Cellular Respiration Process and Energy Transformation
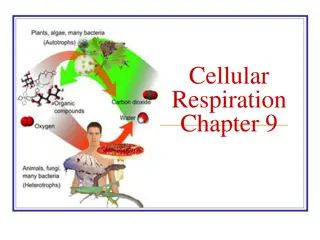
In cellular respiration, energy flow and transformation are highlighted. The process involves the conversion of energy from the Sun into chemical energy in glucose, the role of ATP, different phases such as glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, enzyme actions, and the chemical equation. Mitochondria, lysosomes, and energy release mechanisms are also discussed in depth.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CELLULAR RESPIRATION: TRUE/FALSE
TRUE OR FALSE? The Sun is the source of all energy on Earth. Energy cannot be changed from one form to another. Plants convert energy from the Sun into chemical energy in glucose. Cells can use energy directly from glucose. ATP is made up of an adenine, glucose and three phosphate molecules. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Energy is released from ATP when a phosphate bond is broken. ADP molecules can be recharged with energy from glucose. The lysosome breaks down molecules to release energy. Mitochondria have their own DNA. 10. Cellular respiration is a process separated into two phases. 6. 7. 8. 9.
11. Glycolysis is the first phase of cell respiration and occurs in the mitochondria. 12. The Krebs cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion, and the Electron Transport chain occurs in the inner membrane. 13. In glycolysis, glucose is split into one molecule of pyruvic acid. 14. Glycolysis requires 4 ATP to start the reaction.
15. Enzymes allow the process of cellular respiration to occur in a slow and controlled way. 16. The chemical equation for cellular respiration is the following: C6H12O6 + 6CO2 6H2O + 6O2