribosomes- small spherical structures that are where protein molecules are created using instructions supplied from the DNA in the nucleus. 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 22
Plant Cell Plant cells are bounded by a cell wall made of cellulose fibres that forms a rigid box that although permeable to all but the largest molecules provides support for the cell and the plant as a whole. To the inside of the cell wall is the cell membrane that controls entry and exit of substances and is composed of proteins and phospholipids. The cytoplasm is the factory part of the plant cell in which chemical reactions take place to manufacture various substances. The nucleus holds the DNA molecules (chromosomes) that are composed of sections called genes. Genes code for the making of proteins that control the activity of the cell. Embedded in the cytoplasm are mitochondria- sausage shaped structures with a smooth outer membrane and a folded inner membrane. It is in the mitochondria that aerobic respiration (respiration that uses oxygen) takes place. Also in the cytoplasm of plant cells free or attached to membranes are ribosomes- small spherical structures that are where protein molecules are created using instructions supplied from the DNA in the nucleus. Chloroplasts are the site of photosynthesis in green plant cells. Vacuoles are fluid filled sac containing cell sap which are important in controlling water balance within the cell. 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 23
Fungal Cell Fungal cells are bounded by a cell wall made of chitin that forms a rigid box that provides support for the cell. To the inside of the cell wall is the cell membrane that controls entry and exit of substances and is composed of proteins and phospholipids. The cytoplasm is the factory part of the fungal cell in which chemical reactions take place to manufacture various substances. The nucleus is the control centre of the cell. It holds the DNA molecules (chromosomes) that are composed of sections called genes. Gene codes for the making of proteins that control the activity of the cell. Embedded in the cytoplasm are mitochondria- sausage shaped structures with a smooth outer membrane and a folded inner membrane. It is in the mitochondria that aerobic respiration (respiration that uses oxygen) takes place.Also in the cytoplasm of fungal cells free or attached to membranes are ribosomes- small spherical structures that are where protein molecules are created using instructions supplied from the DNA in the nucleus. Vacuoles are fluid filled sac containing cell sap which are important in controlling water balance within the cell. 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 24
Bacterial Cell Bacterial cells are bounded by a cell wall made of peptidoglycan that forms a rigid box that provides support for the cell. To the inside of the cell wall is the cell membrane that controls entry and exit of substances and is composed of proteins and phospholipids. The cytoplasm is the factory part of the bacterial cell in which chemical reactions take place to manufacture various substances. In a bacterial cell the DNA is free in the cytoplasm usually in one large mass. The DNA is composed of sections called genes. Genes code for the making of proteins that control the activity of the cell. In bacterial cells smaller circles of DNA called plasmids are found. Plasmids are freely exchanged between bacterial cells and are now used in genetic engineering . Also free in the cytoplasm of bacterial cells are ribosomes- structures that are where protein molecules are created using instructions supplied from the DNA. 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 25
In animal cell? In plant cell? In fungal cell? In bacterial cell? Structure Function Holds cell contents and controls entry and exit of substances. cell membrane Yes Yes Yes Yes cytoplasm Cell s factory chemical reactions occur here. Contains DNA which holds the information to make proteins which control the activity of the cell. Site of aerobic respiration. Yes Yes Yes Yes nucleus Yes Yes Yes No mitochondrion Yes Yes Yes No ribosome Manufacture of protein using instructions from DNA. Yes Yes Yes Yes cell wall Yes- cellulose Yes- chitin Yes- Rigid box gives organism support. No peptidoglycan vacuole Fluid filled sac which helps the cell No Yes Yes No chloroplast Site of photosynthesis where carbohydrate is made. No Yes No No plasmid No No No Yes Ring of DNA exchanged readily between cells. 26 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a
Unit 1: Cell Biology Ka1.1a Cell ultrastructure and functions. Lesson 3: Organelles/ultrastructure: consolidating the comparison of animal, plant, bacterial and fungal cells. 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 27
Cells have differences in structure Close examination of 4 types of cells sown below show they have some features in common but also differ from one another in other ways. 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 28
Animal Cell Structure 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 29
Example animal cells nerve cell blood cells ciliated epithelial cells sperm and egg cells 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 30
Plant Cell Ultrastructure Cellulose And the structures also found in an animal cell 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 31
Example Plant Cells root hair cells onion epidermal cells xylem cells phloem cells leaf cells 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 32
Fungal Cell Ultrastructure chitin Penicillium notatum This fungus produces penicillin a molecule that is used as an antibiotic Yeast cells, Ferments sugars into alcohol and carbon dioxide, used in baking and brewing Fusarium mycelial cells Is a soil mould (micro fungus) used to make the meat substitute Quorn. Mushroom mycelial cells These allow the fungus to grow, mushrooms can be edible, poisonous or medicinal 6/9/2025 33 Mrs Smith KA1.1a
Bacterial Cell Ultrastructure Peptoglycan Vibrio cholerae Found in contaminated water, damages intestine leading to severe diarrhoea and Mrs Smith KA1.1a Rhizobium Live inside root nodules to fix nitrogen Escherichia coli Often associated with food poisoning, some strains are 6/9/2025 harmless but some are every nasty 34 Mrs Smith potential death
Cell Rap 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 35
The Cell Song 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 36
6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 37
Cell Structure Notes cells All living things are composed of one or more _______ , the basic unit of life. The cells of green plants, animals and fungi have several structures in common, including a ________, and mitochondria. ___________ cells lack a nucleus and store genetic material within strands of free floating DNA and a ________. nucleus Bacterial plasmids Only green plants contain __________, but all cells contain ribosomes, a cell membrane and cytoplasm. chloroplasts The cell s activities are controlled by the nucleus. A plant cell is __________ by the cell wall and its cell _____ is stored in its vacuole. supported sap Bacterial Cells Supported Nucleus Plasmids Chloroplasts Sap 6/9/2025 Mrs Smith KA1.1a 38