Understanding Pox Virus and Its Effects
Learn about the characteristics and effects of the pox virus, including its structure, viability, antigens, growth, and associated diseases such as smallpox, cowpox, and molluscum contagiosum. Explore how the virus can be grown on a chick embryo and the importance of vaccination.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
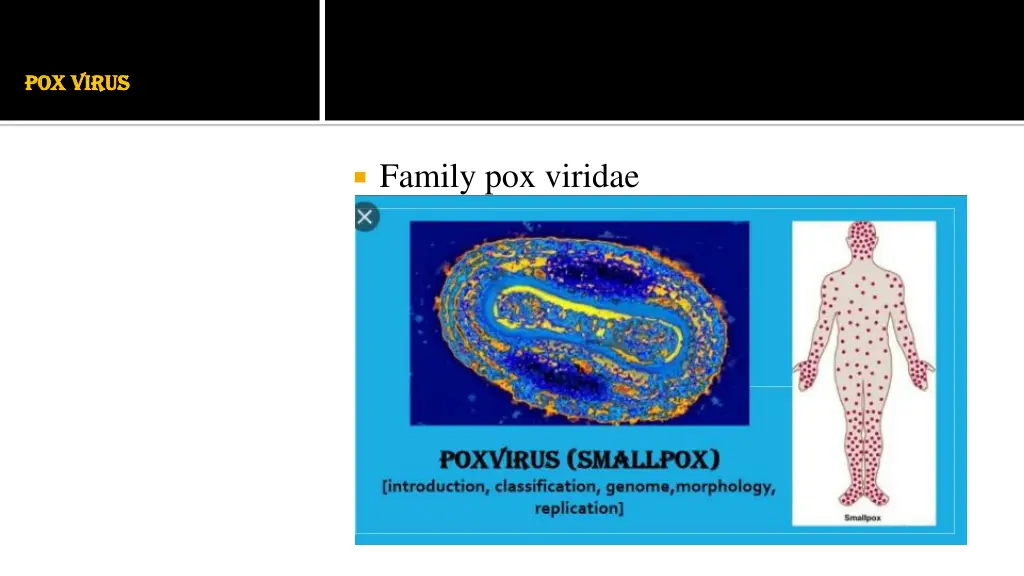
POX VIRUS POX VIRUS Family pox viridae
Brick shaped Largest animal virus Can be seen under light microscope It has biconcave double stranded DNA, surrounded by double layered membrane The envelop is the outermost layer and it surrounds the outer membrane On either side of the DNA is a lens shaped structure called lateral body
May remain viable for months in room temperature In cold it survive for years Inactivated by formalin
Nucleoprotein antigen LS antigen Agglutinogen Haemagglutinin
Grows in chorioallantoic membrane of chick embryo and in tissue culture Both vaccinia and variola produces pocks within 48-72 hrs Variola pocks: small, shiny, white convex, non necrotic and non hemorrhagic Vaccinia pocks: larger, irregular, greyish, flat necrotic and hemorrhagic
Variola: it causes small pox which is irradicated Vaccinia: it is an artificial virus which causes skin infections
Cowpox: it produces ulcers in the udder and causes human infection by milking. The lesions (macules pustules) appears on the hands of the man
Molluscum contagiosym: benign epidermal tumour like lesion that occur only in human. It involves arms, legs, buttocks and genital areas
It can be grown on chick embryo Vaccination