Understanding Matter and Its Properties
Discover the fundamental concepts of matter, including its definition, types, properties like mass, volume, and states. Explore the differences between physical and chemical changes in matter through engaging visuals and explanations. Dive into the world of matter with this comprehensive guide.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
MATTER MATTERS BY: HARPER, JORDAN
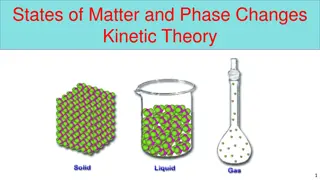
WHAT IS MATTER? Matter is anything that has mass or volume. Everything we see is matter like plants, animals, rocks and a lot more. Matter can be in living and also non-living objects.
WHAT IS VOLUME? Volume is a quantity of three dimensional space occupied by a liquid solid gas common units used to express volume are liters, cubic meters, gallons, millilitres, teaspoons and ounces.
WHAT IS MASS? Mass is a measurement of how much matter is in a object mass is a combination a a total numbers of atoms, and the type of atoms in an object.
CHEMICAL CHANGE New bonds are formed while other bonds are broken resulting in new substances with new properties. Colour Heat, light, and sound A precipitate
PHYSICAL CHANGE Appearance of substances may change, but chemically the substance is the same no new substances are formed. No bonds holding atoms together have been broken and no bonds form. Ripping Grinding, cutting, tearing, melting, freezing, boiling, grinding and Dissolving are examples of physical change
DREAM We could've added more information More pictures Had better ideas Created more problems
DEBRIEF We explained the different sections of matter Could've put more examples of matter and how it works Add more pictures