Utilizing Hash Tables in C++ STL for Unique Element Handling
Explore how to effectively employ hash tables in C++ STL for managing unique elements, including examples like word puzzles and removing duplicates from vectors. Dive into the functionalities of unordered_set and unordered_map to enhance your C++ programming skills.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
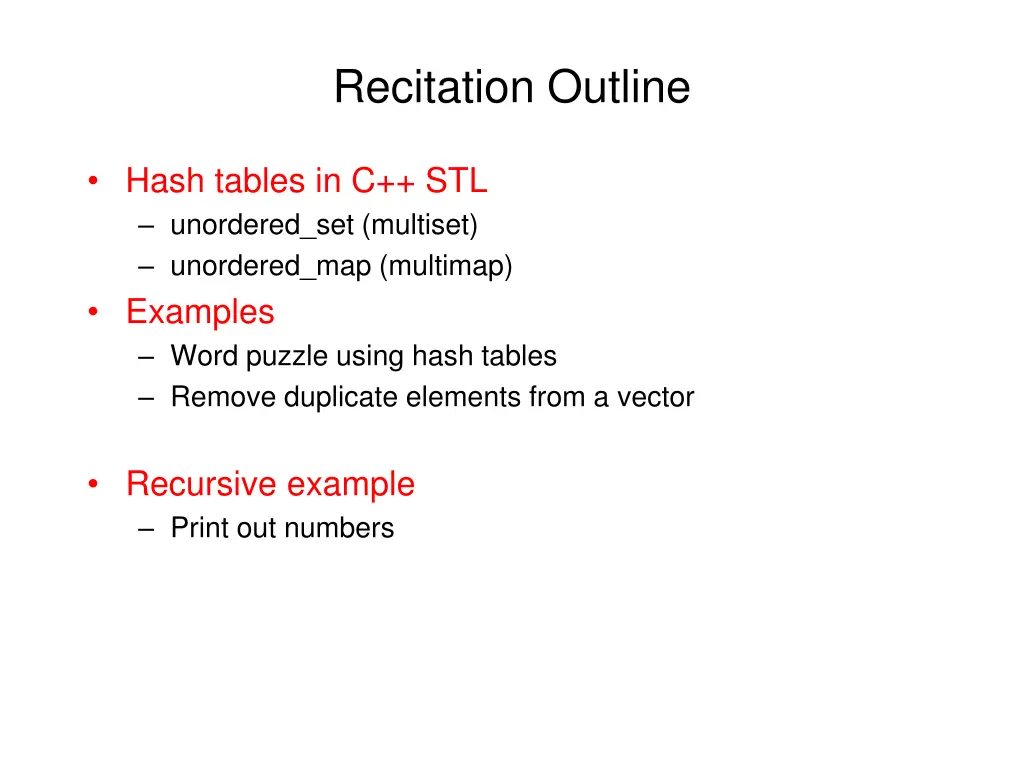
Recitation Outline Hash tables in C++ STL unordered_set (multiset) unordered_map (multimap) Examples Word puzzle using hash tables Remove duplicate elements from a vector Recursive example Print out numbers
unordered_set #include <unordered_set> using namespace std; std::pair<iterator, bool> insert(const value_type& val); Insert an element val into hash table iterator find(const key_type& k); Search key k void erase(const_iterator position); size_type erase(const key_type& k); Delete an element begin() end() iterators
unordered_map #include <unordered_map> Using namespace std; std::pair<iterator, bool> insert(const value_type& obj); Insert an element typedef std::pair<const Key, T> value_type; void erase(const_iterator position); size_type erase(const key_type& k); Delete an element (with a given iterator or key) iterator find(const key_type& k); Search an element (with given key) begin(), end() Iterators mapped_type& operator[](const key_type& k); Return value if key k exists in map Otherwise an element with key k and default value will be inserted
Word Puzzle using hash table In this version we store word dictionary in an unordered_set See examples/r7/word_puzzle_ht.cpp, word_puzzle_ht.h, rotation.cpp What you need to do Review the code To compile: make To run: word_puzzle_ht.x (you can read the source code to see the supported commands)
Remove Duplicate Elements Remove duplicate elements from a vector Examples/r7/remove_duplicate1.cpp This version uses a hash table to record unique elements What you need to do Review the code To compile: make remove_duplicate1.x To run: remove_duplicate1.x
Recursive Function Convert the following function into recursive one void printnumber(size_t k) { for (size_t I = 0; I <= k; ++i) { cout << I << ; } } See Examples/r7/printnumber_nonrecursive.cpp And printnumber_recursive.cpp What you need to do Review the code To compile: make printnumber_recursive.x To run: printnumber_recursive.x some_integer_value
STL Algorithm std::swap Function signature template <class T> void swap (T& a, T& b) template <class T, size_t N> void swap(T (&a)[N], T (&b)[N]) Swap values of a and b Note that when a and b are pointers, we are swapping content of a and b (i.e., address stored in a and b), not values that a and b refer to See Example1.cpp Example2.cpp What you need to do Please review the code Please play with the code (compile and run)
STL Algorithms std::iter_swap() Function signature Template <class ForwardIterator1, class ForwardIterator2> void iter_swap(ForwardIterator1 a, FowardIterator2 b) This function swap the elements referred by the two iterators a and b Examples Example3.cpp What you need to do Please review the code Please play with the code (compile and run)
