AP Coordination in UHR Networks for Improved Network Reliability
Explore considerations, problem statements, and design principles for AP coordination in Ultra-High Rate (UHR) networks to enhance network reliability, reduce latency, and improve throughput by facilitating coordinated medium access among access points. The design principles involve ending transmissions at predetermined times, introducing hooks like Restricted TWT, and implementing coordinated medium access at two levels for efficient traffic delivery. The proposed Coordinated Medium Access scheme enables multiple APs to synchronize their medium access, enhancing the delivery of latency-sensitive traffic and reducing contention among stations.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
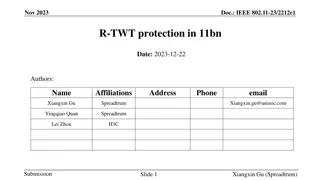
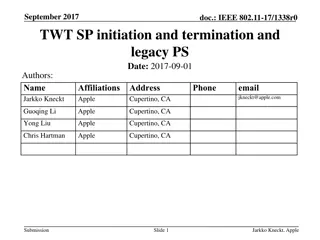
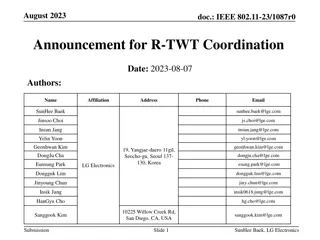
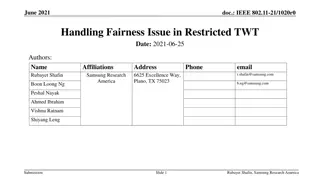
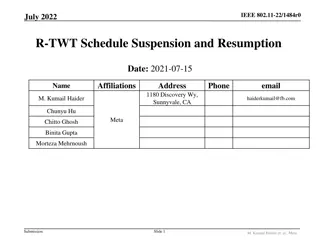
July 2023 doc.: IEEE 802.11-23/226r2 Considerations for AP coordination in UHR: Coordinated Medium Access Date: 2023-01-30 Authors: Name Affiliations Address Phone email Abdel Karim Ajami Qualcomm Technologies Inc. 5665 Morehouse Dr., San Diego CA 92121 aajami@qti.qualcomm.com Alfred Asterjadhi Abhishek Patil Duncan Ho George Cherian Gaurang Naik Yanjun Sun Submission Slide 1 Abdel Karim Ajami et Al., Qualcomm
July 2023 doc.: IEEE 802.11-23/226r2 Problem Statement Problem: today, in most deployments, APs don t hear each others preamble which leads to overlapping transmissions within different BSSs resulting in higher latency due to collisions, retransmissions, hidden node issues, etc. In addition, single BSS transmissions efficiency may drop significantly with OBSS transmissions occupying the medium Objective: improve the reliability of the network in terms of latency and throughput by increasing the chances for APs to listen to each others' transmissions and have a better coordination among them Submission Slide 2 Abdel Karim Ajami et Al., Qualcomm
July 2023 doc.: IEEE 802.11-23/226r2 Design Principles Coordinating APs need to end transmissions at predetermined time to be able to listen to each others' transmissions Some hooks (e.g., Restricted TWT) have been introduced in EHT where STAs end the TXOP before the start time of a service period Restricted TWT is per single BSS UHR design can be built on top of the existing hooks The coordination scheme between APs will facilitate the transmissions between the Coordinating APs at the start of the service periods This will help to reduce the unsynchronized transmission that may result from hidden nodes Submission Slide 3 Abdel Karim Ajami et Al., Qualcomm
July 2023 doc.: IEEE 802.11-23/226r2 Coordinated Medium Access Coordinated Medium Access allows several APs to coordinate their medium access to provide enhanced latency sensitive traffic delivery Two levels of coordination: Level 1: Only APs end the TXOP before the other APs Coordinated SP APs can setup Trigger-enabled R-TWT SPs and use MU EDCA to reduce contention from STAs Level 2: STAs within each BSS end the TXOP with respect to the start of Coordinated SPs of other coordinating APs Associated AP will announce the Coordinated SP of other coordinating APs Coordinated SP can be announced through an R-TWT SP R-TWT supporting STAs will also end the TXOP before the R-TWT SP announced by the associated AP Submission Slide 4 Abdel Karim Ajami et Al., Qualcomm
July 2023 R-TWT TXOP rules per BSS, Coordinated Medium Access is for multi-BSS doc.: IEEE 802.11-23/226r2 11be R 11be R- -TWT TWT Coordinated Medium Access Coordinated Medium Access Coordinated SP R R- -TWT SP TWT SP TXOP TXOP BSS-1 BSS-1 t t R R- -TWT SP TWT SP TXOP TXOP BSS-2 BSS-2 t t TXOP TXOP BSS-3 BSS-3 t t Within the BSS, R-TWT supporting STA shall end TXOP before start of R-TWT SP announced by the associated AP BSS-3 extend over the start of the R-TWT SP of BSS-1 and BSS2. Hence delay the transmissions. Level 1: APs end TXOP before Coordinated SP of its BSS and coordinating APs SP Level 2: in addition, STAs that support Coordinated Medium Access end TXOP before the coordinated SP of other BSS Submission Slide 5 Abdel Karim Ajami et Al., Qualcomm
