Understanding Moments of Inertia and Kinetic Energy in Mechanics
Concepts of moment of inertia, rotational motion, and kinetic energy through scenarios involving bars, balls, and objects rolling down hills. Understand the relationships between mass, length, speed, and energy in various mechanical systems.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
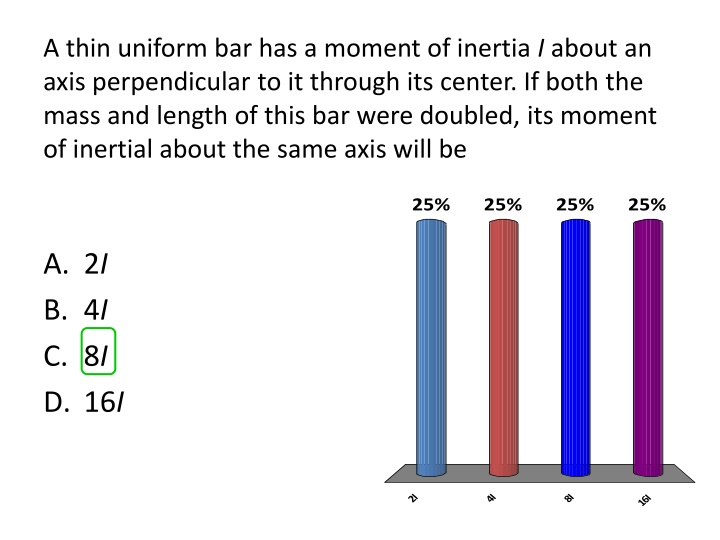
A thin uniform bar has a moment of inertia I about an axis perpendicular to it through its center. If both the mass and length of this bar were doubled, its moment of inertial about the same axis will be 25% 25% 25% 25% A. 2I B. 4I C. 8I D. 16I 2I 4I 8I 16I
A uniform ball rolls without slipping toward a hill with a forward speed V. In which case will this ball go further up the hill? A. There is enough friction on the hill to prevent slipping of the ball. B. The hill is frictionless. C. Conservation of energy implies the ball will roll to the same height for both of the above cases. 33% 33% 33% The hill is frictionless. There is enough friction .. Conservation of energy i...
Four uniform objects have the same mass and diameter are released from rest at the same distance from the bottom of a hill and roll down without slipping. The objects are a solid sphere, solid cylinder, hollow cylinder, and a thin-walled hollow cylinder. Which object will be the first to reach the bottom of the hill? A. Solid sphere B. Solid cylinder C. Hollow cylinder D. Thin-walled hollow cylinder E. They all arrive at the same time! 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% Solid sphere Solid cylinder Hollow cylinder Thin-walled hollow cylinder They all arrive at the sam...
Four uniform objects have the same mass and diameter are released from rest at the same distance from the bottom of a hill and roll down without slipping. The objects are a solid sphere, solid cylinder, hollow cylinder, and a thin-walled hollow cylinder. Determine which of the following statements are correct: A. All the objects have the same forward speed at the bottom of the hill. B. All the objects have the same kinetic energy at the bottom of the hill. C. All the objects have the same rotational kinetic energy at the bottom of the hill. D. All the objects have the same angular velocity at the bottom of the hill. 25% 25% 25% 25% All the objects have the... All the objects have the... All the objects have the... All the objects have the ...
Two point like objects of mass M each are attached to a thin rod of mass M and Length L. The rod and the masses are spinning at a constant rate about an axis perpendicular to that of the rod. What is the kinetic energy of the composite object (rod + 2 point objects)? ML2 2/12 7ML2 2/12 7ML2 2/24 ML2 2/24 5ML2 2/12 7ML2 2/6 ML2 2/3 ML2 2/4 A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H.