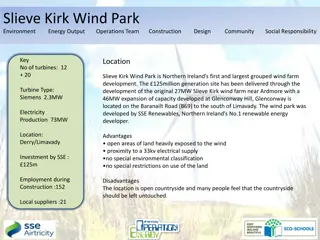
Wind Turbines: History, Technology, and Future Trends
Explore the evolution of wind turbines from ancient Persia to modern-day technology, learn how wind turbines work to convert wind energy into electricity, discover the current state of wind power adoption, and uncover future improvements in wind energy technology. The article covers Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWTs) and Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWTs), providing insights into their uses and potential advancements in the renewable energy industry.
Uploaded on | 1 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
HAWTs vs. VAWTs Bayley Costner Jason Cosma Tristan Fitzwater
History of Wind Turbines Persians first to use windmills between 500 and 900 B.C. Spread to middle east, used in food production 1,000 A.D., wind power technology spread north to Europe http://www.geek.com/ 1850, U.S. Wind Engine Company creates the Halladay Windmill 1880, steel blades invented for windmills 1970, skyrocketing gas prices renew interest in wind power http://energy.gov/eere/wind/history-wind-energy 1980, first large wind farms are installed
How do Wind Turbines Work? Convert wind energy into electricity Use uneven propellers to catch wind Wind turns the propellers which turns a generator Generator converts mechanical energy into electricity http://www.iowaenergycenter.org/wp- content/uploads/2012/03/wem-07_fig01.gif
Current State of Wind Turbines 4% of the power grid in the US is currently windpower1 Some towns, like Rock Port, MO, are completely powered by wind turbines.2 Wind turbines are ranked #7 on the list of most used renewable energy sources on listverse.com3 1 "American Wind Power Reaches Major Power Generation Milestones in 2013." American Wind Power Reaches Major Power Generation Milestones in 2013. Awea.org, 5 Mar. 2014. Web. 26 Oct. 2015. 2 Thompson, Andrea. "First U.S. Town Powered Completely By Wind."LiveScience. TechMedia Network, 15 July 2008. Web. 26 Oct. 2015. Top 10 Renewable Energy Sources - Listverse." Listverse. 1 May 2009. Web. 26 Oct. 2015.
What is a HAWT? Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine Much larger than others Mostly in rural areas Most common type of turbine https://www.mitchelltech.edu/media/library/Videos/48/cover/hond a-windfarm.jpg
What is a VAWT? Vertical Axis Wind Turbines Used in Urban areas Much Smaller than HAWTs Much rarer due to being a newer technology Provides small amounts of energy in a small space1 http://qph.cf.quoracdn.net/main-qimg- 0c134d468d7cbb56d12fc559a17ef711 1 Hill, N., R. Dominy, G. Ingram, and J. Dominy. "Darrieus Turbines: The Physics of Self-starting." Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part A: Journal of Power and Energy (2008): 21-29. Print.
Future Improvements of Wind Energy Wind energy is a newer industry, but already makes sense economically Cost of wind energy is trending downwards1 The U.S. Department of Energy has found that wind energy can be a viable source of energy in all 50 states by 20501 As HAWT continues to dominate onshore wind farms, VAWT will begin to be used for large offshore wind farms2 https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/f/f0/Barrow_ Offshore_wind_turbines_edit1.jpg 1 "Wind Vision." Wind Vision. N.p., n.d. Web. 27 Oct. 2015. 2 Sahin, A. "Progress and Recent Trends in Wind Energy." Progress in Energy and Combustion Science 30.5 (2004): 501-43. Web.
Future Uses/Improvements of VAWT Because VAWT blades can be assembled at the installation site, they are more efficient to transport than HAWT blades2 Several large-scale multi-megawatt offshore VAWT projects are currently being built2 HAWT are not capable of withstanding high wind speeds, so they cannot be used efficiently offshore (where wind speeds are generally much higher), where VAWT will begin to be built1 1 Sahin, A. "Progress and Recent Trends in Wind Energy." Progress in Energy and Combustion Science 30.5 (2004): 501-43. Web. 2 Tjiu, Willy, Tjukup Marnoto, Sohif Mat, Mohd Hafidz Ruslan, and Kamaruzzaman Sopian. "Darrieus Vertical Axis Wind Turbine for Power Generation II: Challenges in HAWT and the Opportunity of Multi-megawatt Darrieus VAWT Development." Renewable Energy 75 (2015): 560-71. Web.
Why is this important? According to the Department of Energy, wind energy can help avoid the emission of 250,000 metric tons of air pollution1 Wind energy can save consumers up to $280 billion by 2050 due to low vulnerability of price spikes, and can support 600,000 jobs by 20501 http://www.world- nuclear.org/uploadedImages/org/Nuclear_Basics/Lifecycle %20greenhouse%20gas%20emissions.png Wind energy will help to avoid over 12 gigatonnes of greenhouse gases by 20501 1 "Wind Vision." Wind Vision. N.p., n.d. Web. 27 Oct. 2015.
Sources "American Wind Power Reaches Major Power Generation Milestones in 2013." American Wind Power Reaches Major Power Generation Milestones in 2013. Awea.org, 5 Mar. 2014. Web. 26 Oct. 2015. Thompson, Andrea. "First U.S. Town Powered Completely By Wind."LiveScience. TechMedia Network, 15 July 2008. Web. 26 Oct. 2015. Top 10 Renewable Energy Sources - Listverse." Listverse. 1 May 2009. Web. 26 Oct. 2015. Hill, N., R. Dominy, G. Ingram, and J. Dominy. "Darrieus Turbines: The Physics of Self-starting." Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part A: Journal of Power and Energy (2008): 21-29. Print. "Wind Vision." Wind Vision. N.p., n.d. Web. 27 Oct. 2015. Sahin, A. "Progress and Recent Trends in Wind Energy." Progress in Energy and Combustion Science 30.5 (2004): 501-43. Web. Tjiu, Willy, Tjukup Marnoto, Sohif Mat, Mohd Hafidz Ruslan, and Kamaruzzaman Sopian. "Darrieus Vertical Axis Wind Turbine for Power Generation II: Challenges in HAWT and the Opportunity of Multi-megawatt Darrieus VAWT Development." Renewable Energy 75 (2015): 560-71. Web.