Covalent and Acid Naming Guide for Chemistry Students
Learn how to name covalent compounds and acids in chemistry with step-by-step examples. Understand the prefixes used in covalent naming and the rules for naming binary and oxy acids. Master the process of converting acid names to formulas for a comprehensive understanding of chemical nomenclature.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Covalent and Acid Naming Chapter 9
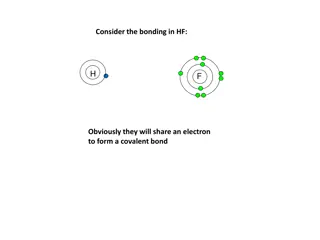
Covalent Naming Covalent compounds are compounds with ONLY non-metals. Covalent bonds form by SHARING electrons. 1. Write the name of the 1stelement in the compound 2. Write the root name of second element followed by suffix ide. 3. Add prefixes to indicate the NUMBER of atoms present for each element. {NEVER use mono for first element)
Covalent Naming Prefixes 1 = mono 2 = di 3 = tri 4 = tetra 5 = penta Prefixes 6 = hexa 7 = hepta 8 = octa 9 = nona 10 = deca
Covalent Naming Examples 1. N2O3 2. ClO2 3. BF3 4. As4010 5. Carbon monoxide 6. Diphosphorous pentoxide 7. Nitrogen dioxide Examples 1. Dinitrogen trioxide 2. Chlorine dioxide 3. Boron trifluoride 4. Tetrarsnic decoxide 5. CO 6. P2O5 7. NO2
Naming Acids Acids are covalent compound that begin with hydrogen Two types of acids Binary acids are acids with hydrogen and another element Oxy acids are acids with hydrogen and a polyatomic ion 5
Naming Binary Acids 1. Write hydro- 2. Followed by root name of element 3. End with ic acid Example HBr is hydrobromic acid HCl is hydrochloric acid H2S is hydrosulfuric acid 6
Naming Oxy Acids 1. Determine the name of the polyatomic that made the acid a. If polyatomic s name ends in -ate it become ic acid b. If polyatomic s name ends in ite it becomes ous acid Example H2SO4 is from sulfate so name is sulfuric acid H2SO4 is from sulfite so name is sulfurous acid 7
Acid Names to formulas In forming acids hydrogen will have a +1 charge Determine the charge of the anion and use hydrogen to balance it Example: Hydroiodic acid = H+1 I-1 so is HI Phosphorous acid = H+1 PO3-3 so is H3PO3 8
Writing Acid Formulas Use the name of the acid to determine the charge of the second element (polyatomic) Add hydrogen to balance the charge to the front of the compound Example Hydroiodic acid hydro means binary acid, iodic = I-1 formula is HI Phosphorous acid no hydro means oxy acid, ending ous = ite phosphite is PO3-3 formula is H3PO3 9
Mixed Naming/Formula Writing guidelines Writing Names Look at elements to determine if it is Ionic ( starts with a metal), use roman # only if transition metal Covalent (only non-metals), uses prefixes Acid (starts with Hydrogen), all end with word acid Writing Formulas If there are prefixes in name write the number of atoms said in name If there is no prefixes (acid or ionic) then you MUST balance charges [write ion s first] REMEMBER chemical formulas do NOT have charges in the formula.