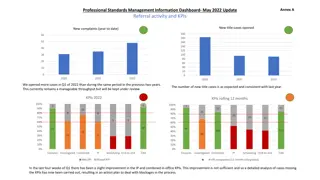
Understanding Subordination in English Grammar
Learn about subordination in English grammar, including clauses of reason, purpose, manner, result, condition, and contrast. Discover how subordinating conjunctions are used to connect ideas in complex sentences.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
SUBORDINATION Reason purpose Manner Result Condition contrast
Reason and purpose clause So that subordinating conjunctions of reason and purpose In order that (more formal) So (informal)
Adverb clause of reason My parents are studying in California because they don t like snow.
Adverb clause of purpose My parents are going to move to California so that they can be closer to my brothers. (A note: try to differentiate between this conjunction (SO THAT) which is used to express purpose that ) used to express result where its two parts are always separated.) (so and the conjunction My parents are going to move to California in order that they can be closer to my brothers. (more formal) We made airline reservations early so we would be sure of a seat. (informal)
Adverb clause of manner The subordinate conjunctions used are the following: as means the way - time as if/ as though He writes as he talks In California, we can enjoy the beach as we used to in Florida.
It looks as if it is going to rain (real situation) A Note: We can also say: (It might rain) (instead of using simple sentence , a complex sentence with adverb clause can be used) It looks as though everyone has gone home. He sounds as if / as though he got a cold. She treats me as if /as though she were/was my mother. (unreal situation)
Adverb clause of result A variety of conjunctions introduced this clause: So So that (It was so hot that we couldn t sleep) Such ..that( It was such a hot day that we couldn t sleep)
The flood caused such a panic that everyone had to evacuate. The movie theater had such a long line that we had to wait an hour.
Adverb clause of condition The conjunctions: If/ in case/ unless/whether or not I ll leave whether you give me a permission or not.
Adverb of contrast The conjunctions: Although/though/ eventhough/while/in spite of the fact While has two meanings: time and contrast If it expresses contrast the adverb clause always come first Ex: While I don t like studying English grammar, I know I have to