July 2023 doc.: IEEE 802.11-23/226r2 Initial Gain Analysis Parameters values Bandwidth 80MHz @ 5 GHz, 2 SS max TXOP 4 ms MCS Fixed MCS 5 AP TXPw 21 dBm Low latency traffic DL VR (Data rate: 60 Mbps, Frame Generation rate: 60 fps) Submission Slide 6 Abdel Karim Ajami et Al., Qualcomm
July 2023 doc.: IEEE 802.11-23/226r2 Initial Gain Analysis (Cont d) Submission Slide 7 Abdel Karim Ajami et Al., Qualcomm
July 2023 doc.: IEEE 802.11-23/226r2 For Level 2: TSF may be different at different APs, two candidate solutions If AP2 announces Coordinated SP1 without correcting the Target Wake Time, then AP2 will announce a start time that is different from the correct start time of SP1 Beacon of AP1 Coordinated SP information SP 1 SP 1 SP 1 t t t1 AP2 Correct start time t1 AP1 (w.r.t AP2) (w.r.t AP1) Option 1:APs synchronize their TSF Option 2: each AP corrects the start time of SPs announced by other APs before announcing other APs Coordinated SP information to its associated STAs (e.g., in its transmitted Beacon frames) requires extensions for TWT field to support different offsets between APs when Coordinated SP is communicated through R-TWT Submission Slide 8 Abdel Karim Ajami et Al., Qualcomm
July 2023 doc.: IEEE 802.11-23/226r2 Conclusion We introduced the Coordinated Medium Access framework that can be considered for UHR Two levels of coordination has been proposed in the Coordinated Medium Access framework Coordinated Medium Access will facilitate the transmissions between the Coordinating APs at the start of the service periods and hence increase the reliability of the network Submission Slide 9 Abdel Karim Ajami et Al., Qualcomm
July 2023 doc.: IEEE 802.11-23/226r2 FOLLOW UP ON COORDINATED MEDIUM ACCESS Submission Slide 10 Abdel Karim Ajami et Al., Qualcomm
July 2023 doc.: IEEE 802.11-23/226r2 Additional Aspects on Coordinated Medium Access Coordinated Medium Access allows several APs to coordinate their medium access to provide enhanced latency sensitive traffic delivery Within Level 1 or Level 2 (see slides 4 and 5), APs are expected to end the TXOP at coordinated TSF timestamps (e.g., start of coordinated SPs) Coordinating APs need to ensure efficient medium access after ending the TXOP (e.g., within the Coordinated SPs) One aspect of such efficient medium access would, for example enable coordination of the EDCA parameters used by each coordinated AP Aiming at reducing collisions between APs after the coordinated TSF timestamps (e.g., within the Coordinated SPs) where several APs may use prioritized EDCA parameters without coordination Provide a subset of AP(s) a prioritized access over other AP(s) during the Coordinated SPs Submission Slide 11 Abdel Karim Ajami et Al., Qualcomm
July 2023 doc.: IEEE 802.11-23/226r2 Additional Aspects on Coordinated Medium Access (Cont d) Coordinated EDCA allow the APs to coordinate the channel access parameters among the coordinated APs The coordinated APs will use the Coordinated EDCA parameters at the coordinated TSF timestamps (e.g., during the coordinated SPs) At the coordinated TSF timestamps, the coordinated APs will contend for channel access using the Coordinated EDCA Parameter Set Coordinated APs may fall back to other EDCA parameters outside the coordinated SPs which can be either coordinated or selected independently at each coordinated AP The Coordinated EDCA Parameter Set may be carried in transmitted management frames Submission Slide 12 Abdel Karim Ajami et Al., Qualcomm