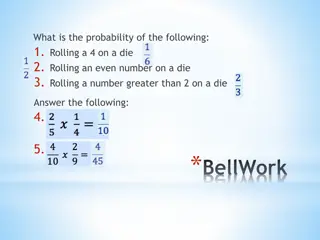Understanding Compound Probability with Fair Number Cube Example
Explore compound probability concepts through a hands-on example involving a fair number cube labeled 1-6. Learn how to calculate the probability of rolling specific numbers on the cube using organized lists, tables, and fractions. Enhance your skills in probability calculations and prepare for more complex scenarios.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Lesson Compound Probability
[OBJECTIVE] The student will find probabilities of compound events using organized lists, tables, tree diagrams, and simulations.
[MYSKILLS] Simple Probability Relative Frequency
[ESSENTIALQUESTIONS] 1. What is compound probability? 2. How does compound probability differ from simple probability? 3. Explain how compound probability can be calculated.
[Warm-Up] Begin by completing the warm-up for this lesson
SOLVE Problem INTRODUCTION TO COMPOUND PROBABILITY
SOLVE Leslie has a fair number cube labeled 1 6, and she is trying to figure out what the chances are of rolling specific numbers on the cube. What is the probability that Leslie will roll a 2 or a 3 on the number cube? S Study the Problem Underline the question. This problem is asking me to find the probability that Leslie will roll a 2 or a 3 on the number cube.
Leslie has a fair number cube labeled 1 6, and she is trying to figure out what the chances are of rolling specific numbers on the cube. What is the probability that Leslie will roll a 2 or a 3 on the number cube? O Organize the Facts Identify the facts. Eliminate the unnecessary facts. List the necessary facts. 6 sides labeled 1 6 Favorable outcome = rolling 2 or 3
L Line Up a Plan Write in words what your plan of action will be. Identify the probability of rolling 2 or 3 with the number cube. Choose an operation or operations. Use fractions to create probabilities.
V Verify Your Plan with Action Estimate your answer. Less than 1 but more than 0. Carry out your plan. Probability of rolling 2 or 3: 2 out of the 6 possible outcomes are favorable. The probability of rolling 2 or 3 is 2 6 1 3 =
E Examine Your Results Does your answer make sense? (Compare your answer to the question.) Yes, because I found the probability Leslie will roll a 2 or 3. Is your answer reasonable? (Compare your answer to the estimate.) Yes, because my answer is between 0 and 1.
Is your answer accurate? (Check your work.) Yes. Write your answer in a complete sentence. The probability of rolling 2 or 3 is 2 6 1 3 =
Extend the SOLVE Problem COMPOUND PROBABILITY WITH A LIST
Extend the SOLVE Problem Compound Probability with a List In the SOLVE Problem on the previous page, we determined that the probability of rolling a 2 or 3 on the number cube was ___. Part of Leslie s math project was to work with the probability of two separate events and determine the probability of certain outcomes. The teacher asked Leslie to add flipping a red and yellow counter as a second event with the desired outcome of a red. ? ?
Extend the SOLVE Problem Compound Probability with a List How many events are involved in this scenario? 2 What are the two events? The probability of rolling a 2 or 3, and then the probability of flipping a red
Extend the SOLVE Problem Compound Probability with a List Explain how we determined the probability of rolling a 2 or 3. We created a fraction with a numerator of the number of favorable outcomes over the number of total possible outcomes. How can we determine the probability of flipping the counter and having it land on red. Create a fraction with the number of favorable outcomes over the total number of possible outcomes.
