USA History Overview 1929-2000 Study Topics
Explore key topics in USA history from 1929 to 2000 including economic downturn, civil rights, political change, social change, Cold War rivalry, and the search for world peace, with a focus on significant events and developments shaping American society.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
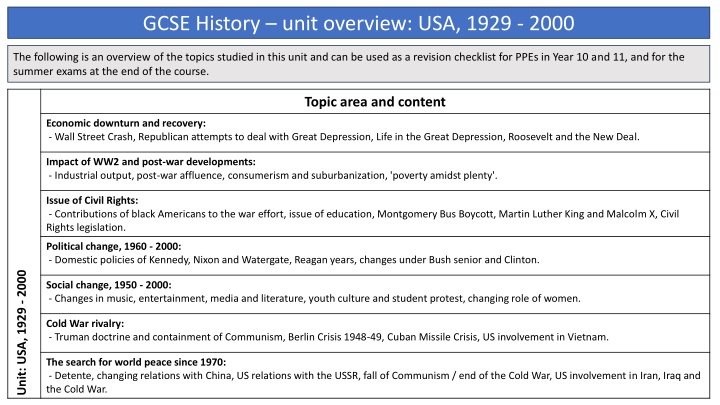
GCSE History unit overview: USA, 1929 - 2000 The following is an overview of the topics studied in this unit and can be used as a revision checklist for PPEs in Year 10 and 11, and for the summer exams at the end of the course. Topic area and content Economic downturn and recovery: - Wall Street Crash, Republican attempts to deal with Great Depression, Life in the Great Depression, Roosevelt and the New Deal. Impact of WW2 and post-war developments: - Industrial output, post-war affluence, consumerism and suburbanization, 'poverty amidst plenty'. Issue of Civil Rights: - Contributions of black Americans to the war effort, issue of education, Montgomery Bus Boycott, Martin Luther King and Malcolm X, Civil Rights legislation. Political change, 1960 - 2000: - Domestic policies of Kennedy, Nixon and Watergate, Reagan years, changes under Bush senior and Clinton. Unit: USA, 1929 - 2000 Social change, 1950 - 2000: - Changes in music, entertainment, media and literature, youth culture and student protest, changing role of women. Cold War rivalry: - Truman doctrine and containment of Communism, Berlin Crisis 1948-49, Cuban Missile Crisis, US involvement in Vietnam. The search for world peace since 1970: - Detente, changing relations with China, US relations with the USSR, fall of Communism / end of the Cold War, US involvement in Iran, Iraq and the Cold War.
GCSE History exam skills / timing overview: USA, 1929 - 2000 The development of the USA, 1929 - 2000 : Component 2, Breadth Studies: period study - 45 mins Question stem / command words Describe Q n Marks Skill Core advice Timing 1 Recall Give information Range of information (2 3 developed points) Highlight topic of question and dates Suggested info: definition, cause, purpose, famous example, relevant time period 5 mins 5 2 How far did... change... Recall Judgement essential how far did the issue in the question change? Evidence of change Evidence of limits to change / lack of change need to include scale / extent of change. Consider change or all, or only some groups, local / national / international change, short term or long term change? Supported with examples Judgement essential must give an order Support each judgement with reasons for choice = why this was significant? Consider criteria for significant scale of change, scope of change, long term / short term change, temporary or permanent change Highest level answers = why is one factor more / less significant than others? Give 3 clear reasons Key words: reason and because Link each reason to the question This led to change because Use paragraphs / separate using a line 5 mins 6 3 3 features... Arrange the developments in order of their significance in... Recall 10 mins 9 4 Explain why... Recall 10 mins 8 5 How important was... Extended writing Factors 2 paragraphs and conclusion structure P1 = factor in the question. Focus on impact, not just description. Link to question. Give judgement. P2 = other important factors (not mentioned in the question). WHY were these more or less important than the factor in the question. Focus on IMPACT, not just description. Link to question. Give judgement. Conclusion = compare judgements. Give definite overall decision. 15 mins 12
GCSE History unit overview: Crime and Punishment, 500 - present The following is an overview of the topics studied in this unit and can be used as a revision checklist for PPEs in Year 10 and 11, and for the summer exams at the end of the course. Topic area and content Causes of crime over time: - Problems in the Medieval era, economic pressures in the 16th century, religious change in 16th/17th centuries, industrialisation and urbanisation, 20th century pressures. Nature of crimes over time: - Common crimes of the Medieval era, 16th and 17th centuries (vagrancy, heresy and treason), 18th century (highway robbery and smuggling), Industrial crimes, 20th century (car, computers, hooliganism and terrorism). Unit: Crime and Punishment, 500 - present Enforcing law and order over time: - Saxon / medieval responsibility of the family + community, late medieval role of courts, parish responsibilities in Tudor England, state police forces in 19th century, changing nature of policing from 20th century. Methods of