Understanding Sampling Techniques in Research Studies
Learn about different types of sampling methods including non-probability and probability sampling techniques such as simple random sample, systematic random sample, stratified random sampling, and cluster sampling. Explore why sampling is crucial in research, and how it helps in saving time and cost while ensuring representative results.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
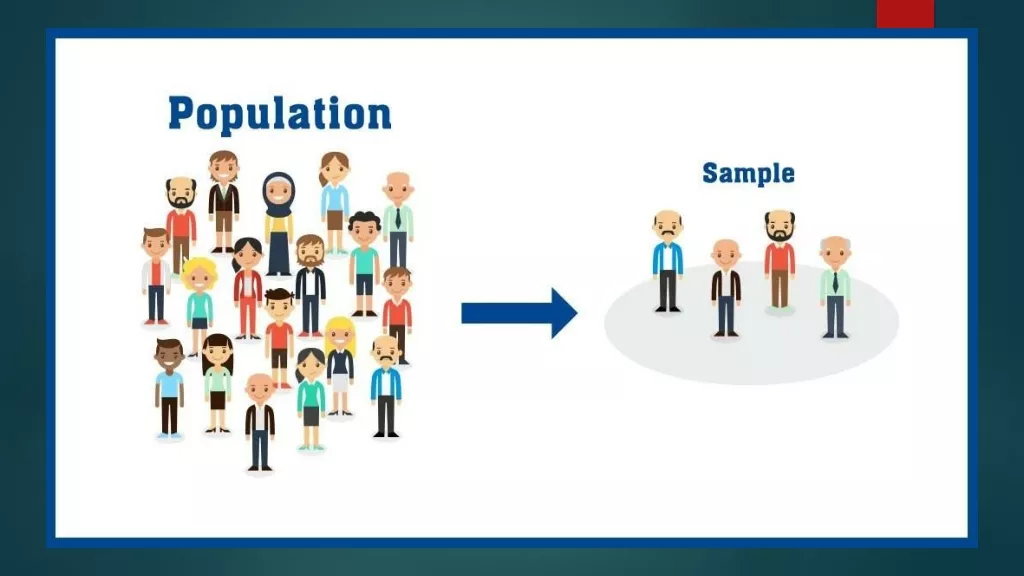
Sample Surveys and Sampling Techniques
Why Sample? The two main reasons that apply to most research are: Time Cost
Types of sampling Non- Probability Sampling Some elements of population have no chance of selection where the probability of selection can't be accurately determined. Ex convenience Sample Probability Sampling or Every unit in the population has a non zero probability of being selected in the sample, and this probability can be accurately determined. Probability samples are the only type of samples where the results can be generalized from the sample to the population.
Types of sampling methods Non Probability Probability sampling Sampling Systematic Random Sample Cluster Sample Simple random Sample Ex. Convenience Sample Stratified Sample
Simple random Sample All samples selected of equal size (n ) has the same probability of being chosen, and each unit has an equal chance of being chosen There are many ways to obtain a simple random sample. One way is that the researcher must prepare a complete list including all members of the population ( Sampling Frame) then each member in the population is given a number. These numbers must be unique. By using a Table of Random Digits the units are chosen from the sample ie Population members having the selected numbers are included in the sample.
Systematic Random Sample We first randomly select one member from the first K units, then every kth member ( ie we add k to the first random digit) is chosen note : k refers to the ratio of the population to the sample k= N/n It is important that the starting point is not automatically the first in the list, but is instead a randomly chosen number from within the first to the kth element in the list
Stratified Random Sampling Divide the population into strata ( sub groups ) that are mutually exclusive , then an independent simple random sample is drawn from each of these strata (ex. You can divide the University students into the different faculties and then from each faculty chose a sample.)
Cluster Sampling The whole population is divided into groups called clusters. Then a sample of these clusters is picked and all the elements in the cluster are included in the final sample. Cluster sampling is frequently employed when the researcher is unable to compile a comprehensive list of all the elements in the population of interest.