Understanding Context Switching in Operating Systems
Explore the concept of context switching in operating systems, including processes, threads, hardware registers, and control blocks. Learn about practical examples in Linux and Windows environments for process management.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
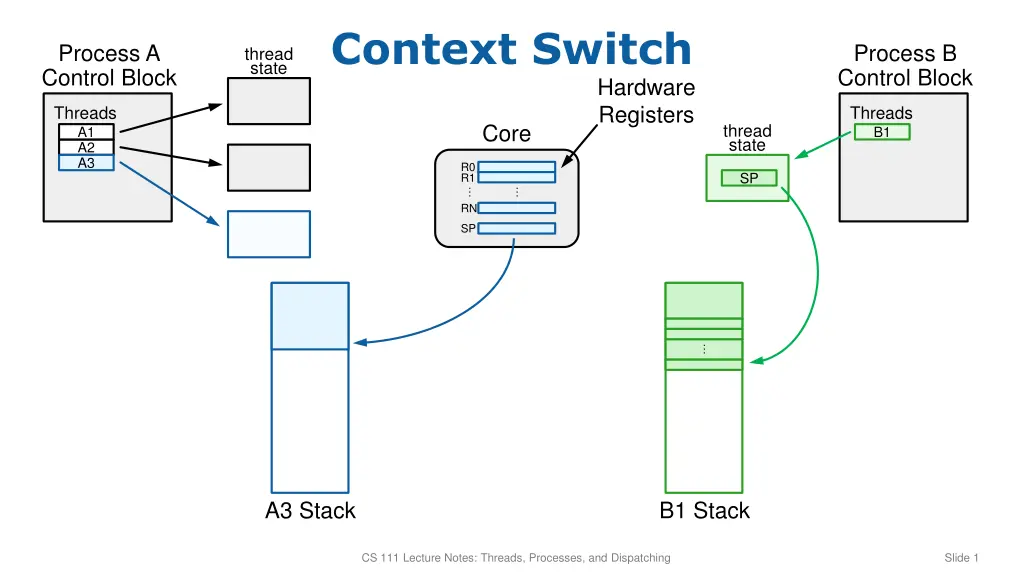
Context Switch Process A Control Block Process B Control Block thread state Hardware Registers Threads Threads Core thread state A1 B1 A2 A3 R0 R1 SP RN SP A3 Stack B1 Stack CS 111 Lecture Notes: Threads, Processes, and Dispatching Slide 1
Context Switch Process A Control Block Process B Control Block thread state Hardware Registers Threads Threads Core thread state A1 B1 A2 A3 R0 R1 SP RN SP Saved Registers (all but SP) A3 Stack B1 Stack CS 111 Lecture Notes: Threads, Processes, and Dispatching Slide 2
Context Switch Process A Control Block Process B Control Block thread state Hardware Registers Threads Threads Core thread state A1 B1 A2 A3 R0 R1 SP RN SP SP A3 Stack B1 Stack CS 111 Lecture Notes: Threads, Processes, and Dispatching Slide 3
Context Switch Process A Control Block Process B Control Block thread state Hardware Registers Threads Threads Core thread state A1 B1 A2 A3 R0 R1 SP RN SP SP A3 Stack B1 Stack CS 111 Lecture Notes: Threads, Processes, and Dispatching Slide 4
Context Switch thread state Hardware Registers Threads Threads Core thread state A1 B1 A2 A3 R0 R1 RN SP Process A Control Block Process B Control Block SP A3 Stack B1 Stack CS 111 Lecture Notes: Threads, Processes, and Dispatching Slide 5
Linux Fork/Exec Example int pid = fork(); if (pid == 0) { execvp( ls , argv); } else { waitpid(pid, &status, options); }; Child process Parent process CS 111 Lecture Notes: Threads, Processes, and Dispatching Slide 6
Windows Process Creation BOOL CreateProcess( LPCTSTR lpApplicationName, LPTSTR lpCommandLine, LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpProcessAttributes, LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpThreadAttributes, BOOL bInheritHandles, DWORD dwCreationFlags, LPVOID lpEnvironment, LPCTSTR lpCurrentDirectory, LPSTARTUPINFO lpStartupInfo, LPPROCESS_INFORMATION lpProcessInformation ); WaitForSingleObject(lpProcessInformation->hProcess, INFINITE); CS 111 Lecture Notes: Threads, Processes, and Dispatching Slide 7