Understanding Gout and Pseudo Gout: Symptoms and Management
Learn about gout and pseudo gout, two metabolic diseases that mainly affect middle-aged to elderly individuals. Characterized by joint inflammation, these conditions result from increased uric acid levels in the body. Explore symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options for acute and chronic arthritis caused by crystal deposition and tophi formation.
Uploaded on | 2 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Gout and Psudo Gout Dr.Suketha Associate Professor Dept of Kayachikitsa KAHER s Shri BMK AMV Belagavi
Metabolic disease often affect middle aged to elderly men and post menopausal women Result from an increased body pool of urate with hyperuricemia
Characterised by episodic acute and chronic arthritis caused by deposition of MSU crystals in joints and connective tissue tophi and risk for deposition in kidney interstitium or uric acid nephrolithiasis
Acute and chronic arthritis Acute arthritis is the most common early clinical manifestation of gout Initially-one joint is affected But in subsequent episodes polyarticular episodes will develop
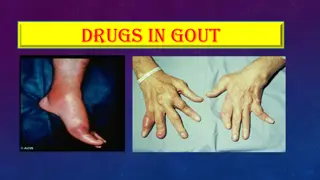
Metatarsophalangeal joint of the first toe often is involved But tarsal joints,ankle and knee also involved In elderly patients or in advanced diseases finger joints may be involved
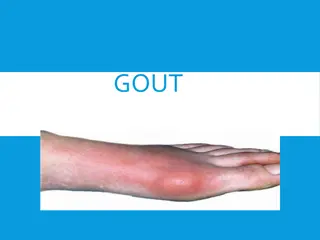
The first episode of acute gouty arthritis frequently begins at night with dramatic joint pain and swelling. Joint rapidly become warm, red and tender with clinical appearance that mimics the cellulites Early attacks tend to subside spontaneously within 3 to 10 days And most patients have interval of varying length with no residual symptoms until the next episode
Precipitating factors Dietary exess Trauma Surgey Excess ethanol ingestion Hypouricaemic therapy Serious medical illness such as MI,stroke
Other symptoms Chronic non symmetric synovitis(confused with RA) Women 5 to 10% cases postmenopausal gout:rare Strong family history Young females: decrease renal urate clearance,renal insufficiency Associated disease in women:osteoarthritis,arterial hypertension that cause mild renal insufficiency and usually are receiving diuretics
Lab Synovial fluid leukocyte count is elevated From 2000 to 60000/uL Apppearance:cloudy(due to leukocytes) Serum uric acid level elevated Excretion of >800 mg of uric acid per 24 h on a regular diet suggest over production of purnes
Urinalysis LFT WBC Lipid Should be obtained to see the possible pathological squeal of gout and other associated disorder requiring treatment.
Ayu Pitta pradhana vatarakta
Acute attack NSAIDs Ice pack application and rest on the joints can be helpful Prednisolone 30-50 mg /d Later gradually tapered the dose Single joint:methylprednisolone 25-50 mg
Amratottara kashaya 15 ml with water 2 spoon Hareetaki churna with guda with guduchi kashaya Kokilaksha 3 part,amrita 2 part,pippali 1 part
Shaddharana tablet Kaishora guggulu Ghritam GTG 20 ml
Virechana with nimbhamrita eranda 2 tsf Pinda taila Madhuyashtadi taila Dhanyamla taial for application Guduchyadi yapana basthi in sever and chronic cases
Dashamula ksheera dhara to reduce the pain) Chyavana prasha Guduchi ksheera kashaya