Understanding Enzymes: Protein Catalysts in Chemical Reactions
Dive into the world of enzymes, special proteins that accelerate chemical reactions essential for life processes. Discover how enzymes function as protein catalysts, shaping the intricate web of metabolic pathways within living organisms.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
DO NOW What do you remember about enzymes??
WELCOME TO BOOTCAMP Coach Taylor
WE HAVE 6 WEEKS! 4 weeks review Practice Regents Last 2 weeks will be review of most missed/most important topics IF YOU FOCUS NOW, YOU WILL PASS!!! YOU CAN DO IT!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Living things have MANY metabolic processes that keep them alive.
Living things have MANY metabolic processes that keep them alive. Metabolism is the build-up or break-down of molecules
In other words, living things have many different chemical reactions that keep their cells in homeostasis
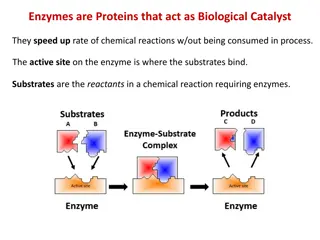
ENZYMES are special proteins that speed up the rate of chemical reactions
ENZYMES are special proteins that speed up the rate of chemical reactions Enzymes are protein catalysts Without enzymes, the chemical reactions of life would not happen fast enough
Chemical reactions turn reactants into totally different products Each enzyme is designed to work with ONE specific chemical reaction. Each enzyme has a specific shape that fits ONE reactant, also known as the substrate.
Enzymes fit reactants (substates) like a LOCK AND KEY. Only ONE KEY will open a lock Only ONE SUBSTRATE is catalyzed by an enzyme
Enzymes fit reactants (substates) like a LOCK AND KEY. Only ONE KEY will open a lock Only ONE SUBSTRATE is catalyzed by an enzyme ENZYMES HAVE SPECIFIC SHAPES!!!!!
Enzymes build things up, or break things down. An enzyme can turn simple sugars into An enzyme can turn a protein into An enzyme can turn starch into
Enzymes build things up, or break things down. An enzyme can turn simple sugars into carbohydrates An enzyme can turn a protein into amino acids An enzyme can turn starch into glucose
Each enzyme works (functions) in a SPECIFIC temperature range. In general, enzymes work as temperature increases.
Each enzyme works (functions) in a SPECIFIC temperature range. In general, enzymes work faster as temperature increases. If an enzymes goes too far out of its temperature range, it will .
Each enzyme works (functions) in a SPECIFIC temperature range. In general, enzymes work faster as temperature increases. If an enzymes goes too far out of its temperature range, it will LOSE ITS SHAPE and will no longer function! It will
Each enzyme works (functions) in a SPECIFIC temperature range. In general, enzymes work faster as temperature increases. If an enzymes goes too far out of its temperature range, it will LOSE ITS SHAPE and will no longer function! It will DENATURE and will no longer catalyze reactions!
The temperature at which an enzyme works the FASTEST is called the optimum temperature. An enzyme is catalyzing the most reactions possible at the optimum temperature
Each enzyme works in a specific pH range. If an enzyme goes out of it s pH range, it will LOSE IT S SHAPE and will NO LONGER FUNCTION It will denature and will no longer catalyze reactions.
Enzymes in the stomach work in a very acidic pH range. Stomach enzymes would denature in other parts of the body.
ACID NEUTRAL BASE LABEL: 0-6 = ACID 7 = NEUTRAL 8-14 = BASE
How are Enzymes SPECIFIC? They are proteins with specific shapes They catalyze specific reactions They fit a specific substrate They work in specific temperatures only They work in specific pH levels only