Engineering Design Process Overview
In this overview, explore the significance of engineering in solving problems by utilizing math and science. Learn about STEM, the design process, vocabulary, problem-solving steps, and more.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Engineering Design Process
Agenda: November 10, 2015 What is STEM? Engineering Design Process Review of Marshmallow Mania DC Design Exit Pass
Science Study of the natural world Technology Study of the manmade world Engineering Math Study of numbers and quantity
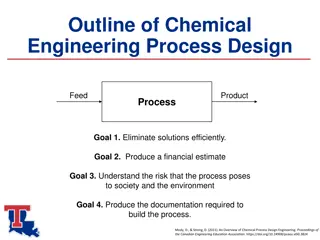
What is engineering and why is it important in science class? Engineering is solving problems by using both math and science.
Engineering Vocabulary 1. Criteria: Must Haves 2. Constraints: Limitations 3. Prototype: First model
Understand the Problem Communicate Engineering Design Process: a series of steps that engineers follow to come up with a solution to a problem. DESIGN PROCESS Research & Brainstorm Redesign Design Test Build
What is the problem? UNDERSTANDING THE PROBLEM/ DESIGN BRIEF What are the criteria and constraints? How can you solve it? DESING BRIEF: A written plan that identifies a problem to be solved, its criteria, and its constraints. The design brief is used to encourage thinking in all aspects of a problem before attempting a solution
Find out what others have done. Think up lots of ideas. Research & Brainstorm Observe the materials. Examine current state of the issue and current solutions BRAINSTORM: A method of shared problem solving in which all members of a group spontaneously and in an unrestrained discussion generate ideas. RESEARCH: Identifying what information you know and what you need to know about your problem to create your solutions.
Draw sketches and make a final decision Design Sketches include measurements (including units) and labels. Brainstorm possible solutions Articulate the possible solutions in two and three dimensions Draw on mathematics and science An iterative decision-making process that produces plans by which resources are converted into products or systems that human needs and wants or solve problems.
Use your plan to build your ideas. Determine which solution(s) best meet the original requirements Build Does my model work? Does it solve the problem? Test your idea. Test
Think about how your design can be improved. Redesign Modify your design and try again. Overhaul the solution(s) based on information gathered during the tests and presentation An iterative decision-making process that produces plans by which resources are converted into products or systems that human needs and wants or solve problems. *
Communicate your results with others. COMMUNITCATE / EVALUATE Make an engineering presentation Make an engineering presentation that includes a discussion of how includes a discussion of how the meet(s) the needs of the meet(s) the needs of the initial opportunity, or opportunity, or need. need. that best problem, the best initial problem, Discuss societal impact and tradeoffs of the solutions
Guidelines, rules, or tests by which something can be judged. Criteria are specific and measurable. Must Haves Constraints A full-scale working model used to test a design concept by making actual observations and necessary adjustments. First model A limit to a design process. Constraints may be such things as appearance, funding, space, materials and human capabilities Limitations Criteria Prototype