Understanding the Anatomy of the Urinary Bladder
Explore the detailed gross features and relations of the urinary bladder, including its shape, position, and connections in both males and females. Learn about the interior structure and mucosa folds to understand its role in urine storage.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
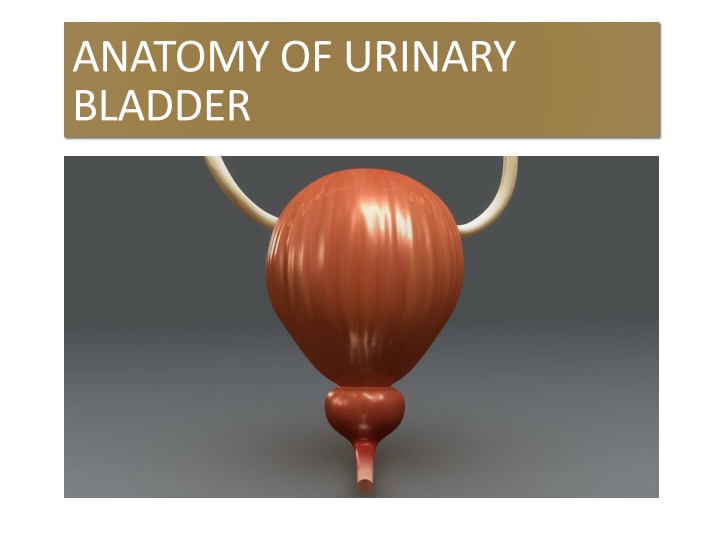
ANATOMY OF URINARY BLADDER
Introduction The urinary bladder is a muscular organ which lies in the anterior part of pelvic cavity and helps in the storage of urine. Shape, size and position of bladder varies according to the amount of urine contained in it. An empty bladder lies entirely within the pelvis but as it fills it extends into abdominal cavity.
GROSS FEATURES An empty bladder is tetrahedral in shape & has: 1. Apex 2. Base or fundus 3. Neck 4. 3 surfaces: superior, right & left inferolateral. 5. 4 borders: anterior, posterior & 2 lateral lateral borders.
GROSS FEATURES 4 4/28/2025
Relations Apex: Directed forward. Connected to the umblicus by the median umblical ligament. Base: Directed backward. It is related to; In male: Vas deferens, seminal vesicles, rectum, rectovesical pouch and peritoneum.
In female: Vagina and cervix of the uterus. Neck: Inferior and most fixed part. In male: Related to prostate. Surrounded by smooth muscle fibres which form preprostatic sphincter. In female: Related to pelvic fascia.
Superior surface: In male: Peritoneum, coils of ileum & sigmoid colon. In female: Peritoneum (covers the greater part) & Uterine cervix. Inferolateral surfaces: Related to the pubis, the retropubic fat, levator ani & the obturator internus in both male and female.
Puboprostatic ligaments in male & pubovesical ligaments in female.
Interior of the bladder Mucosa of the bladder shows irregular folds except in a small triangular area over the base. This area is k/a trigone of the bladder. Here, the mucosa is smooth. Internal urethral orifice opens in the apex of this trigone.
The ureters open at the posterolateral angle of the trigone. Uvula vesicae: It is a small elevation on the trigone posterior to the urethral orifice produced by median lobe of prostate.
Ligaments of the bladder True ligaments They are the condensations of pelvic fascia. They provide support to the bladder. 1. Lateral true ligament 2. Lateral puboprostatic ligament 3. Medial puboprostatic ligament 4. Medial umblical ligament 5. Posterior ligament False ligaments They are the peritoneal folds. They don t provide support to the bladder. 1. Median umblical fold 2. Medial umblical fold 3. Lateral false ligament 4. Posterior false ligament 13 4/28/2025
HISTOLOGY OF BLADDER The wall of urinary bladder shows following features: i. Inner mucosa Lined by transitional epithelium. i. Middle muscle layer Consists of outer & inner longitudinal muscle layer and middle circular/ oblique fibres. The smooth muscle is also called detrusor muscle whose contraction helps in voiding of urine. i. Outer serous layer: It is the peritoneum of bladder. 15 4/28/2025
Histology of bladder 16 4/28/2025