Understanding Soil Properties and Impacts on Agriculture
Learn about the importance of soil, how it forms, and its key properties like porosity and permeability. Discover how land use can influence soil erosion and make recommendations for sustainable agricultural practices. Understand soil components, water flux, and the effects of soil erosion due to runoff.
Uploaded on | 2 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
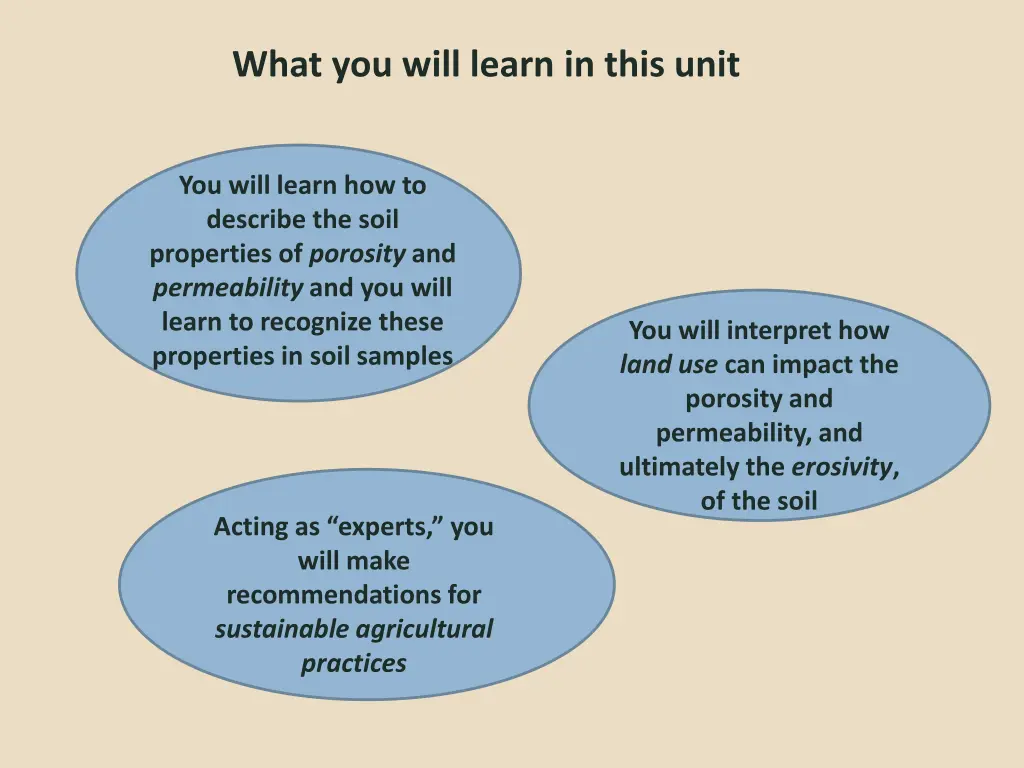
What you will learn in this unit You will learn how to describe the soil properties of porosity and permeability and you will learn to recognize these properties in soil samples You will interpret how land use can impact the porosity and permeability, and ultimately the erosivity, of the soil Acting as experts, you will make recommendations for sustainable agricultural practices
What is soil? Soil is a mixture of: minerals water air organic matter organisms It plays many roles, including: providing a medium in which plants (including our food) and a large number of the microorganisms on earth grow filtering our water interacting with the atmosphere to cycle important substances in and out of the air serving as engineering media for construction of foundations, roadbeds, dams, and buildings Soil is important to us simply because life as we know it would not exist without it! Source: Author
What is soil? How does soil form? Every soil originally formed from parent material: a deposit at the Earth's surface. The material could have been bedrock that weathered in place or smaller materials carried by flooding rivers, moving glaciers, or blowing winds. Soils form in differently in different places because of CLORPT: climate, organisms, relief (landscape), parent material, and time. Over time, sun, water, wind, ice, and living creatures help transform, or change, the parent material into soil. As a soil ages, it changes because its components minerals, water, air, and organic matter constantly change. Important characteristics of soil that indicate how it may behave: Texture (is it sand, silt, clay, or a mixture of these?) Structure (peds) Color
On average, soil contains these components
Water Flux The flux (J), or flow of water, through this soil is the quantity of water (Q) moving through a cross-sectional area (A) per unit of time (t) Source: USDA NRCS In the How Full is Full activity, we are looking at flux as a reflection of the permeability of our soil samples. The formula above can be used to calculate the actual flux.
Soil Erosion Due to Runoff Source: http://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detailfull/la/home/?cid=stelprdb1097517
Slake test Photo: U.S. Dept. of the Interior, Bureau of Land Management http://www.blm.gov/wo/st/en/prog/more/soil2/soil2/indicators.html