Understanding Sustainable Competitive Advantage in Business
Learn about the sustainability of a competitive advantage, including the factors influencing it, external and internal analyses, resource management, decision-making, and core competencies. Discover how firms can develop and maintain a competitive edge in the ever-changing business landscape.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Sustainability of a Competitive Advantage Sustainability of a competitive advantage is a function of: the rate of core-competence obsolescence due to environmental changes, e.g., technological shifts the availability of substitutes for the core competence the imitability of the core competence, e.g., diffusion of an innovation whether the firm is properly organized to capture value
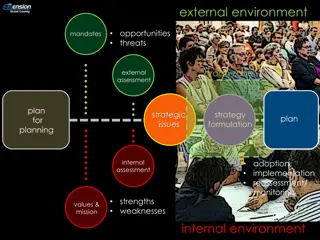
External and Internal Analyses By studying the external environment, firms identify what they might choose to do Environment Sociocultural Industry Environment (Structure>Conduct>Performance) Opportunities and threats Competitor Environment Technological General
External and Internal Analyses By studying the firm s (internal) capabilities & resources, firms identify what they can do (over time) Unique resources, capabilities, and competencies (sustainable competitive advantage)
Internal Analysis (Resources, Capabilities) How do we effectively manage current core competencies while simultaneously developing new ones? (exploit/explore) How do we assemble bundles of resources, capabilities and core competencies to create value for customers? How do we learn to change rapidly?
What affects decisions about Resources, Capabilities, and Core Uncertainty regarding curCrenot/mfutpureetencies characteristics of the general and industry environments Complexity - the interrelationship among factors that shape a firm s environment(s), and top management perceptions of these environments Intraorganizational Conflicts among people making and affected by resource allocation decisions
Components of Internal Analysis Strategic Competitiveness Identify sustainable competitive advantages Core IdentifyingCore Competencies Competencies Capabilities Four Criteria of Sustainable Advantage Value Chain Analysis Resources Tangible Intangible In/Outsource decisions Valuable Rare Imitation/Substitutes = costly Organized properly
Discovering Core Competencies Resources Tangible Intangible Resources are what a firm draws upon to create value -- its assets and valuable resources are embedded and difficult to trade in markets Resources are inputs into a firm s production process... IP, capital equipment, skills, brands, organizational routines, access to financial capital, talented managers, etc.
Discovering Core Competencies Resources Tangible Intangible Intangible Technological Innovation Reputation Organizational activity systems Knowledge Tangible Financial Physical Labor markets for resources are often imperfect resources are not intrinsically valuable
Discovering Core Competencies Capabilities Capabilities describe the firm s ability to create, deploy, modify, reconfigure, and leverage resources. Valuable capabilities permit resources to be combined in unique ways to create core competencies markets for capabilities are imperfect
Discovering Core Competencies Core Competencies are resources and capabilities that are a source of competitive advantage over rivals make a firm distinctive McKinsey and Co. recommends isolating 3-4 competencies when framing strategic actions Consider Amazon (culture, transaction scale economies, bundling, virtualization)
Discovering Core Competencies Four Criteria of Sustainable Advantage Valuable Rare Imitation/Substitution = Costly Organized Valuable: Capabilities that help a firm neutralize threats or exploit opportunities Rare: Capabilities that are not possessed by many others
Discovering Core Competencies Four Criteria of Sustainable Advantage Valuable Rare Imitation/Substitution = Costly Organized Costly to imitate: capabilities that other firms cannot develop easily, usually due to Unique historical conditions - e.g., founder, culture Causal ambiguity - capabilities hidden Social complexity - capabilities distributed Time diseconomies
Discovering Core Competencies Four Criteria of Sustainable Advantage Valuable Rare Imitation/Substitution = Costly Organized Nonsubstitutable: capabilities that do not have strategic equivalents Invisible to competitors Firm-specific knowledge Trust-based working relationships between managers and nonmanagerial personnel
Core Competence as a Strategic Capability Resources Inputs to a firm s production process Core Competence Capability that is strategic Y Does it satisfy the criteria of sustainable competitive advantage? Capability integration of resources Affected by N Capability Capability that is not strategic
Performance Implications Competitive Consequences Performance Implications Competitive Disadvantage Below Average Returns No No No No Competitive Parity Yes/ No Yes No No Average Returns Temporary Com- petitive Advantage Above Average to Average Returns Yes/ No Yes Yes No Sustainable Com- petitive Advantage Above Average Returns Yes Yes Yes Yes
Value creation Profit determined by : The amount of value customers place on firm s goods or services (V) Firm s cost of production (C) Consumer surplus occurs when price charged by a firm on a good or service is less than value placed on it by a customer Value creation = V-C
Porters Value Chain Firm Infrastructure Human Resource Management Technology Development Support Activities Procurement Primary Activities Upstream value activities activities Downstream value
Value Chain in Communicaattiions Technology Industtrryy Source MIT Sloan School Architectures and roadmaps for communications and media
Global Value Chain Management Supplier A Supplier B Supplier N Assembling, Manufacturing and Sales Distribution Center Supplier X Supplier Y Supplier Z Assembling , Manufacturing and Sales Country Market A Country Market B Whheere wi l you design, assemble, innvveennttory, marrket, and manag e?
Outsourcing SupportActivities Outsourcing is the purchase of some or all of a value-creating activity from an external supplier Firm Infrastructure Human Resource Mgmt. Technological Development Procurement Usually this is because the specialty supplier can provide these functions more efficiently PrimaryActivities Inbound Logistics Operations Outbound Logistics Marketing & Sales Service
Strategic Rationales for Outsourcing Improve Business Focus lets company focus on broader business issues by having outside experts handle various operational details Provide Access to World-Class Capabilities the specialized resources of outsourcing providers makes world-class capabilities available to firms in a wide range of applications
Strategic Rationales for Outsourcing Accelerate Business Re-Engineering Benefits achieves re-engineering benefits more quickly by having outsiders--who have already achieved world-class standards--take over process Share Risks reduces investment requirements and makes firm more flexible, dynamic and better able to adapt to changing opportunities
Strategic Rationales for Outsourcing Free Resources for Other Purposes permits firm to redirect efforts from non- core activities toward those that serve customers more effectively
Outsourcing Issues Greatest Value outsource only to firms possessing a core competence in terms of performing the primary or support activity being outsourced Evaluating Resources and Capabilities don t outsource activities in which the firm itself can create and capture value Environmental Threats and Ongoing Tasks do not outsource primary and support activities that are used to neutralize environmental threats or complete necessary ongoing organizational tasks
Outsourcing Issues Nonstrategic Team of Resources do not outsource capabilities that are critical to their success, even though the capabilities are not actual sources of competitive advantage Firm s Knowledge Base do not outsource activities that stimulate the development of new capabilities and competencies
Core Competencies: Cautions and Reminders Never take for granted that core competencies will continue to provide a source of competitive advantage All core competencies have the potential to become core rigidities Core rigidities are former core competencies that now generate inertia and stifle innovation