Effect of Nm Blockers on Frog Rectus Abdomens Muscle
Voluntary muscle, the rectus abdomens, receives motor somatic innervations lacking ganglia. The receptor is Nm, different from autonomic ganglia receptors. Explore the impact of neuromuscular blockers and cholinergic agonists on muscle function in this lab experiment.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
PHL 313 (Lab. 4) Effect of Nm blockers on Frog Rectus Abdomens Muscle 1
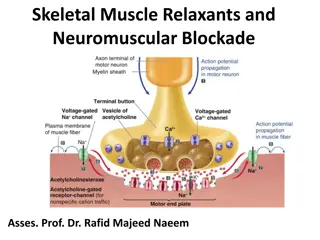
Rectus Abdomens Muscle . Voluntary muscle which receive motor somatic innervations (lack the ganglia ) Receptor is Nm which is different from receptor in the autonomic ganglia. It contains Ach-esterase for destruction of Ach. 2
Nm drugs Cholinergic agonists (direct acting ) Ach Carbachol Anticholinesterases (indirect acting ) reversible : Neostigmine, physostigmine, pyridostigmine Irreversible : (e.g Organophosphates ) (isoflurophate, echothiophate ) Neuromuscular Blockers A. Non-depolarizing : e.g. D-tubocurarine B. Depolarizing : e.g. suxamethonium 3
Depolarization 1- Resting potential: In order to maintain the cell membrane potential, cells keep a low concentration of sodium ions and high levels of potassium ions within the cell (intracellular). The sodium-potassium pump moves 3 sodium ions out and moves 2 potassium ions in, thus in total removing one positive charge carrier from the intracellular space. 2- Depolarization is a positive-going change in a cell's membrane potential, making it more positive, or less negative. In neurons and some other cells, a large enough depolarization may result in an action potential. 3- Hyperpolarization is the opposite of depolarization, and inhibits the rise of an action potential. 4
SUCCINYLCHOLINE SUCCINYLCHOLINE is a muscle relaxant. It relaxes muscles during surgery or before investigational procedures. Succinylcholine is double Ach Unlike Ach, it is not hydrolysed by Achesterase. It is degraded more slowly than Ach causing an endplate depolariztaion which lead to Action potential. It is a persist depolarization of endplate because Na channel remain inactivated leading to relaxation of muscle fiber (paralysis). 5
Requirements Frog-ringer solution -No Mg+2 (no relaxation) -(Ca ,K ,PO4, Na ,HCO3 ) -Glucose -Tension 0.5-4 gm -Temp. 25 C 6
Procedure 1- Add 0.2ml of Ach ,record ,wash . 2- Add 0.2ml of prostagmine , wait 2 min. ,add 0.2ml Ach , record ,wash. (compare between the response in step 1 and 2) 3- Add 0.2ml carbacol ,record ,wash .(compare between the response in step 1 and 3) 4- Add 0,2ml succinylcholine ,record , No wash , add 0.2ml of Ach and record the response then wash. 5- Add 0.2ml atracurium, no wash and wait 2 min, add 0.2 ml Ach and record the response. 7