Approach to Bleeding Disorders: Understanding the Basics and Coagulation Cascade
Explore an in-depth guide on bleeding disorders, covering the importance, confusion, basic science, normal responses, vascular and platelet phases, coagulation phase, and the Roman numbers. Gain insights into the coagulation cascade and essential factors to know.
Uploaded on | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Approach to bleeding Disorders BY MOHANNAD IBN HOMAID
A few points Content Structure 1sthalf 2ndhalf
Overview Why is it important ? Why is it so confusing ? Basic Science Clinical manifestations Laboratory tests
Basic Science Review Blood is gold The 2 arms of Heamostasis Platelets Clotting Factors Small Vessel Response To Injury
Normal Response Always Goes Through the following: Vascular Phase Platelet Phase Coagulation Phase Fibronlytic Phase Pointless ? Or useful ?
Vascular Phase Not Very important for understanding Vasoconstriction TXA2 and Aspirin
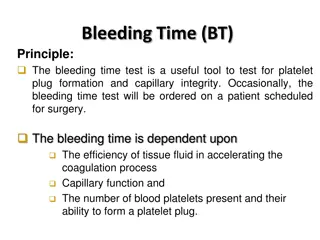
Platelet Phase Unfortunately Very important The following occurs: Platelet Adhesion (vWF later) Platelet Release Reaction ADP TXA2 Temporary Plug < < BLEEDING STOPS HERE Bleeding time The Tile
Coagulation Phase VERY IMPORTANT and VERY CONFUSING Why is it Confusing ? Not Tangible Coagulation Phase and 12 factors Cofactors Ca and PF3 Extrinsic vs intrinsic Vitamin K factors Anti-Thrombin 3 And last but not least .
Coagulation Cascade What do you need to know ? Simple Steps : extrinsic vs intrinsic Content of both How to test them Where they are made ( liver ) Vitamin K AT-3
Extrinsic System: 7 Intrinsic System: 12-11-9-8 Final Common Pathway :10-5-2-1 Vitamin K : 2-7-9-10 AT-3 : 12 -11-10-9 PTT vs PT
Fibrinolytic Phase Kinnnd of important but very easy Tissue plasminogen Activator Plasmin Test Fibrin Degradation Products D-Dimer Assay
Back to the clinical world Presentation of platelet Defects Blood leaks out of vessels Skin and mucosal surfaces Prolonged bleeding ( temporary plug plug ) Presentation Deep Tissue Bleeding Late Rebleeding ( permanent plug Defect )
Laboratory Test Platlets Count Bleeding Time Aggregation Test Clotting Factors PT and PTT Factor Assay Fibrinolysis FDP D-Dimer
Platelet Disorders Quantitative vs Qualitative Thrombocytopenia Immune Thrombocytopenic Prupura Bernard Soulier Syndrome Glanzmanns Thrombasthenia Thrombotic thrombocytopenic Purpura
Thrombocytopenia Pathology :Increase Destruction or decrease Productions > > Clinical Features : depend on degree Labs: Treatment:
ITP Pathology : Auto antibodies Agains Platlets Clinical Features: Labs: Treatment:
Bernard Soulier Syndrome Pathology :GP1B receptor Defiency Clinical Features: Labs:
Glanzmann Thromboasthenia Pathology :GPIIb-IIIa Defiency Clinical Features: Labs: Treatment:
TTP Pathology :Unkown Clinical Features: Pentad : HUS + Fever Neurological Labs: Treatment :Plasmapharesis
Diorders of Coagulations Hemophilia Von Willebrand Disease
Hemophilia Pathology :Factor 8 or 9 Clinical Features: Acute Hemoarthrosis Intracranial Bleeding Hematomas Labs: Treatment: Factor Replacement DDAVP
Von willebrand Disease Function of vWF Made in platelets and endothelium Adhesion of platelets to exposed Collagen Protection of Circulating Factor 8 Pathology Deficiency of vWF Secondary decrease in Factor 8
Von Willebrand Disease Pathology : Mentioned Clinical Features: Labs: Treatment: DDAVP And factor concentrates 1.
DIC Pathology :Inappropriate Activation of platelets and clotting Factors due to : Sepsis ( 50%) Obstetric Complications Malignancy Trauma Clinical Features: Labs: Treatment: ICU and supportive = Treatment of underlying Cause