Comparison of Series and Parallel Circuits: Advantages and Disadvantages
Explore the advantages and disadvantages of series and parallel circuits, including factors such as current distribution, voltage sharing, resistance, and circuit completeness. Understand how these circuit configurations affect the flow of electric charge and power distribution. Dive deep into the differences between series and parallel circuits to enhance your understanding of electrical circuits.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
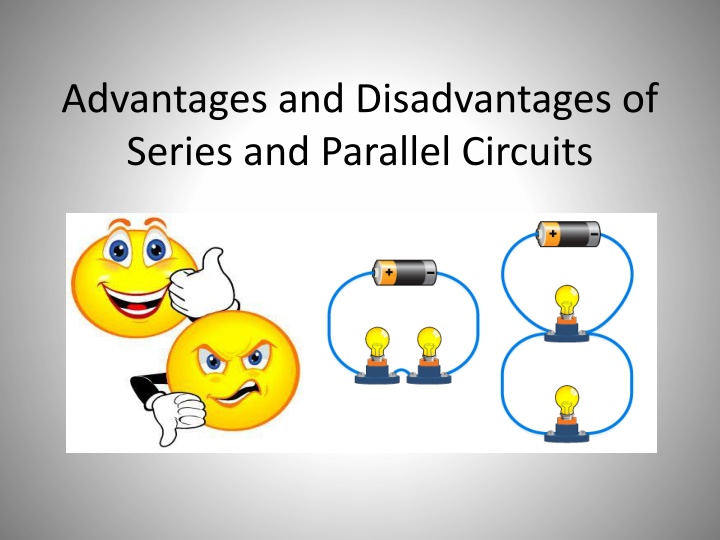
Advantages and Disadvantages of Series and Parallel Circuits
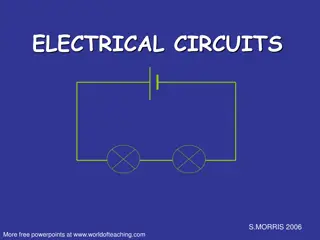
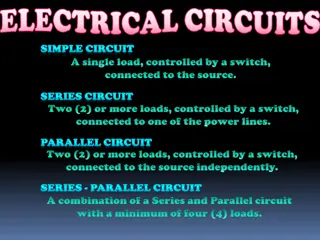
Parallel Circuit Series Circuit Two or more pathways Current splits, passes through pathways, and adds up again Voltage across each pathway equals supply voltage One pathway (circuit) Current (flow of electric charge) same anywhere in the circuit Voltage (measure of strength of electrical power) shared in ratio to resistance
Parallel Circuit Series Circuit Resistance (reduction of electrical current) adds up, draws less current = battery (power source) lasts longer Total resistance less than the least resistance, current drawn is less = battery life short
Parallel Circuit Series Circuit One bulb (load) fuses, circuit incomplete (open or broken) Brightness of bulbs less because P = IV One bulb fuses, the others will still work Brightness of bulbs more P (Power), I (Current), V (Voltage)
Similarities Converts electrical energy to light, heat, sound, etc.