combatting crime: - Communal methods in Saxon / medieval times, Tudor JPs, Bow Street Runners, Metropolitan Police, extension of police forces, 20th century developments (transport, communication, specialisation, community). Methods of punishment over time: - Harsh punishment in Saxon / medieval times, treatment of Vagabonds - Tudor times, public punishment - 19th century, transportation, prison reform, silent and separate systems, alternative punishments from 20th century. Attitudes to crime and punishment over time: - Concepts of retribution and deterrence, purpose of public punishment, concept of banishment, changing purposes of prisons as punishment, attitudes in the 20th century, young offenders, abolition of death sentence, rehabilitation and restitution. Historic site study: - Lincoln Castle Gaol (2024/2025)
GCSE History exam skills / timing overview: C&P, 500 - present Crime and Punishment, 500 - present: Component 2, Breadth Studies: Thematic - 1 hour 15 mins Question stem / command words Use Sources A, B and C to identify one sim and one dif in ... Q n Marks Skill Core advice Timing 1 Source comprehension Use all 3 sources. 2 of the sources will have similar content / info 1 source will show something different Make sure you link the content of the sources (similarity / difference) to the topic of the question 2 paragraphs + conclusion Must give a definite judgement / answer / decision which is most reliable, even if it s a close call (relative reliability)! Consider the CONTENT of the source and add own knowledge to support (linked to topic of the question) Consider the CAPTION of the source (AUTHOR / AUDIENCE) does this make the source more or less likely to be reliable Give information Range of information (2 3 developed points) Highlight topic of question and dates Suggested info: definition, cause, purpose, famous example, relevant time period Give 3 clear reasons Key words: reason and because Link each reason to the question This led to ____ because Use paragraphs / separate using a line 4 paragraphs and a conclusion structure focus on change and continuity essential Must include all time periods one time period per paragraph Layers of answers: 1) Content relevant to each time period in separate paragraphs 2) Include reference to changes and areas of continuity in each paragraph (new / old) 3) Consider scale / extent of change, with comparisons between time periods Summarise change / continuity in conclusion 5 mins 4 2 Which of the 2 sources is more reliable... Source analysis 10 mins 6 3 Describe... Recall 5 mins 5 4 Explain why... Recall 10 mins 9 5 Outline how... changed from c.500 to the present day. Narrative Extended writing Change and continuity 20 mins 16 (+4 SPaG) 6a Describe 2 main features of... Recall Give a range of information link this to the specific historical site 2 x describe questions = 2 paragraphs 20 mins 8 6b Explain why... led to changes in... Recall 2 stages: 1) 2) Describe changes 3 clear reasons why this historical site led to change / was important in demonstrating change 12
GCSE History unit overview: Germany in Transition, 1919 - 1939 The following is an overview of the topics studied in this unit and can be used as a revision checklist for PPEs in Year 10 and 11, and for the summer exams at the end of the course. Topic area and content Impact of WWI: - Impact of Versailles, weaknesses of the Weimar government, political instability (Spartacist, Kapp, Munich Putsches), Ruhr Crisis, hyperinflation. Recovery of the Weimar: - Recovery from hyperinflation, Dawes and Young Plans, Locarno Pact, League of Nations, US investment, social and political developments. Unit: Germany in Transition, 1919 - 1939 End of the Weimar, 1929 - 1933 (Rise of Hitler): - Social and political impact of the Great Depression on Weimar Republic, electoral appeal of Hitler, role of the SA, propaganda, political extremism and scheming 1929 - 1933. Consolidation of Hitler s power, 1933-1934: - Hitler and Chancellor, Reichstag Fire, 1933 election and Enabling Act, trade unions and political parties, Night of the Long Knives, Hitler becomes Fuhrer. Nazi economic, social and racial policy: - Reducing unemployment, policy towards workers, women and the Threes Ks, controlling education, Hitler Youth Movement, treatment of Jews. Terror and persuasion: - SS and the Gestapo, control of the legal system, Goebbels and propaganda, use of rallies, radio and cinema, censorship of newspapers and the arts. Hitler s foreign policy: - Hitler's foreign policy aims, rearmament, and conscription, Rhineland 1936, Anschluss 1938, Sudetenland 1938, Nazi-Soviet Pact 1939.