Extend the SOLVE Problem Compound Probability with a List What is the probability of flipping a counter and having it land on red? 1 out of 2, or ? ? What is another word for all possible outcomes? Sample space
Extend the SOLVE Problem Compound Probability with a List 1 - Red 2 - Red 3 - Red 4 - Red 5 - Red 6 - Red 1 - Yellow 2 - Yellow 3 - Yellow 4 - Yellow 5 - Yellow 6 - Yellow Working in pairs, create a list of the possible outcomes of the first event and then the second event
Extend the SOLVE Problem Compound Probability with a List 1 - Red 2 - Red 3 - Red 4 - Red 5 - Red 6 - Red 1 - Yellow 2 - Yellow 3 - Yellow 4 - Yellow 5 - Yellow 6 - Yellow How many total outcomes are possible? 12
Extend the SOLVE Problem Compound Probability with a List 1 - Red 2 - Red 3 - Red 4 - Red 5 - Red 6 - Red 1 - Yellow 2 - Yellow 3 - Yellow 4 - Yellow 5 - Yellow 6 - Yellow How many outcomes have a 2 or 3 and Red? Circle and List them. Two: 2 Red and 3 Red
Extend the SOLVE Problem Compound Probability with a List 1 - Red 2 - Red 3 - Red 4 - Red 5 - Red 6 - Red 1 - Yellow 2 - Yellow 3 - Yellow 4 - Yellow 5 - Yellow 6 - Yellow What is similar about finding the probability using a list and using the fraction method? You still need to know the total number of outcomes and the favorable outcomes. Any other similarities?
Extend the SOLVE Problem Compound Probability with a List 1 - Red 2 - Red 3 - Red 4 - Red 5 - Red 6 - Red 1 - Yellow 2 - Yellow 3 - Yellow 4 - Yellow 5 - Yellow 6 - Yellow How did we find the probability? We placed the number of favorable outcomes over the total possible outcomes.
Extend the SOLVE Problem Compound Probability with a List 1 - Red 2 - Red 3 - Red 4 - Red 5 - Red 6 - Red 1 - Yellow 2 - Yellow 3 - Yellow 4 - Yellow 5 - Yellow 6 - Yellow What is the probability of rolling a 2 or 3 and then the counter landing on red? ? ??=? Remember to simplify your answers! ?
COMPOUND PROBABILITY WITH A TREE DIAGRAM
Compound Probability with a Tree Diagram Mia is rolling a number cube and pulling marbles out of a bag. The bag contains one red marble, one green marble, and one blue marble. If Mia rolls the number cube and then picks one marble out of the bag, what is the probability that she will roll a number greater than 4 and pick a blue marble? What do you notice about the problem at the top of the page? It is the same problem from the previous page.
Compound Probability with a Tree Diagram We can also determine the probability of multiple events using a second method. Identify the possible outcomes for the toss of the number cube. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
Compound Probability with a Tree Diagram Below each of the possible outcomes for the first event, list the 3 possibilities for the second event. 1 2 3 4 5 6 R G BR G B R G B R G BR G B R G B
Compound Probability with a Tree Diagram Where can you look on the tree diagram to determine the number of possible outcomes? At the bottom row How many outcomes are there? 18 1 2 3 4 5 6 R G BR G B R G B R G BR G B R G B
Compound Probability with a Tree Diagram Which numbers are greater than 4? 5 and 6 How many of the branches represent a possible outcome of a number greater than 4 and a blue marble? Circle them. 2 favorable outcomes 1 2 3 4 5 6 R G BR G B R G B R G BR G B R G B
Compound Probability with a Tree Diagram How do we determine the probability? Place the number of favorable outcomes over the total possible outcomes. What is the probability of rolling a number greater than 4 and choosing a blue marble? ? ??=? ? 1 2 3 4 5 6 R G BR G B R G B R G BR G B R G B
COMPARING SIMPLE AND COMPOUND PROBABILITY
Comparing Simple and Compound Probability Let s review the three events in the graphic organizer. These are all of the events that we used in the previous problems we completed.
