Understanding State Variables in Electrical Physics
Explore the key state variables including electric field strength, potential difference, current, cross-sectional area, and more in electrical physics. Learn about their significance and relationships in circuits and conductors.
Uploaded on | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
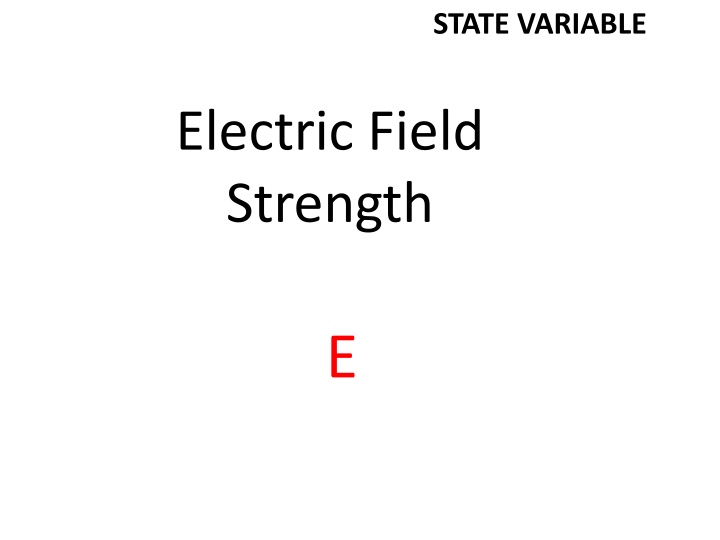
STATE VARIABLE Electric Field Strength E
STATE VARIABLE Potential Difference V
STATE VARIABLE Current I
STATE VARIABLE Cross-sectional area of a wire A
STATE VARIABLE Length of a conductor L
STATE VARIABLE Resistivity
STATE VARIABLE Electrostatic constant k
STATE VARIABLE Electrical energy W
STATE VARIABLE Power P
STATE VARIABLE charge q
STATE VARIABLE time t
STATE VARIABLE Electrostatic force Fe
STATE THE UNIT Current Amperes or C/s
STATE THE UNIT Potential difference V or J/C
STATE THE UNIT charge C or e
STATE THE UNIT Power Watts (W) or J/s
STATE THE UNIT Resistance or ohms
STATE THE UNIT Resistivity m or ohm-meter
COMPLETE THE TRIANGLE q I t
COMPLETE THE TRIANGLE V I R
COMPLETE THE TRIANGLE W P t
COMPLETE THE TRIANGLE P I V
COMPLETE THE TRIANGLE W V q
Equations to memorize Equation for area of a sloped (triangle) graph Area = 1/2bh or [(x-value)(y-value)]/2
Equations to memorize Equation for area of a straight line (rectangular) graph Area = bh or (x-value)(y-value)
Name the type of relationship represented by the graph Inverse or inverse square y does the opposite of x y does the opposite square of x
Name the type of relationship represented by the graph Direct y does the same thing as x
Name the type of relationship represented by the graph Direct Square y does the same thing as x squared
Vocabulary or Concept The area where an object feels the force of another object with the same fundamental force carrier Field
Vocabulary or Concept The process by which the electrons in an object are redistributed due to attraction or repulsion when brought near a charged object. Induction (always causes attraction because of temporary polarity)
Vocabulary or Concept The process by which two objects obtain the same charge due to contact. Conduction (always like charge)
Vocabulary or Concept The rate of energy or work Power
Vocabulary or Concept Amount of charge that flows per second Current
Vocabulary or Concept The amount of energy (or work done) on each charge Potential difference
Vocabulary or Concept A circuit in which electrons have a choice of paths Parallel Circuit
Vocabulary or Concept A circuit in which electrons all follow the same path Series circuit
Vocabulary or Concept A device to measure current Ammeter
Vocabulary or Concept A device to measure potential difference voltmeter
Vocabulary or Concept The difficulty and electron has in completing a circuit Resistance
Vocabulary or Concept Force that acts between an electron and a proton Electromagnetic force
Vocabulary or Concept Measure of energy when working with small charges such as an electron or other elementary charge Electronvolt eV
Vocabulary or Concept The base unit for electric charge of a particle. Coulomb
Vocabulary or Concept The charge in coulombs of an electron or a proton. 1.6 x 10-19C
Vocabulary or Concept The term for the smallest possible quantity of charge on a particle Elementary charge
Vocabulary or Concept Field lines are represented as arrows that show what a Positive test particle would do if placed in the field (always move away from + and toward -)
Vocabulary or Concept Magnetic field lines align with the field with arrows that point in the direction of The north end of a compass needle (ie away from north and toward south)
Vocabulary or Concept In order for a charged particle to create a magnetic field, the particle must be moving
Vocabulary or Concept In a parallel circuit, the equivalent resistance must be Less than the value of the smallest resistor
State the variable for the alternate unit Volt-Coulomb W=Vq so Work or energy (alternate for a Joule)
State the variable for the alternate unit Volt/Amp R=V/I so Resistance (alternate for an ohm)
