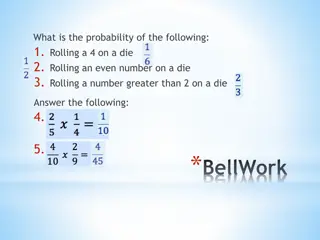Understanding Probability: Concepts and Examples
Explore the fundamental concepts of probability including probability experiments, sample space, and terms like complementary events, independent events, and mutually exclusive events. Dive into examples and calculations to grasp the essence of probability theory.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Probability Probability can be defined as the chance of an event occurring or how likely things are to happen.
Some terminologies Probability experiment: any process that generates a set of data . These data are the outcomes of the experiment. Sample Space: is the set of all possible outcomes of an experiment.
Example 2 Calculate the probability that the outcomes add to give 6 if 2 dice are rolled together. List the sample space: ) 1 , 3 ( SS ) 1 , 1 ( ) 2 , 1 ( ) 3 , 1 ( ) 4 , 1 ( ) 5 , 1 ( ) 6 , 1 ( ) 1 , 2 ( ) 2 , 2 ( ) 3 , 2 ( ) 4 , 2 ( ) 5 , 2 ( ) 6 , 2 ( ) 2 , 3 ( ) 3 , 3 ( ) 4 , 3 ( ) 5 , 3 ( ) 6 , 3 ( = ) 1 , 4 ( ) 2 , 4 ( ) 3 , 4 ( ) 4 , 4 ( ) 5 , 4 ( ) 6 , 4 ( ) 1 , 5 ( ) 2 , 5 ( ) 3 , 5 ( ) 4 , 5 ( ) 5 , 5 ( ) 6 , 5 ( ) 1 , 6 ( ) 2 , 6 ( ) 3 , 6 ( ) 4 , 6 ( ) 5 , 6 ( ) 6 , 6 (
Tree diagrams for SS Use a tree diagram to find the sample space for the experiment of tossing a coin three times (or tossing 3 coins simultaneously).
Independent events Two or more events are independent if the outcome of one is not affected by the other.
Determine whether the following are M.E or not 1) Getting an odd number card and getting an even number card. 2) Getting a 4 and a spade card 3) Getting a head and a tail in one toss of a coin
Exercise A die is rolled once. Find the probability of the following events:
Example How many four digit numbers can be made from the digits 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 0 a) With no restrictions b) If each digit is used only once. Solution: a) ____ ____ _____ ____ 7 possibilities 7 possibilities 7 possibilities7 possibilities Answer: 7 x 7 x 7 x 7 = 2401 numbers
Example If each digit is used only once. Solution: ____ ____ _____ ____ 7 possibilities 6 possibilities 5 possibilities4 possibilities Answer: 7 x 6 x 5 x 4 = 840 numbers
Exercise 2 adults take their 3 children to the cinema, how many sitting arrangements can be made if the adults need to sit on either ends of the children. _A____ __C__ _C___ __C__ __A___ Answer: 2x 3x 2x1 x 1 = 12 arrangements
Conditional Probability Read as conditional probability of B given A Read as conditional probability of A given B