Comparing Simple and Compound Probability SOLVE Problem Leslie s Problem Mia s Problem Rolling 2 or 3 Rolling 2 or 3 and Flipping Red Rolling a Number > 4 and picking a blue marble. Event(s) Number of Events Type of Probability Method(s) for Finding Probability
Comparing Simple and Compound Probability In Column 1, how many events were there in the SOLVE problem? 1 What type of probability do we have when there is only one event? Simple
Comparing Simple and Compound Probability SOLVE Problem Leslie s Problem Mia s Problem Rolling 2 or 3 Rolling 2 or 3 and Flipping Red Rolling a Number > 4 and picking a blue marble. Event(s) Number of Events One Type of Probability Simple Method(s) for Finding Probability
Comparing Simple and Compound Probability In Columns 2 and 3, how many events were there to consider? 2 When we have more than one event what do we call this? Compound Probability
Comparing Simple and Compound Probability SOLVE Problem Leslie s Problem Mia s Problem Rolling 2 or 3 Rolling 2 or 3 and Flipping Red Rolling a Number > 4 and picking a blue marble. Event(s) Number of Events One Two Two Type of Probability Simple Compound Compound Method(s) for Finding Probability
Comparing Simple and Compound Probability What method did we use to determine the probability in Column 1? Create a fraction of favorable outcomes over total outcomes. What method did we use to determine the probability in Column 2? Create a list of possible outcomes; create a fraction of favorable outcomes over total outcomes.
Comparing Simple and Compound Probability What method did we use to determine the probability in Column 3? Create a list of possible outcomes and a tree diagram; create a fraction of favorable outcomes over total outcomes. Record the methods in the graphic organizer.
Comparing Simple and Compound Probability What is similar between the simple probability scenario and the compound probability scenario? In both cases, we still found the favorable outcomes over the total outcomes.
Comparing Simple and Compound Probability What are some differences between scenarios with simple and compound probability? Compound probabilities involve more than one event, and we found it helpful to use lists and tree diagrams to help us find all of the favorable outcomes as well as all of the possible outcomes. Now, let s complete the next SOLVE problem.
SOLVE Problem COMPOUND PROBABILITY
SOLVE Lashelle is playing a game where she must spin a spinner and roll a die. The spinner contains three equal sections colored blue, red and yellow. The die has eight sides labeled 1 8. What is the probability that when Lashelle spins she will not land on blue and will roll a number 5 or greater? S Study the Problem Underline the question. This problem is asking me to find the probability of not spinning blue and rolling a number 5 or greater.
Lashelle is playing a game where she must spin a spinner and roll a die. The spinner contains three equal sections colored blue, red and yellow. The die has eight sides labeled 1 8. What is the probability that when Lashelle spins she will not land on blue and will roll a number 5 or greater? O Organize the Facts Identify the facts. Eliminate the unnecessary facts. List the necessary facts. 3 equal sections: blue, red and yellow 8-sided die labeled 1 8.
L Line Up a Plan Write in words what your plan of action will be. Create a tree diagram showing all of the outcomes of the two events and then find the favorable outcomes and the possible outcomes. Choose an operation or operations. Create a fraction with favorable outcomes over total outcomes.
V Verify Your Plan with Action Estimate your answer. More than 0, but less than one-half Carry out your plan. Blue Red Yellow 78 23 4 1 1 78 1 78 23 23 6 6 6 5 4 5 5 4 8 favorable outcomes, 24 total: ? ?? = ? ?
E Examine Your Results Does your answer make sense? (Compare your answer to question.) Yes, because I found the probability of not spinning blue and rolling a number 5 or greater. Is your answer reasonable? (Compare your answer to the estimate.) Yes, because I estimated that the probability would be less than one-half but more than 0.
Is your answer accurate? (check your work.) Yes. Write your answer in a complete sentence. The probability of not spinning blue and rolling a number 5 or greater is ? ?.
Extend the SOLVE Problem MULTIPLICATION WITH COMPOUND PROBABILITY
Extend the SOLVE Problem Multiplication with Compound Probability What is the first event for Lashelle s game scenario? Not spinning blue on the spinner. What is the number of favorable outcomes for the first event? 2