Virtualization in Cloud Computing
Explore the concept of virtualization in cloud computing, how it creates virtual counterparts of systems, the benefits it offers, and the differences between cloud and virtualization. Learn about types of virtualization and why it should be considered for IT infrastructure optimization.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Virtualization in Cloud Computing Asst. Prof. Surbhi Shriwastav Department of CSE Eshan College of Engg.
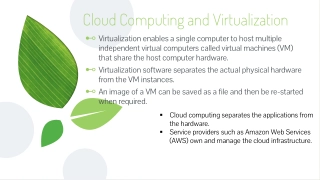
Introduction to Virtualization in Cloud Computing Virtualization translates to creating a virtual counterpart of an existing system such as a desktop, server, network resource or an operating system. Holistically speaking, it is a technique that allows multiple users or organizations to make use of a single resource thread or an application among themselves.
Virtualization as a concept Virtualization is known as the virtual machines that exist in the likeness of being a counterpart to actual hardware or an operating system. A virtual machine makes up for an ecosystem that logically separates itself from the underlying hardware. The machine that is used to create the foundation of a virtual machine is called the Host Machine and the virtual machine is labeled as the Guest Machine.
Types of virtualization Hardware Virtualization Operating System Virtualization Server Storage Virtualization Virtualization
Why should virtualization be even considered? Machines can run multiple instances of a single application simultaneously. Streamlining the IT cost and minimizing the IT administration structure. Effective management of large scale installation and server farms. Enhanced reliability, security, scalability, device dependence. Options to enable multiple OS use on the same hardware.
Cloud vs Virtualization Clouds are created for cloud computing where workloads run within the concerned system. Cloud architecture can consist of virtualization, container software or even bare-metal which is used to pool, share and abstract any scalable resource spread across a network creating a cloud. There is a stable operating system that lies at the base of any cloud computing venture, like for instance, Linux. This layer of the operating system provides users the independence across hybrid, private and public environments.
If you have internet, intranet access, then you can make use of virtualization to create a cloud environment. In the case of virtualization, the hypervisor is used which is a software that sits on top of physical hardware, abstracting the resources from the machine. The resources are often just raw processing of storage, power of cloud-based software applications that contain the respective runtime code and resources which are required to deploy it. But if the process ends here, it will be known as virtualization not cloud. Virtualization has its own set of benefits, like server consolidation and better use of hardware resources. It greatly cuts down on the resources used.
Conclusion Virtualization helps in outsourcing the hardware used, eliminating extra energy costs and minimizing the use of particular resources. Even though it doesn t work for every user, it surely provides enhanced security, efficiency and cost advantages.