Understanding Medicare Advantage Plan Data for Improved Healthcare Decision-Making
Explore comprehensive information on Medicare Advantage Plan data, including enrollment details, plan types, quality star ratings, and financial aspects. Learn about the strengths, weaknesses, key variables, and measures associated with MA plan data for strategic insights.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Health Data Bootcamp Breakout Session Medicare Advantage Plan Data Medicare Advantage Encounter Data Speakers: Abigail Barker, PhD RJ Waken, PhD April 23, 2025 1
Agenda (1) More background on the Medicare Advantage Plan Data (2) More background on the Medicare Advantage Encounter Data (3) Q & A For further information: https://www2.ccwdata.org/documents/10280/19002246/ccw-medicare-encounter-data-user-guide.pdf To request data and partner with CAHSPER: https://github.com/CAHSPER/ 2
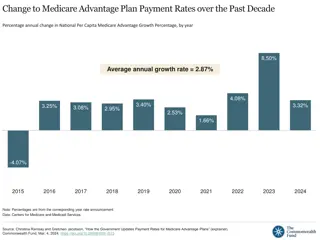
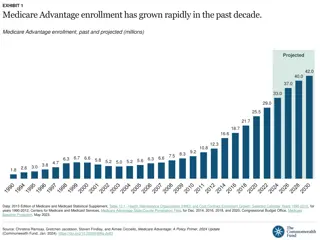
Background on Medicare Advantage Plan Data All Private Insurers Participating in the MA Program at the County Level About 600 contracts, some spanning multiple states, most of which include many different plans Multiple plan types, with composition that has changed over the years and is now predominately Local HMOs, Local PPOs, and Regional PPOs Also includes data on Special Needs Plans of various types Part-D Only plans are also included, but most plans are Part C+D Premium data are available, although many plans are zero-premium to the participant, meaning that the benchmark rate for the county covers the premium entirely Overview Monthly enrollment data are available at the granularity of Contract/Plan/State/County cells < 10 persons are censored Service area of each contract, and overall MA penetration rates, are available monthly by county Landscape files provide more details about plan characteristics Quality star rating data decompose the star ratings into 5 domains and 30+ subdomains Cost and rate data provide more detail about the methods by which payment per enrollee in each county is determined, in addition to available bonuses for high quality
Background on Medicare Advantage Plan Data Strengths All MA issuers and enrollees are included Most files go back to 2007-2008 Data are very clean and easy to merge Counties are coded with FIPS and SSA so can readily merge with other data sources, e.g., rural status Weaknesses Quality star ratings are reported at the contract level Quality star ratings may not be reported if the contract is too new Actual premiums paid by CMS to the plan are not available, so it s not possible to calculate exact costs when issuers bid below the benchmark Key Variables and Measures Contract ID, Organization Name, Plan ID, plan type, enrollment counts, star ratings, contract start date SNP status and additional details, drug benefit type and additional details Bidding benchmarks, risk adjustment, rate calculation data, maximum OOP spending and CS limits
Background on Medicare Advantage Encounter Data Availability Years Available: 2015 2022(ish) Claims delivered approximately 15 months after close (and finalized 6 months later) Available in the VRDC environment Offline use requires cells representing 1 N 10 beneficiaries to be suppressed Overview Files created similarly to FFS RIF data Contains procedure/diagnosis/HCPCS/CPT code info, for example No Hospice data There have been recent changes to hospice care in Medicare no word (so far) on how this will be represented No chronic condition (or similar) data provided 5
Background on Medicare Advantage Encounter Data Key differences from FFS RIF files No costs available Cost information is proprietary information Components allowing standardized cost calculation largely left intact otherwise, ResDAC has recommendations for cost creation Early versions (< 2016) were found to be less complete Led to the creation of crosswalks of high data quality plans More recent research has found that, in some cases, claim representation of services rendered surpassed that represented in FFS RIF files 6
Background on Medicare Advantage Encounter Data Key differences from FFS RIF files (cont) No CMS Certification Numbers/Provider Numbers available Organizational NPIs provided instead Can make linking claims to other common resources, such as the American Hospital Association Data, difficult There is a crosswalk algorithm (and we re in the process of implementing it) Chart Reviews included in Encounter data Chart reviews are a mechanism by which MA plan carriers can add or remove missed DXs to a claim record. Often believed to be a source of over coding to inflate risk 7
Q & A Guide Can you think of any research questions you would like to answer with the Medicare Encounter data? Who is your target study population? What are your dependent and independent variables? What other health and health care variables are you interested in? Other audience questions? 8
Health Data Bootcamp Breakout Session Midwest Health Initiative Regional Commercial Claims Data Warehouse April 23, 2025 Kelci Hannan, PhD, ATC Director, Research & Analytics
Agenda 1. More background on commercial claims data set 2. Deeper dive into the Milliman MedInsight analytical tools 3. Q & A 10
MHIs Data Set Data Elements ICD, CPT, DRG, NDC and J-codes Age, gender, geography (zip) Blinded patient IDs Service and billing provider Date of service (incurred, paid, admit, discharge) Utilization and service units Standardized ( Proxy ) price Strengths Large sample population (average 1.7 million lives/year) Line level detail 12 years of data Zip code can be used to integrate other data (e.g. CDC social vulnerability index, Census data) Limitations Real cost data is not available proxy pricing is used Population changes over time, which can affect ability to track patient care and outcomes No race and ethnicity data Illinois Kansas Missouri 11
Analytical Applications Health Cost Guidelines (HCG grouper) A tool that sorts claims into 5 basic settings (Inpatient, Outpatient, Professional, Prescription Drug, Ancillary) and then further based on procedures and care episodes Example: 1. Setting: 3. Professional 2. Line: P59 - Radiology Office - CT/MRI/PET 3. Detail: P59 Radiology Office PET Imaging PMPM Spending Utilization per 1,000 150 $15.00 Compare cost and utilization at different sites of service (hospital outpatient vs. free standing imaging center) 55 $10.00 100 $7.56 $5.25 30 $5.00 50 80 $6.00 $3.17 46 8 $3.45 $0.83 PET $0.00 4 0 MRI CT MRI CT PET Free-standing clinic HOPD Free-standing clinic HOPD 13
Analytical Applications Evidence-Based Measures (EBMs) Quality metrics developed and maintained by organizations such as the National Quality Forum (NQF), the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ), and the National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA) Potential questions to answer: 1. Is there variation in care quality across different demographics? 2. Is lower care quality correlated with adverse health outcomes (readmission, infections, ED admits) or increased health costs? 14
Analytical Applications Waste Calculator Measures utilization and spending of wasteful and potentially wasteful health care services that are not evidence-based and may lead to unnecessary spending or patient harm Total Spending for Two Highest- Spend Low-Value Services, 2023 An estimated $80 million was spent on low-value opioid prescriptions from 2016 to 2023. $8.2 million Low-value opioid prescriptions have a high risk of patient harm 100% of the time. $3.1 million 85% of the opioid prescriptions filled for non-cancer pain in 2023 were considered low-value. Opioid Prescriptions Coronary Angiography Potential questions to answer: 1. Is there variation in rate of low-value care across different demographics? 2. Are certain providers or facilities more likely to perform low-value care? 15
How could you use the MHI data? Any other questions or comments? 16