Understanding Direct and Inverse Proportional Equations
Discover the concepts of direct and inverse proportionality through writing equations. Engage in a mini-lesson using whiteboards to explore relationships between variables and their proportionalities. Practice and reinforce your understanding with provided examples and solutions.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
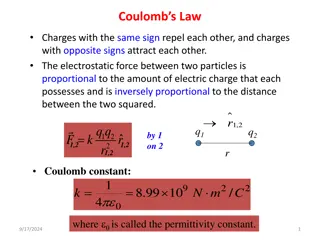
Directly and inversely proportional Use with student whiteboards, or paper Objective- a mini lesson on writing equations based on definitions that use the words directly and inversely proportional
B A = C A is directly proportional to B A is inveresly proportional to C
A= B C A is directly proportional to B A is directly proportional to C
1 In the equation = A BC A is inveresly proportional to B A is inveresly proportional to C
On your whiteboards- practice writing the equations according to the definitions provided.
#1 weight(w) is directly proportional to mass(m) and directly proportional to acceleration due to gravity(g)
#2 Pressure(P) is directly proportional to the Force(F)and inversely proportional to the area(A)
#3 Frequency(f) is inversely proportional to the time(t)
#4 Acceleration(a) is directly proportional to the Force(F) and inversely proportional to the mass(m)
#5 is directly proportional to the , directly proportional to the and inversely proportional to the
#1 weight(w) is directly proportional to mass(m) and directly proportional to acceleration due to gravity(g) w=mg
#2 Pressure(P) is directly proportional to the Force(F)and inversely proportional to the area(A) P=F/A
#3 Frequency(f) is inversely proportional to the time(t) f=1/t
#4 Acceleration(a) is directly proportional to the Force(F) and inversely proportional to the mass(m) a=F/m
#5 is directly proportional to the , directly proportional to the and inversely proportional to the = ( )/
This powerpoint was kindly donated to www.worldofteaching.com http://www.worldofteaching.com is home to over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a completely free site and requires no registration. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching.