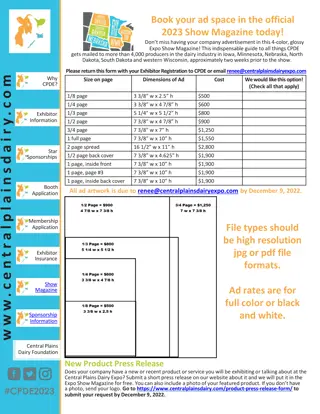
Understanding DSL Technology: Architecture, Protocols & Flavors
Explore the world of DSL technology - from its architecture and protocols to the different types and configurations available. Learn how DSL works, its benefits, and troubleshooting methods for DSL modems. Discover the evolution of DSL versions and comparisons to make informed decisions.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Internet Architecture & Protocol DSL & its Flavors
Todays Agenda Intro to DSL How DSL Works Types of DSL DSL CPE DSLAM B-RAS DSL Modem Configurations Troubleshooting of DSL Modem DSL Service Providers in World
DSL Digital Subscriber Lope Allow transmission of information over existing copper lines PSTN Network ISDN Network DSL over PSTN Always Connected High Bandwidth Fast Speed Voice, Video & Data Transmission
DSL Digital Data Transmission High Speed Network Voice, Video and Data Communication Benefit of 25Khz Above Frequency of PSTN Upstream & Downstream Channels Traditional PSTN Infrastructure dependent
DSL Digital Subscriber Lope Network Existence
How DSL works ? DSL Modulation Guard Band
DSL Modulation / DMT Discrete Multitone Method of Conversion Digital data into Frequencies Splits value of frequencies into smaller sub-channels Method of Frequency Division Multiplexing ADSL1 and ADSL2 = 256 Sub-Channels ADSL2+ = 512 Sub-Channels
How DSL works ? ADSL - DMT
How DSL works ? DSL Versions and Comparison Downstre am Start Downstre am Tones ADSL Type ADSL Standard Speed Up to Maximum Frequency Upstream Start Upstream Tones Total BINs ADSL 1 G.992.1 8 Mbps 1.1 MHz 25 kHz 6-31 142.3 kHz 33-255 256 G.992.3 ADSL 2 12 Mbps 1.1 MHz 25 kHz 6-31 142.3 kHz 33-255 256 ADSL 2+ G.992.5 24 Mbps 2.2 MHz 25 kHz 6-31 142.3 kHz 33-511 512
How DSL works ? ADSL Versions and Comparison
DSL Digital Subscriber Lope Network Existence
DSL CPE Customer Premises Equipment Customer Side Device Sync with the DSLAM Connect with the RAS for Internet Services Username / Password
DSL CPE Customer Premises Equipment
DSL CPE Customer Premises Equipment
DSL CPE ADSL Values for Better Performance Faculty of Information Technology | SABAC
SNR Margin Signal to Noise Ratio SNR = Signal Value / Noise Value High SNR = Stable Connection & Less Errors 1. 6dB. or below = Bad and will experience no line synchronization and frequent disconnections 7dB-10dB. = Fair but does not leave much room for variances in conditions. 11dB-20dB. = Good with little or no disconnection problems 20dB-28dB. = Excellent 29dB. or above = Outstanding 2. 3. 4. 5.
Line Attenuation Loss of Signal over Distance Distance Cabling Joints PSTN Network 1. 20bB. and below = Outstanding 2. 20dB-30dB. = Excellent 3. 30dB-40dB. = Very Good 4. 40dB-50dB. = Good 5. 50dB-60dB. = Poor and may experience connectivity issues 6. 60dB. and above = Bad and will experience connectivity issues
DSL Service Commissioning DSL Line Quality / LOPE Test
How DSL works ? DSL Network
ADSL Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line SDSL Symmetrical Digital Subscriber Line RADSL Rate Adaptive Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line HDSL High Bit Rate Digital Subscriber Line VDSL Very High Bit Rate Digital Subscriber Line G.SHDSL Single Line High Bit Rate Digital Subscriber Line 21
ADVANTAGES The primary advantage of DSL is the speed. Independent service Customers have dedicated lines. Good for "burst" traffic patterns. Always On Does not require new wiring DSL available in multiple speeds to meet your requirement Offers simultaneous data and voice capability DISADVANTAGES Not available for everyone. Difficult to install Expensive Distance dependence 22
Summary Intro to DSL How DSL Works Types of DSL DSL CPE DSLAM B-RAS DSL Modem Configurations Troubleshooting of DSL Modem DSL Service Providers in World
Recommended Reading Search Google for ADSL
Assignment - 1 Design a fully functional ADSL Setup from user to ISP Including Home PC ADSL Modem PSTN Exchange DSLAM RAS Internet Cloud Explain Diagram in Bullets as Well