Understanding Species Distribution Models and Their Applications
Explore the concept of Species Distribution Models (SDM) and their significance in characterizing suitable environments for species, identifying potential areas for disease outbreaks, examining niche evolution, and more. Discover the approaches, data input requirements, general steps, and tips for successful implementation of SDM.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
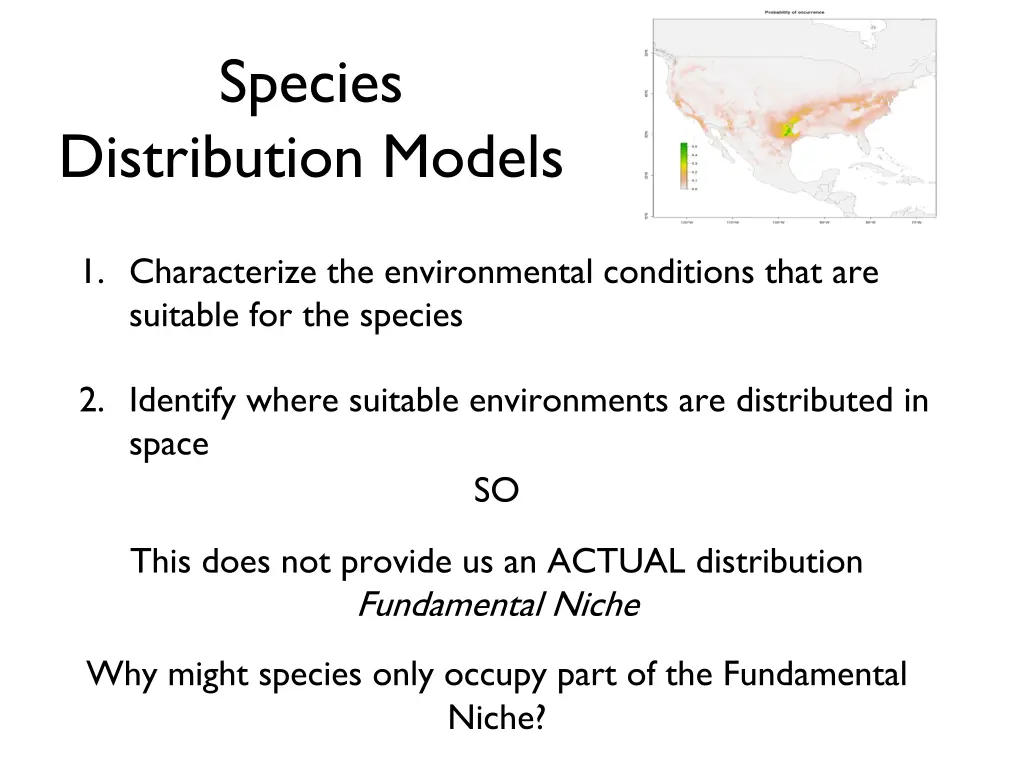
Species Distribution Models 1. Characterize the environmental conditions that are suitable for the species 2. Identify where suitable environments are distributed in space SO This does not provide us an ACTUAL distribution Fundamental Niche Why might species only occupy part of the Fundamental Niche?
Utility of SDM Identifying potential areas for disease outbreak Examine niche evolution Inform taxonomy Conservation reintroduction of species identify priority sites for conservation projecting spread of invasive species and disease
SDM Approaches Mechanistic Models Correlative Models Use physiologically limiting mechanisms to determine ability of species to live in an environment Estimates environmental conditions suitable for a species by associating species occurrence records with environmental data that likely will affect species physiology and probability of persistence Required: detailed understanding of the physiological response of species to environmental factors Required: Species occurrence records Environmental variables Algorithms to connect the two
Data input for Correlative Models Environmental Data Used to define the space based on environmental variables (climate, topography, soil type, land cover) Set of environmental conditions within which a species can survive and persist Biological or Geographical Data Actual locality data or known distribution of species Where to get it! iNaturalist GBIF eButterfly Museum/Herbarium Records GPS data from field work Where to get it! BioClim WorldClim
General Steps in SDM 1. Study area is modeled as a raster map composed of grid cells at a specified resolution (for us, North America excluding Mexico) 2. Dependent variables = occurrence records (from iNat) 3. Suite of environmental variables (obtained from BioClim or WorldClim) and used to characterize each cell 4. Function of the environmental variables is generated to predict the degree to which each cell is suitable for the species = +
Tips for Success Today No spaces in file names. NoSpacesInFileNames.doc CaPitALIzatiON matters Follow the directions carefully! Keep all members of the group at the same step - help each other when need be! Only CAN-DO attitudes:) Patience. Goal: Complete SP-2 Assignment using instructions handed out today






















