Boron and Its Compounds: Properties and Uses
Explore the properties and chemical compounds of boron, including its structure, atomic properties, dissimilarities with other elements, chemical reactions, and important boron compounds like boranes. Learn about the preparation methods and properties of boranes, as well as their applications in various industries.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
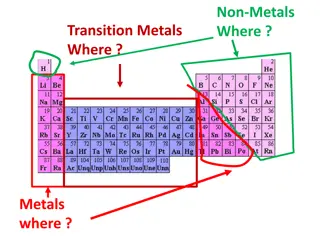
BORON & ITS COMPOUNDS BORON: BORON: Atomic Number: 5 Atomic Symbol: B Group: 13th Period: 2 Electronic Configuration: 1s22s22p1 1s22s12p2 (Excited state) Other elements of the group: B, Al, Ga, In, Tl (Ground state)
Dissimilarities of Boron with other elements of this group: Boron is a non-metal, while all other elements of this group are metals. Boron forms only covalent compounds, while other elements of this group form both covalent and ionic compounds. Boron shows a maximum covalency of four, while other elements of this group show a maximum valency of six due to absence of vacant d- orbitals.
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF BORON CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF BORON: 4B + 3O2 2B2O3(Boric anhydride) 2B + 3N2 2BN(Boron nitride) 2B + 3X2 2BX3(Boron trihalide) Boron 2B + 3 H2SO4 2H3BO3(boric acid) + 3SO2 2B + 3 HNO3 H3BO3(boric acid) + 3NO2 2B+ 6NaOH 2Na3BO3 ( Sodium Borate) + 3H2
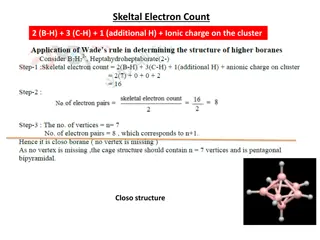
SOME IMPORTANT COMPOUNDS OF BORON BORON HYDRIDES (BORANES): At room temperature boranes are gaseous substances. The general formula of the two important series of boranes are BnHn+4 and BnHn+6 In view of boron having three valence electrons we would expect it to form a simple hydride BH3. However the simplest stable boron hydride is diborane (B2H6).
PREPARATION: PREPARATION: 1. By the action of LiAlH4 on BCl3 4 BCl3 + 3 LiAlH4 Ether 2B2H6 + 3LiCl +3AlCl3 2. By passing electric discharge at low pressure through a mixture of BCl3 or BBr3 and excess of hydrogen. 2 BCl3 + 6H2silent electric discharge B2H6 + 6 HCl 3. By reacting LiH with BF3 8BF3 + 6 LiH B2H6 + 6 LiBF4
PROPERTIES: PROPERTIES: a) It is a colourless gas which is stable at low temperature. At higher temperature it decomposes to give Boron and Hydrogen B2H6 2B + 3H2 b) It burns in oxygen to give B2O3 B2H6 + 3O2 B2O3 + 3H2O c) It readily reacts with water liberating H2 gas B2H6 + 6H2O 2H3BO3 + 6H2 d) It reacts with Cl2 forming boron trichloride B2H6 + 3Cl2 2 BCl3 + 3HCl
e) At low temperature an addition product is obtained with NH3 B2H6 + 2NH3 B2H6.2 NH3 When the addition product is heated up to 2000C, borazine is formed, which is also known as inorganic benzene. 3B2H6.2 NH3 2B3N3H6 +12H2 USES OF DIBORANE: a rocket fuel for supersonic aeroplanes a starting material for preparing higher boranes, metal boron hydrides such as LiBH4, NaBH4 etc. a catalyst in polymerisation reactions a reducing agent in organic reactions.
Boric acid (H3BO3): PREPARATION: From Boric Acid: Boric acid is obtained by treating a hot conc. solution of borax with HCl or sulphuric acid. The resulting solution on concentration and cooling gives crystals of boric acid. Na2B4O7 + 2HCl + 5H2O 4H3BO3 +2NaCl prepared by the hydrolysis of boron compounds. From hydrolysis of boron compounds: It can also be B2H6 + 6 H2O H3BO 3 +6H2 BCl3 + 3H2O H3BO 3 +3HCl
PROPERTIES: Sparingly soluble in cold water but highly soluble in hot water. It acts as a weak acid. White crystalline solid with a soft soapy touch. Action of heat: H3BO3 370 K HBO2 + H2O 410 K HBO2 H2B4O7 (Tetra boric acid) H2B4O7 Red heat 2B2O3 + H2O
BORAX (Na2B4O7.10 H2O) From boric acid: Borax can also be obtained in small quantities from boric acid by neutralising it with Na2CO3. 4H3BO3 + Na2CO3 Physical & Chemical Properties: Na2B4O7 + 6 H2O + CO2 a)White crystalline solid. b)Its aqueous solution is basic in nature. Borax is therefore used as a water softener and cleansing agent. Na2B4O7 + 2 H2O H2B4O7 + 2NaOH
c. Action of heat: On heating it loses its water of crystallisation. On further heating, it gives a transparent glassy bead of boron oxide and sodium Metaborate. Na2B4O7.10H2O Na2B4O7 + 10H2O heat Na2B4O7 Sodium Metaborate Boron oxide This transparent glassy bead is commonly known as Borax- bead and is used in the qualitative analysis of certain coloured ions such as Nickel, cobalt, chromium, cupric ions etc. This test is performed on a platinum wire with the salts containing these cations. On heating the salts are converted into their oxides which form coloured metaborates with B2O3. MnO + B2O3heat Mn(BO2)2 Manganese Metaborate (pink) heat 2NaBO2 + B2O3
CoO + B2O3heat Co(BO2)2 Cobalt Metaborate ( blue) d.Action with NaOH: With NaOH it forms sodium metaborates Na2B4O7 + 2 NaOH 4NaBO2 + H2O e. Action with sulphuric acid: (Calculated amount of acid) Na2B4O7 + H2SO4 H2B4O7 + H2O 4H3BO3 Tetra boric acid Na2SO4 + H2B4O7
SOME IMPORTANT QUESTIONS: 1. Why boron halides are Lewis acids? 2. Why boric acid is considered as non protic acid? 3. What name is given to the bond present in diborane? 4. Why boron cannot extend its covalency beyond four? 5. What will be nature of aqueous solution of borax and why? 6. What happens when borax is heated? Write the chemical equation.