GCSE History exam skills / timing overview: Germany in Transition Germany in Transition, 1919 1939: Component 1, Depth Studies: non-British - 1 hour Question stem / command words Use Source A and your own knowledge to describe... What was the purpose of Source B? Q n Marks Skill Core advice Timing 1 Source comprehension / recall Directly use the source (content only) to infer This source shows that This is linked to Give info from own knowledge (that is not in the source). Clearly describe the actual issue in the question. Link to topic in question This tells us that This suggests that 6 mins 5 2 Source analysis CONTENT - Summarise the message of the source . CAPTION - Include type of source and purpose (general). Include author and audience (more specific who is this message intended for, and why)? Evaluate why does this person give this message at this time what is the historical context? Include own knowledge of wider events / changes 2 paragraphs + conclusion. For each interpretation: - Summarise view. How far it agrees with issue in question add own knowledge about the key issue in the q n. Consider focus of the historian, their likely audience and the type of publication they have written for. Conclusion: compare and analyse views and their differences. How are the views different? Which view agrees to the greatest extent? Why are they different why do different people have different views? 2 paragraphs + conclusion. For each source: - Consider CONTENT of source and add own knowledge. Consider CAPTION of the source (author / audience). Judgement about how useful linked to topic in question. Conclusion: compare relative usefulness of the 2 sources. Make a definite judgement and give reasons. Historical context = which fits most with your generally understanding of what was happening at the time? Need to show some own knowledge to show you understand the context of the sources. 3 paragraphs + conclusion - Focus on the content of the interpretation... Include own knowledge that could be used to support this view point. - Include the author and audience of the interpretation do these make you agree or disagree more / less? Use focus of historian and title of book (is it a broad or narrow perspective / topic?). Strengths and limitations of the author what is their view based on, how have they reached their interpretation? Keep focus on interpretation (not on reliability). - Counter argument who / why would others disagree with the interpretation? What other views could they give? Comment on HOW and WHY interpretations can differ. - Conclusion overall, how accurate is the interpretation and therefore how far do you agree with it? If you disagree, what interpretation is more accurate? 10 mins 8 3 Do the interpretations support the view that... Interpretation 12 mins 10 4 Which of the sources is more useful to an historian studying... Source analysis 12 mins 11 5 To what extent do you agree with this interpretation? Interpretation / recall 20 mins 16 + 3 SPaG
GCSE History unit overview: Conflict and Upheaval, 1337 - 1381 The following is an overview of the topics studied in this unit and can be used as a revision checklist for PPEs in Year 10 and 11, and for the summer exams at the end of the course. Topic area and content England in the 14th century: - English society in the 1300s, importance of the Church, importance of the wool trade, position of women, rich and poor. Start of the Hundred Years War: - Overseas possessions of English kings, relations between France and Scotland, Isabella of France, Edward III's claim, role of Phillip of France, confiscation of Aquitaine, Edward III's claim. Unit: Conflict and Upheaval, 1337 - 1381 The course of the war: - Alliances, military tactics, battles of Crecy, Calais, Poitiers, role of the Black Prince, Treaty of Bretigny. The Black Death: - Arrival of the Black Death, immediate impact, strains of plague, contemporary views, progress of the plague, factors aiding spread. Legacy of the Black Death: - Population decrease, labour shortages, Statute of Labourers, effects on survivors, art and medicine. Peasant discontent: - Effects of the Black Death, issue of serfdom, religious ideas, John Ball, French Wards, Poll Tax, role of Wat Tyler, events of May - June 1381. The Peasants Revolt: - Richard's broken promises, Poll Tax, control of wages, decline of serfdom and the position of peasants, effects of the Hundred Years' War.
GCSE History exam skills / timing overview: Conflict and Upheaval Conflict and Upheaval, England, 1337 1381: Component 1, Depth Studies: British study - 1 hour Question stem / command words What can be learnt from Sources A and B about... Q n Marks Skill Core advice Timing 1 Source comprehension Use both sources equally. Select 2 pieces of info per source. No extra info needed. Link info to the topic of the question address the key issue in the q n, do not just paraphrase the content of each source. Final sentence = Together, these sources show 5 mins 4 2 To what extent does this source accurately explain... Source comprehension / analysis 2 paragraphs + conclusion There will always be something that is accurate, but it won t always give the full picture. Include a clear judgement = To what extent...? Explain answer = ... because... - CONTENT of source what is accurate / inaccurate? Historical context = Does it fit with your knowledge of what s generally happening at that point? Include own knowledge as support, and to recognise issues / info not included, linked to topic. - CAPTION - Include authorship and audience of the source = who is writing, when and for what audience? Does this support or limit accuracy of the source? Clearly focus on the attribution of the source and the circumstances under which the source was produced. - Give your definite judgement. 10 mins 8 3 Why was there... Recall Main focus = issue in question. Give clear reasons why this was a significant issue. Support with own knowledge. Use key term because to fully explain This was significant because This led to ____ because Highest level answers could include: summary conclusion Was the factor in the question the most significant issue? Other significant factors were... Compared to other significant factors... 15 mins 12 4 Explain the connections between two of the following... Recall Decide on 2 features (they will all be connected, you pick 2). Define each feature and give some background knowledge (historical context) Give reasons why they are linked together (up to 3). Consider: cause / consequence / family link / categories of events etc. Use key terms like because , connected to and linked to . 10 mins 10 5 How far do you agree with this interpretation of... Interpretation / recall 3 paragraphs + conclusion - Focus on the content of the interpretation... Include own knowledge that could be used to support this view point. - Include the author and audience of the interpretation do these make you agree or disagree more / less? Use focus of historian and title of book (is it a broad or narrow perspective / topic?). Strengths and limitations of the author what is their view based on, how have they reached their interpretation? Keep focus on interpretation (not on reliability). - Counter argument who / why would others disagree with the interpretation? What other views could they give? Comment on HOW and WHY interpretations can differ. - Conclusion overall, how accurate is the interpretation and therefore how far do you agree with it? If you disagree, what interpretation is more accurate? 20 mins 16 + 3 SPaG