Anemia: Causes, Diagnosis, and Management
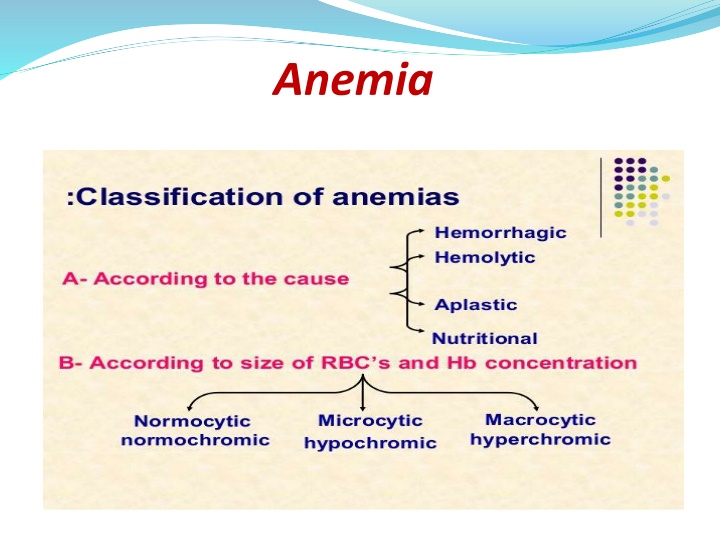
Anemia is a condition characterized by a deficiency of red blood cells or hemoglobin in the blood. It can be caused by various factors, with iron deficiency being a common reason. This content explains the physiology of iron, impaired iron absorption, history taking, examinations, laboratory investigations, and epidemiology related to anemia. It also discusses microcytic anemia, its diagnosis through CBC, PBF, TIBC, ferritin levels, and other tests like stool occult blood and endoscopy. Additionally, it covers tear drop cells, epidemiological aspects, and differentiating factors in related conditions like sideroblastic anemia, iron deficiency anemia, and thalassemia.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Definition: Microcytic anemia caused by iron def. for any reason Iron physiology and metabolism: - normal diet provides =15 mg of iron /day. - 5-10% is absorbed in duod. And upper jejunum. - total body iron stores = 4 gms . - around 1 mg is lost daily in urine, faeces, - menstrual losses(20mg/m), pregnancy(500-1000mg).
Impaired iron absorption : Achlorhydria. Plummer- Vinson syndrome . Gastric surgery. Ciliac dis. pica. Increased iron demands or loss . > chronic bleeding ( GIT , menses , urinary , etc.) infancy pregnancy. lactation. Nutritional . Idiopathic
1- History :- - H/O symptoms of anemia . - H/O blood loss GIT , menses , .. - Drug history NSAIDS. - past history of gastric surgery. - Diet history. - pica. 2- Examination : - pallor , vital signs. - abdominal exam. - P.R. exam. - gynecological exam.
- CBC: HB , RBCS indices (( MCV , MCH , MCHC)). - PBF : M.H.A , anisocytosis , poiklocytosis , tear drop cells. , TIBC (( )). - S. ferritin (( )) . - Stool for occult blood ?! - U/S of abdomen , pelvis. - B.M.A (( iron staining )) infrequently needed. - Endoscopy - S. iron (( ))
Epidemiology : - IDA is the most common nutritional deficiency in developing and developed countries . - IDA is considered to be the leading cause of anemia worldwide , it accounting for as many as 50% of anemic cases . - Prevalence of IDA greatly varies according to : Age Gender , Physiological , Pathological , Enviromental and Socioeconomic conditions .
DID : Peripheral smear Hypochromic & Miciocyhic Anaemia Bone marrow iron INCREASED ABSENT Ringed sideroblasts Hemoglobin electrophoresis Normal Abnormal Normal Diagnosis Sideroblastic anemia Iron def. anemie Thalassemia
- Oral replacement: Fe. Sulphate, gluconate, fumarate 150-200mg /day for six months. - Parenteral replacment either IM or IV (( T.D. indicated for pts who are not tolerating oral iron, poor compliance and for rapid replacement pregnancy )) Pts planned for surgery , cases with malabsorption diseases.
within 3 weeks the HB level will be increased with in MCV and reticulocytosis. after 3 months of treatment the MCV will be normal and HB normal.
Revise the diagnosis (( Thalassemia )) Think of additional complications ch.infection , C.T.D , malignancy . Patient compliance. Persistance of excessive blood loss . Associated other deficiency ((V1t.B12 - folate )).
NORMOCYTIC NORMOCHROMIC ANEMIA Anemia of chronic disease ACD Causes : - Associated with connective tissue diseases. - Hematological disease, Aplastic anemia and MDS , MPD and acute leukemia . - Acute blood loss. - pregnancy and Renal failure. - Mixed deficiency of iron and folic or B12.
Investigations: - CBC , PBF NN RBCs , - S. ferritin : high\ N. - S. iron : N\ Low. - T. BIC : N\ Low. - Specific investigation according to the suspected cause , D/D of NNA: - chronic inflammatory diseases( infection, CTD, IBD ) - recent blood loss . - malignancy , marrow infiltration . - chronic renal failure . - marrow aplasia , hypoplasia . - HIV infection . - early nutritional anemia ( iron , B12 , folate ) .
TREATMENT : * Treat the underlying cause . * Blood transfusion . * Erythropoietin . * iron , folic , B12 supplement . TTT