Understanding Genetics: Chromosome Theory and Heredity
Explore the fascinating world of genetics through the concepts of chromosome theory, gene linkage, sex-linked traits, sex chromosomes, and inheritance patterns. Discover how these factors influence heredity and genetic disorders in humans.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
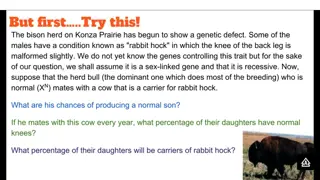
Gene Linkage Where two or more genes occurs on the same chromosome Located in close association with one another Tend to be inherited together Generally do not follow Mendel's law of independent assortment
Sex-Linked Trait Trait that is determined by alleles carried only on a sex chromosome i.e. color blindness, hemophilia
Sex Chromosomes XX in females XY in males In humans the X chromosome is large and the Y chromosome is small In most organisms the sex of the offspring is determined by the gametes from the male parent X chromosomes carry info for both sexes Y chromosomes carries genes related to male development
Sex Chromosomes & Fertilization Gametes Reproductive cells Egg or sperm Contain a single copy of each gene Zygote Sperm and egg unit
Chromosome Information for Humans 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) Autosomes : chromosomes 1-22 Sex Chromosomes: chromosome 23 (determines gender) Normal Male: 46 XY Female 46 XX
Sex-Linked Inheritance Nondisjunction: failure of chromosomes to separate properly during one of the stages of meiosis Produces gametes that contain either an extra copy or no copies of chromosomes Down Syndrome 3 copies of chromosome 21 Turner Syndrome sterile female, lack a second sex chromosome (genotype= 45 XO) Klinefelters Syndrome sterile male, extra sex chromosome (genotype = 47 XXY)
Sex-Linked Disorders Carried on chromosome 23 If found on the X, the males will always have it (if they have the allele) Females must have both X chromosomes with the disorder to show it, otherwise they are carriers
Sex-Linked Disorders (cont.) Colorblindness located on X chromosome Normal: XBXBor XBY Carrier: XBXb Colorblind: XbXbor XbY Hemophilia bleeders disease Muscular Dystrophy gradual wasting of muscles