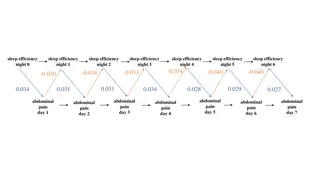
WG Mental Health Work Group Analysis on Anxiety and Depression
The WG Mental Health Work Group conducted an examination of anxiety and depression in Cameroon, Canada, India, and the United States. The research focused on utilizing affect questions to determine prevalence of poor mental health and functioning, with secondary data analysis from various datasets and known tools for measuring mental health.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Financial Reporting Framework for Small- and Medium-Sized Entities An Introduction for [Name of Client or Financial Statement User]
Overview What is the Financial Reporting Framework for Small- and Medium-Sized Entities? Why was it developed? Who can use it? What does it change? When can it be implemented? How will you benefit?
What Is It? New special purpose framework, or OCBOA, for preparing financial statements Developed by the AICPA and released June 10, 2013. Provides an alternative to other frameworks: GAAP Income tax basis Cash basis IFRS for SMEs
Why Was It Developed? In response to Accounting complexity Disclosure overload To better meet the needs of small businesses and their financial statement users
Needs of Small Businesses Relevant, streamlined reporting, more robust than cash or income tax basis Flexibility in choosing accounting policies Simplified guidance for typical, plain vanilla transactions Targeted disclosures Concise, plain-English standards that are easy to follow and keep up with
Who Can Use It? Entities that Are not required to prepare GAAP-based financial statements. Have no plans to go public in the foreseeable future. Operate for profit. Are owner-managed. Do not operate in an industry with highly-specialized accounting guidance, for example, no financial institutions or governments. Have no overly complicated transactions or significant foreign operations. Give their financial statement users direct access to management.
What Does It Change? Basic features Contents of the FRF for SMEs Primary differences from GAAP How your financial statements will change
Basic Features Historical cost based Blend of traditional GAAP and accrual income tax basis Principles-based with little prescriptive guidance Fair presentation framework Same objective as GAAP: To account for transactions according to their economic substance
Contents of the FRF for SMEs General principles Guidance on specific financial statement elements Complete set of disclosure requirements Transition guidance Glossary No industry-specific guidance
Primary Differences from GAAP Income taxes: Choice between taxes payable method (current income tax assets and liabilities only) or deferred income taxes method. No accounting for uncertainties. Intangible assets acquired in a business combination: Choice to not separately recognize them but include them in goodwill. Derivatives: Not recorded in the financial statements; disclosure only.
Primary Differences from GAAP Reporting of subsidiaries: Choice between consolidation or equity method for all subsidiaries. Parent-only financial statements permitted. Leases: Similar to the method used for income tax purposes. Lease classification guidance less prescriptive than GAAP.
Primary Differences from GAAP Asset impairment: No requirement to assess assets for impairment; however, there are disclosures. Left up to judgment. Investments in debt and equity securities: Recorded at cost unless held for sale, in which case recorded at market value with changes recorded in income. No comprehensive income. Variable interest entities: No such concept.
Primary Differences from GAAP Stock-based compensation: Compensation expense not recognized. Certain disclosures required. Defined benefit plans: Choice between current contributions payable method (expense for current year contribution only) or an accrued benefit obligation method.
How Your Financial Statements Will Change [Content to be developed for specific client or financial statement user]
When Can It Be Implemented? Conversion is entirely optional Can be implemented at any time Precondition for implementation: Acceptance by financial statement users
How Will You Benefit? Information in financial statements is more relevant for small business decision-making Disclosures are more targeted and understandable Financial statements are easier and less costly to prepare and audit (or review) Standards are stable; changes over time are expected to be minimal
Additional Resources Read the Financial Reporting Framework for Small- and Medium-Sized Entities Visit our website at [URL address] Read our newsletter Review the AICPA toolkit for small businesses [or financial statement users] at www.aicpa.org/FRF-SMEs