Understanding Sale of Goods Act 1930
Learn about the Sale of Goods Act 1930, which governs contracts of sale of goods, essential elements of a contract of sale, types of goods, conditions, warranties, and the rights of an unpaid seller. Explore the different aspects and implications of this crucial legislation.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
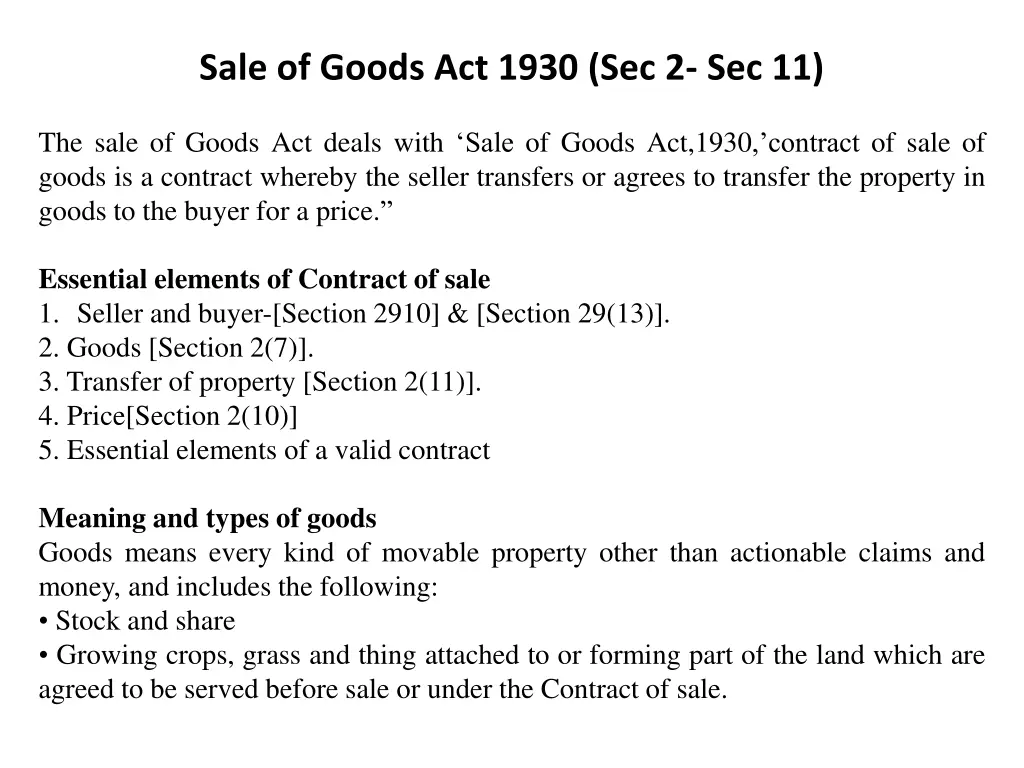
Sale of Goods Act 1930 (Sec 2- Sec 11) The sale of Goods Act deals with Sale of Goods Act,1930, contract of sale of goods is a contract whereby the seller transfers or agrees to transfer the property in goods to the buyer for a price. Essential elements of Contract of sale 1. Seller and buyer-[Section 2910] & [Section 29(13)]. 2. Goods [Section 2(7)]. 3. Transfer of property [Section 2(11)]. 4. Price[Section 2(10)] 5. Essential elements of a valid contract Meaning and types of goods Goods means every kind of movable property other than actionable claims and money, and includes the following: Stock and share Growing crops, grass and thing attached to or forming part of the land which are agreed to be served before sale or under the Contract of sale.
Types of Goods [Section 6] 1.Existing Goods Specific Goods[Section 2(14)]: Ascertained Goods: Unsanctioned Goods: 2. Future Goods[Section 2(6)] 3. Contingent Goods [Section 6(2)] Price Of Goods[Section 2(10)] Price- means the money consideration for a sale of good. Modes of determining Price [Section 9(1)] It may be fixed by the contract or It may be left to be fixed in an agreed manner It may be determined by the course of dealing between the parties.
Conditions and Warranties Meaning of Conditions [Section 12(2)] - A condition is a stipulation Which is essential to the main purpose of the contract The breach of which gives the aggrieved party a right to terminate the contract. Meaning of Warranty[Section 12(3)]- A warranty is a stipulation Which is collateral to the main purpose of the contract The breach of which gives the aggrieved party a right to claim damages but not a right to reject goods and to terminate the contract. In a contract of sale of goods, conditions and warranties may be express or implied 1. Express Conditions and Warranties. These are expressly provided in the contract. For example, a buyer desires to buy a Sony TV Model No. 2020.Here,model no. is an express condition. In an advertisement for Khaitan fans, guarantee for 5 years is an express warranty. 2
Implied Conditions and Warranties -These are implied by law in every contract of sale of goods unless a contrary intention appears from the terms of the contract. Implied Conditions 1. Conditions as to title [ Section 14 (a)] 2. Condition in case of sale by description [Section 15] 3. Condition in case of sale by sample [Section 17] 4. Condition in case of sale by description and sample [Section 15] 5. Condition as to quality or fitness [Section 16(1)] 6. Condition as to merchantable quality[Section 16(2)] 7. Condition as to wholesomeness 8. Conditions implied by custom [Section 16(3)] Implied warranties a)Warranty as to quiet possession [Section14(b)] b)Warranty of freedom from encumbrances [Section 14(c)]
Unpaid seller The seller of goods is deemed to be an unpaid seller - When the whole of the price has not been paid or tendered When a bill of exchange or other negotiable instrument(such as cheque) has been received as conditional payment, and it has been dishonoured[Section 45(1)]. Rights of an Unpaid Seller [Section 46-52,54-56,60-61] -classified under the following two categories: 1.Rights against the goods 2.Rights against the buyer personally
1.Rights against the goods I. Where the property in the goods has passed to the buyer a) Right of Lien [Section 47,48 and 49]-The right of lien means the right to retain the possession of the goods until the full price is received. b) Right of Stoppage of Goods in Transit . c) Right of Resale[Section 46(1) and 54] II Rights against the goods where the property in the goods has not passed to the buyer a) Right of withholding delivery[Section 46(2)] 2.Rights of Unpaid Seller against the Buyer Personally 1. Suit for price (Sec. 55). 2. Suit for damages for non-acceptance (Sec. 56) 3. Suit for Interest [Section 61(2)]
RIGHTS AND DUTIES OF BUYER AND SELLER RIGHTS OF THE BUYER 1. Right to have delivery of goods 2. Right to Reject 3. Right to Cancel 4. Right to claim damages 5. Right to Examine 6. Right to sue for performance 7. Right to take insurance 8. Right to sue for recovery of price 9. Right to claim interest DUTIES OF THE BUYER 1. Duty to accept goods 2. Duty to pay the consideration 3. Duty to pay damages 4. Duty to perform agreement 5. Duty to apply for goods
RIGHTS OF THE SELLER 1. Right to have acceptance of goods 2. 2. Right to claim loss 3. 3. Right to receive the price of goods 4. 4. Right to take legal action 5. 5. Right to interest DUTIES OF THE SELLER 1. 1. Duty to Deliver goods 2. 2. Duty to put goods in deliverable state 3. 3. Duty to refund the price 4. 4. Duty to pay interest 5. 5. Duty to pay damages for breach of warranty






















