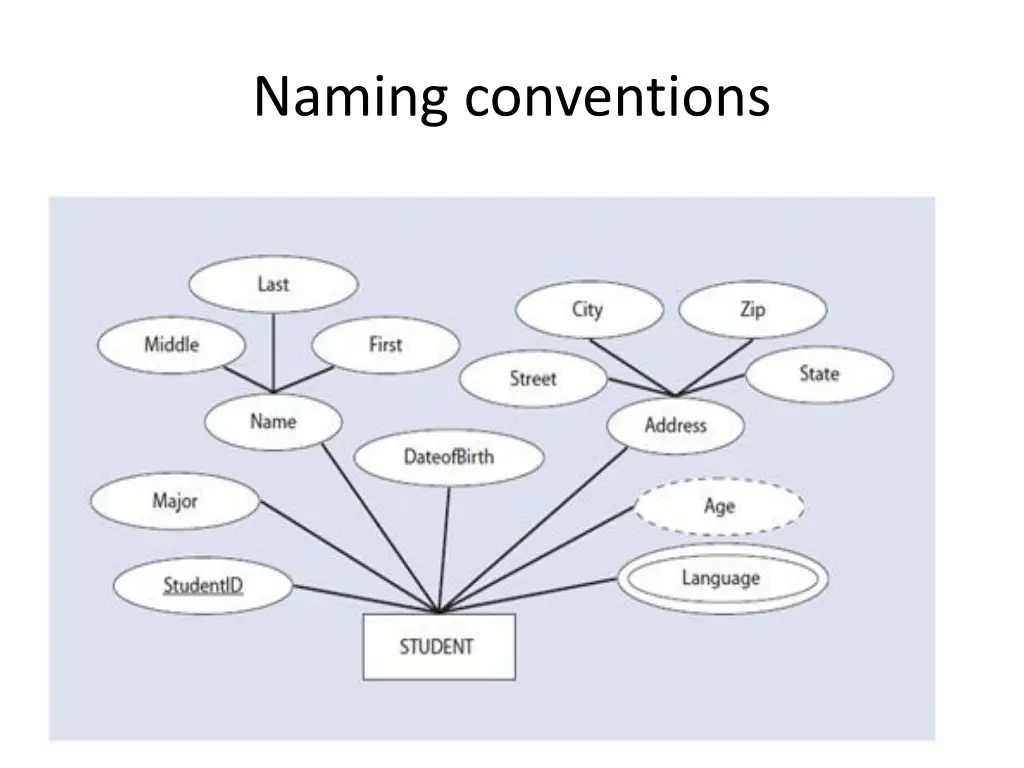
Understanding Entity Relationships and Naming Conventions in Database Schema Design
Explore the concepts of weak and strong entities, entity types, relationships, and degrees in database schema design. Learn how to distinguish between different types of entities and their dependencies in a relational database model.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
weak and strong entity Strong Entity: A strong entity is not dependent of any other entity in the schema. A strong entity will always have a primary key. Strong entities are represented by a single rectangle. The relationship of two strong entities is represented by a single diamond. Various strong entities, when combined together, create a strong entity set.
Weak Entity: A weak entity is dependent on a strong entity to ensure the its existence. Unlike a strong entity, a weak entity does not have any primary key. It instead has a partial discriminator key. A weak entity is represented by a double rectangle. The relation between one strong and one weak entity is represented by a double diamond.
entity type and entity set An entity might be An object existence. E.g. a lecturer, a student, a car An object with existence. E.g. a course, a job, a position An Entity Type collection of similar entities An Entity Set is a collection of entities of an entity type at a point of time. with physical conceptual defines a
Relationship Relationship is nothing but an association among two or more entities. E.g., Tom works in sales For example: You are attending this lecture I am giving the lecture Just loke entities, we can classify relationships according to relationship-types: A student attends a lecture A lecturer is giving a lecture. the Chemistry department.
Relationship Set A set of relationships of similar type is called a relationship set. Like entities, a relationship too can have attributes. These attributes are called descriptive attributes.
Degree of a relationship The number of participating entities in a relationship defines the degree of the relationship. the number of an entity type that is connected to a relationship is the degree of that relationship. Binary = degree 2 Ternary = degree 3 n-ary = degree
