Understanding Decimals and Place Value
Explore the concept of decimals and place value, including identifying decimal types, reading decimals, dealing with zeros after the decimal point, understanding mixed decimals, and practicing decimal exercises. Find information on determining decimal names based on the number of decimal places and recognizing the position of digits in a decimal number. Enhance your knowledge and skills with clear explanations and examples in this informative content.
Uploaded on Apr 16, 2025 | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 1.2 PLACE VALUE WITH DECIMALS
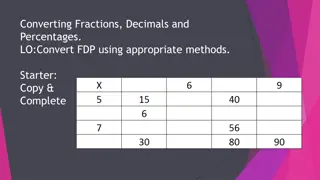
How do I know what kind of decimal it is? The name of a decimal is determined by the number of places to the right of the decimal point Number of Places Decimal Name Example 1 tenths 0.7 2 hundredths 0.05 3 thousandths 0.016
What are mixed decimals? Mixed decimals are numbers with both whole numbers and decimals The name of a whole number is determined by the number of places to the left of the decimal point In the number 128.765, 1 is in the hundreds place, 2 is in the tens place, 8 is in the ones place, 7 is in the tenths place, 6 is in the hundredths place, and 5 is in the thousandths place
How do you read decimals? To read a decimal correctly, first find the decimal point Whole numbers are to the left of the decimal point; any numbers to the right of a decimal point form a decimal fraction Say and for the decimal point The decimal 2164.511 is read as two thousand, one hundred sixty-four and five hundred eleven thousandths
Zeros after the decimal point Writing extra zeros after the decimal point does not change the value! The decimals 0.2, 0.20, and 0.200 are equivalent decimals
Practice HERE ARE SOME PRACTICE PROBLEMS IN WHICH I WILL WORK THROUGH WITH YOU TO MAKE SURE THAT YOU UNDERSTAND THE MAIN CONCEPTS COVERED.
Exercise 1 Write the decimals. 1. Five thousandths 2. Ninety-four thousandths 3. Three hundred thirty-six and sixty-nine hundredths
Exercise 2 Write each decimal in words. 1. 7884.011 2. 5592.4 3. 4.203 4. 612.250 5. 10.44
Exercise 3 In what place (on the place value chart) is the underlined digit? Write the answer. 1. 1.475 2. 3.763 3. 7780.215 4. 412.407 5. 902.103
Exercise 4 Write a decimal that has the same number. 1. 0.2 2. 5.51 3. 410.6 4. 753.809
This powerpoint was kindly donated to www.worldofteaching.com http://www.worldofteaching.com Is home to over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This a free site. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching